A Tapestry Of Cultures: Understanding Ethiopia’s Ethnic Map
A Tapestry of Cultures: Understanding Ethiopia’s Ethnic Map
Related Articles: A Tapestry of Cultures: Understanding Ethiopia’s Ethnic Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Tapestry of Cultures: Understanding Ethiopia’s Ethnic Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Tapestry of Cultures: Understanding Ethiopia’s Ethnic Map

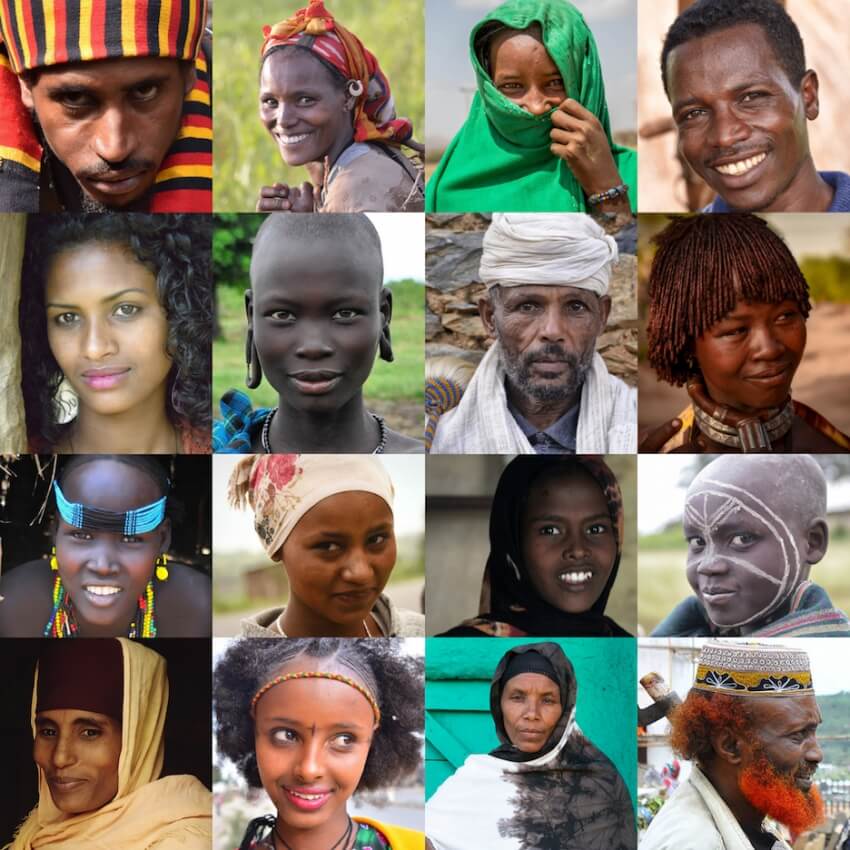
Ethiopia, a nation nestled in the Horn of Africa, is renowned for its rich history, diverse landscapes, and vibrant cultural tapestry. At the heart of this cultural richness lies a mosaic of ethnic groups, each contributing unique traditions, languages, and customs to the nation’s vibrant identity. The ethnic map of Ethiopia, a visual representation of this diversity, serves as a powerful tool for understanding the country’s social, political, and economic landscape.
A Diverse Landscape of Peoples
Ethiopia is home to over 80 distinct ethnic groups, each with its own language, customs, and cultural heritage. The majority of the population identifies with one of the following major ethnic groups:
- Oromo: The largest ethnic group in Ethiopia, accounting for approximately 34.9% of the population, the Oromo people are primarily located in the central and southern regions of the country. Their culture is characterized by strong oral traditions, vibrant music and dance, and a rich agricultural heritage.
- Amhara: The second largest ethnic group, representing around 27% of the population, the Amhara people are concentrated in the north-central highlands. They are known for their strong cultural ties to Christianity, their contributions to Ethiopian literature and art, and their significant role in shaping the country’s history.
