A Geographic Exploration Of Syria: A Crossroads Of History And Culture
A Geographic Exploration of Syria: A Crossroads of History and Culture
Related Articles: A Geographic Exploration of Syria: A Crossroads of History and Culture
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Exploration of Syria: A Crossroads of History and Culture. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Exploration of Syria: A Crossroads of History and Culture
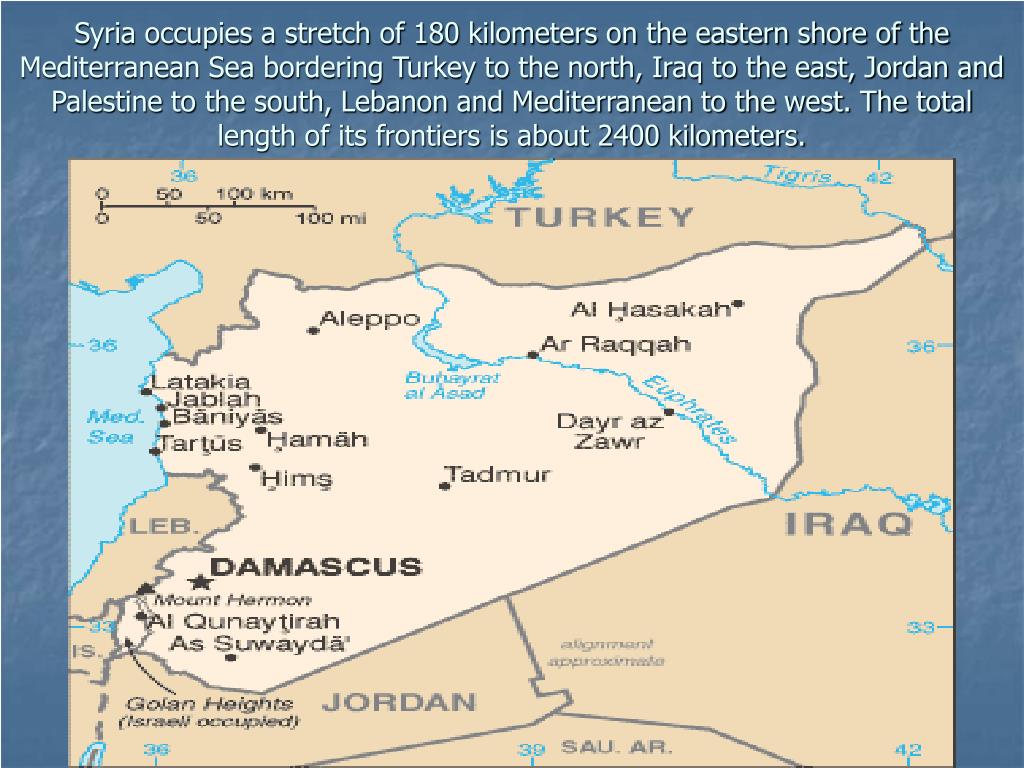
Syria, a nation steeped in history and culture, holds a strategic position in the Middle East. Its location at the crossroads of ancient civilizations has shaped its diverse landscape, rich heritage, and complex geopolitical significance. Understanding Syria’s geographical context is crucial to grasping its past, present, and potential future.
A Land of Contrasts: The Geographical Features of Syria
Syria occupies a land area of approximately 185,180 square kilometers, a territory roughly the size of the United Kingdom. Its diverse landscape is characterized by:
- The Mediterranean Coast: A narrow strip of fertile land along the eastern shores of the Mediterranean Sea, offering a temperate climate and lush vegetation. This region has historically been a vital hub for trade and cultural exchange.
- The Coastal Mountains: The Anti-Lebanon and Jebel Druze mountain ranges rise from the coastal plain, providing a dramatic backdrop and a source of natural resources.
- The Syrian Desert: Covering a vast majority of the country, this arid expanse stretches eastward, offering a stark contrast to the coastal regions. Despite its harsh conditions, the desert is home to unique flora and fauna.
- The Euphrates River: This mighty river flows through the heart of Syria, providing essential water resources for agriculture and supporting a rich ecosystem.
- The Golan Heights: A strategically important plateau overlooking the Jordan Valley, this region has been a source of conflict for decades.
A Crossroads of Civilizations: Syria’s Strategic Location
Syria’s geographic position at the heart of the Middle East has made it a crossroads for trade, migration, and cultural exchange for millennia. This strategic location has influenced the country’s:
- Historical Significance: Syria has been home to some of the oldest civilizations in the world, including the Phoenicians, Greeks, Romans, Arabs, and Ottomans. Its ancient cities, such as Damascus, Aleppo, and Palmyra, are testaments to this rich history.
