A Shifting Landscape: North America In 1763
A Shifting Landscape: North America in 1763
Related Articles: A Shifting Landscape: North America in 1763
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Shifting Landscape: North America in 1763. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Shifting Landscape: North America in 1763
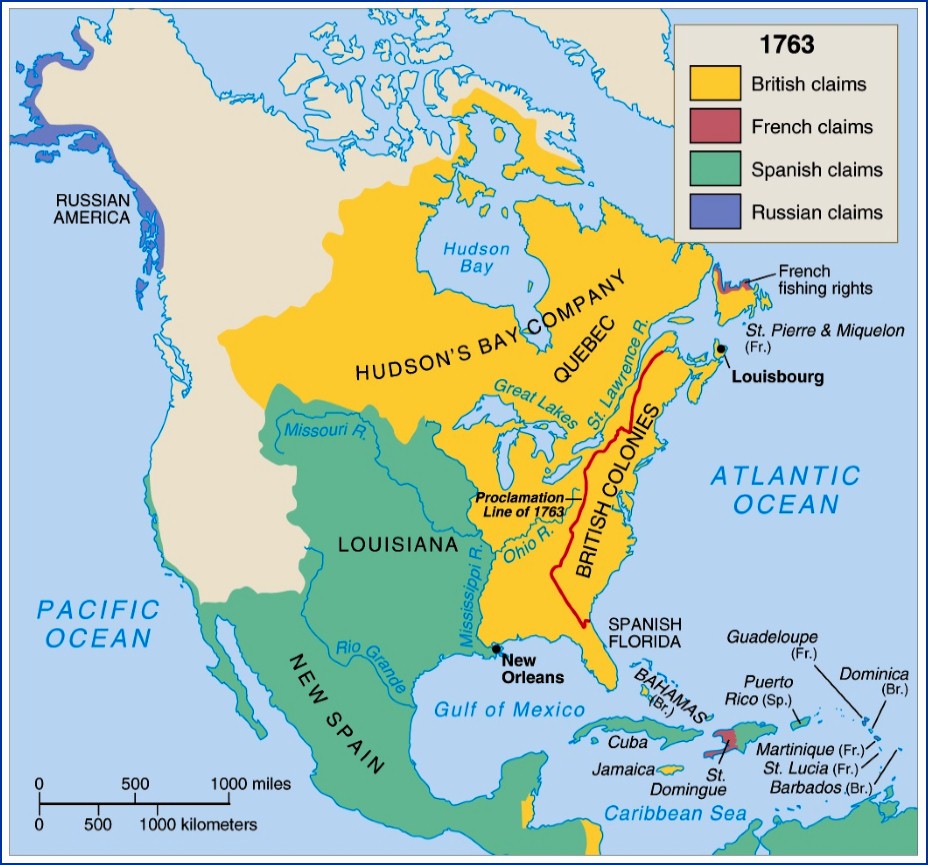
The year 1763 marks a pivotal moment in North American history. The echoes of the Seven Years’ War, a global conflict between Great Britain and France, still reverberated across the continent. The Treaty of Paris, signed that year, dramatically reshaped the political and geographical landscape of North America, leaving an indelible mark on the future of the region.
A New World Order Emerges
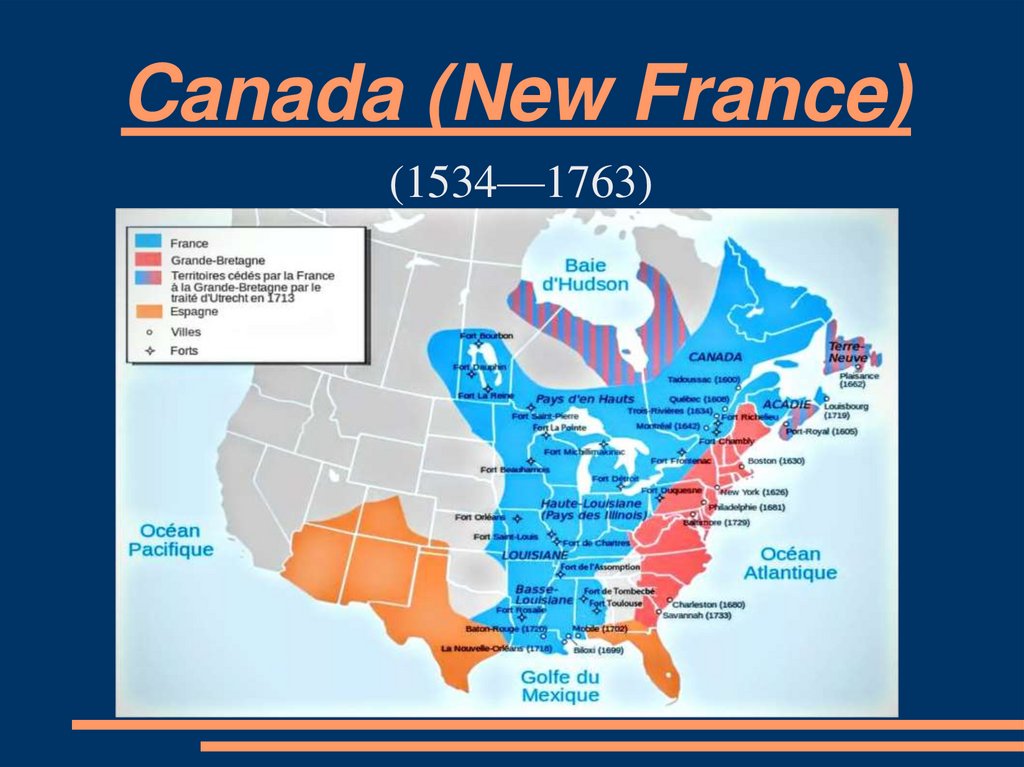
The treaty, negotiated between Great Britain, France, and Spain, effectively transferred vast territories from French to British control. France, weakened by the war, ceded all its North American holdings east of the Mississippi River, including Canada, Nova Scotia, and the strategically important Ohio Valley. This territorial shift significantly altered the balance of power in North America, placing Great Britain in a dominant position.