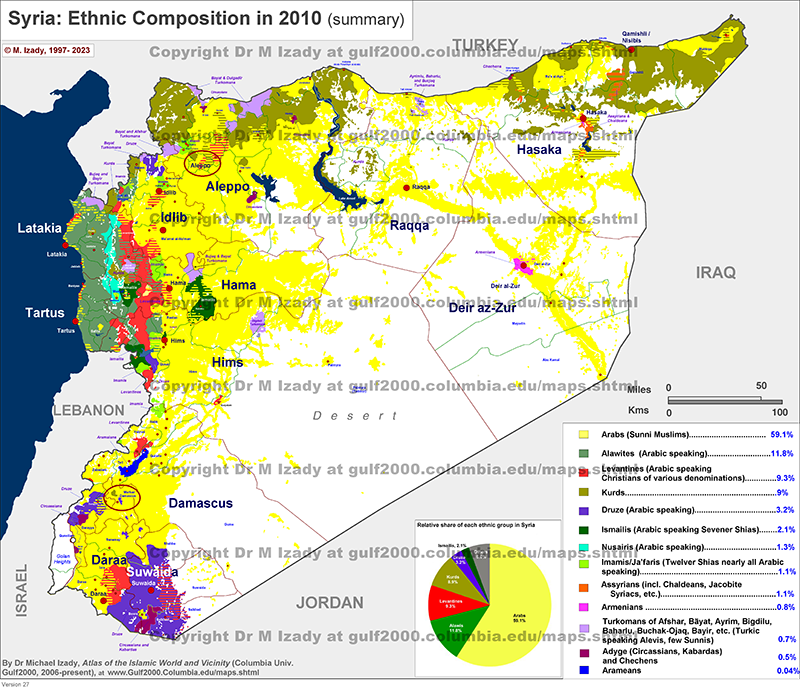
- Cultural Diversity: Syria’s diverse population reflects its history as a melting pot of cultures. The country is home to a rich tapestry of ethnicities, religions, and languages, contributing to its unique cultural identity.
- Geopolitical Importance: Syria’s strategic location has made it a key player in regional politics. Its borders with Lebanon, Israel, Jordan, Iraq, and Turkey have made it a focal point for regional tensions and conflicts.
The Challenges and Opportunities of Syria’s Location
Syria’s geographic location presents both challenges and opportunities:
- Resource Scarcity: The country faces water scarcity due to its arid climate and increasing demand for water resources. This is further exacerbated by the ongoing conflict, which has damaged infrastructure and disrupted agricultural production.
- Political Instability: Syria has been embroiled in a protracted civil war, which has had a devastating impact on its economy, infrastructure, and social fabric. The conflict has also led to a massive refugee crisis, with millions of Syrians displaced from their homes.
- Regional Tensions: Syria’s location in a volatile region has made it a target for regional powers vying for influence. The country’s complex political landscape has also contributed to its instability.
Despite these challenges, Syria’s location also presents opportunities:
- Economic Potential: Syria has the potential to be a regional economic hub, thanks to its strategic location and diverse natural resources. The country’s agricultural sector, particularly in the fertile coastal region, holds significant potential for development.
- Cultural Heritage: Syria’s rich cultural heritage is a valuable asset, attracting tourists and generating revenue. The preservation and promotion of this heritage can contribute to economic growth and national pride.
- Regional Cooperation: Syria has the potential to play a constructive role in regional cooperation and stability. Addressing the country’s challenges requires a collaborative approach, involving regional actors and international partners.
FAQs
Q: What are the major cities in Syria?
A: The major cities in Syria include Damascus (the capital), Aleppo, Homs, Hama, Latakia, and Tartous.
Q: What are the main languages spoken in Syria?
A: The official language of Syria is Arabic. However, other languages are also spoken, including Kurdish, Armenian, and Circassian.
Q: What are the major religions practiced in Syria?
A: The majority of Syrians are Muslims, primarily Sunni and Shia. There are also significant Christian communities, including Greek Orthodox, Catholic, and Protestant denominations.
Q: What are the main natural resources found in Syria?
A: Syria has a variety of natural resources, including oil, natural gas, phosphate rock, and arable land.
Q: What are the major industries in Syria?
A: The main industries in Syria include agriculture, textiles, food processing, and tourism.
Tips
- Learn about the history and culture of Syria: Understanding Syria’s rich past can provide valuable insights into its present and future.
- Engage with Syrian people: Seeking out opportunities to interact with Syrian individuals and communities can help to foster understanding and empathy.
- Support organizations working to address the humanitarian crisis in Syria: There are numerous organizations providing aid and support to Syrian refugees and those affected by the conflict.
- Promote peace and reconciliation: Encourage efforts to resolve the conflict in Syria through dialogue and reconciliation.
Conclusion
Syria’s strategic location at the heart of the Middle East has shaped its history, culture, and geopolitical significance. The country’s diverse landscape, rich heritage, and complex challenges present both opportunities and obstacles for its future. Understanding Syria’s geographic context is essential for navigating the complexities of the region and promoting peace, stability, and prosperity.


/syria-57a92c6f3df78cf4597f7725.jpg)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Exploration of Syria: A Crossroads of History and Culture. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!