The Map of Change
The North American map of 1763 reflects this transformation. The vast expanse of French territory, which once stretched from the Great Lakes to the Gulf of Mexico, is now primarily under British dominion. The French presence is confined to a few islands in the Caribbean and a small area in the St. Lawrence River Valley. Spain, though not directly involved in the war, benefited from the treaty, receiving Louisiana from France as compensation. The Spanish territories now encompass Florida and vast tracts of land west of the Mississippi River, extending all the way to the Pacific Ocean.
The Proclamation of 1763: A Response to Change
The British government, eager to establish control over its newly acquired territories, issued the Proclamation of 1763. This proclamation aimed to prevent further conflict with Native American tribes by prohibiting colonists from settling west of the Appalachian Mountains. While intended to maintain peace, the proclamation was met with resistance from colonists who saw it as an obstacle to westward expansion. This tension, coupled with other grievances, would eventually lead to the American Revolution.
Beyond Borders: The Legacy of 1763
The North American map of 1763 is more than just a geographical representation. It is a testament to the shifting tides of power, the complexities of colonial expansion, and the seeds sown for future conflict. The treaty’s consequences reverberated throughout the 18th and 19th centuries, shaping the political and cultural landscape of North America.
FAQs: Unraveling the Significance of 1763
1. What were the key territorial changes brought about by the Treaty of Paris?
The Treaty of Paris saw France relinquish its North American holdings east of the Mississippi River, including Canada, Nova Scotia, and the Ohio Valley, to Great Britain. Spain gained Louisiana from France and retained Florida, expanding its territory significantly.
2. How did the Proclamation of 1763 impact relations between Britain and its colonists?
The Proclamation of 1763, designed to prevent conflict with Native American tribes, restricted colonial expansion westward. This angered colonists who saw it as an infringement on their freedom and fueled resentment against British rule, ultimately contributing to the American Revolution.
3. What were the long-term consequences of the Treaty of Paris for North America?
The treaty set the stage for a new era of British dominance in North America, paving the way for westward expansion and the eventual formation of the United States. It also established a new power dynamic with Spain, which would continue to influence the region for decades.
4. How did the Treaty of Paris affect the lives of Native American tribes?
The treaty, while aiming to maintain peace, ultimately resulted in the displacement of Native American tribes from their traditional lands. The British government’s inability to enforce the Proclamation of 1763 led to further conflict and instability in the region.
Tips: Navigating the Complexities of 1763
1. Focus on the broader context: Understanding the Treaty of Paris requires examining the events leading up to it, particularly the Seven Years’ War and the complex geopolitical landscape of the time.
2. Explore the diverse perspectives: The Treaty of Paris had profound implications for various groups, including British colonists, Native American tribes, and French settlers. Studying their individual experiences provides a richer understanding of the treaty’s impact.
3. Analyze the map: The North American map of 1763 serves as a visual representation of the territorial shifts and the new power dynamics that emerged after the treaty. Examining the map in detail can offer valuable insights into the era.
4. Connect the dots: The Treaty of Paris is not an isolated event. It is intertwined with other historical developments, including the American Revolution, the westward expansion of the United States, and the ongoing relationship between European powers and Native American tribes.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Transformation
The North American map of 1763 stands as a powerful symbol of change. It reflects a pivotal moment in history, when the continent’s political and geographical landscape was reshaped by the Treaty of Paris. The treaty’s consequences, both immediate and long-term, continue to resonate in the modern world, shaping the political, social, and cultural fabric of North America. By delving into the complexities of this historical period, we gain a deeper understanding of the forces that shaped the continent and the ongoing legacy of 1763.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Shifting Landscape: North America in 1763. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