- Tigray: Comprising about 6.1% of the population, the Tigray people reside primarily in the northern region of Tigray. They are known for their historical resilience, their strong cultural identity, and their significant contributions to Ethiopian art and architecture.
- Somali: Representing approximately 6.2% of the population, the Somali people inhabit the eastern and southeastern regions of Ethiopia, bordering Somalia. Their culture is characterized by a strong nomadic tradition, a rich oral history, and a deep connection to their livestock.
- Sidama: Constituting around 4.1% of the population, the Sidama people are primarily located in the southern region of Ethiopia. They are known for their distinct language, their vibrant traditional ceremonies, and their strong agricultural practices.
Beyond the Major Groups: A Spectrum of Diversity
While these five major groups represent a significant portion of the population, the ethnic map of Ethiopia also reveals a remarkable diversity of smaller ethnic groups, each contributing to the country’s cultural richness. These include the Afar, the Gurage, the Welayta, the Harari, and numerous others, each with their own unique languages, customs, and cultural traditions.
The Significance of the Ethnic Map
The ethnic map of Ethiopia is not merely a visual representation of demographic data. It is a powerful tool for understanding the country’s social, political, and economic landscape. It highlights:
- Cultural Diversity: The map serves as a visual reminder of the rich tapestry of cultures that define Ethiopia. It underscores the importance of preserving and celebrating this diversity, fostering mutual respect and understanding among different ethnic groups.
- Historical Context: Understanding the distribution of ethnic groups provides valuable insights into the historical development of Ethiopia. It sheds light on migration patterns, inter-ethnic relations, and the formation of regional identities.
- Political Dynamics: The ethnic map plays a crucial role in understanding the political landscape of Ethiopia. It highlights the potential for both unity and division, emphasizing the need for inclusive governance and policies that address the concerns of all ethnic groups.
- Economic Development: The ethnic map can inform strategies for economic development by identifying areas with specific cultural and economic strengths. It can also highlight potential challenges related to resource allocation, infrastructure development, and social services.
Challenges and Opportunities
While Ethiopia’s ethnic diversity is a source of strength and cultural richness, it also presents challenges. Historical tensions, land disputes, and resource scarcity have led to conflict and instability in some regions.
However, the ethnic map also offers opportunities for progress. Recognizing and respecting cultural diversity can foster social cohesion, promote economic development, and strengthen national unity. By embracing the unique contributions of each ethnic group, Ethiopia can harness its diversity to build a more inclusive and prosperous future.
FAQs about Ethiopia’s Ethnic Map
Q: What is the significance of the ethnic map in understanding Ethiopian history?
A: The ethnic map provides insights into migration patterns, inter-ethnic relations, and the formation of regional identities. It helps us understand how different ethnic groups interacted and shaped the historical landscape of Ethiopia.
Q: How does the ethnic map influence political dynamics in Ethiopia?
A: The ethnic map highlights the potential for both unity and division in Ethiopian politics. It underscores the need for inclusive governance and policies that address the concerns of all ethnic groups.
Q: What are some of the challenges associated with Ethiopia’s ethnic diversity?
A: Challenges include historical tensions, land disputes, and resource scarcity, which have led to conflict and instability in some regions.
Q: What are some opportunities presented by Ethiopia’s ethnic diversity?
A: Opportunities include fostering social cohesion, promoting economic development, and strengthening national unity by recognizing and respecting cultural diversity.
Tips for Understanding Ethiopia’s Ethnic Map
- Explore the cultural traditions of different ethnic groups: Engage with the rich tapestry of languages, music, dance, art, and customs that define Ethiopia’s diverse ethnic groups.
- Learn about the history of inter-ethnic relations: Gain an understanding of the historical interactions and conflicts that have shaped the country’s ethnic landscape.
- Support initiatives that promote cultural exchange and understanding: Encourage programs and events that foster dialogue and collaboration among different ethnic groups.
- Advocate for inclusive governance and policies: Support policies that address the concerns of all ethnic groups and promote equitable access to resources and opportunities.
Conclusion
Ethiopia’s ethnic map is more than a visual representation of demographic data. It is a reflection of the nation’s rich cultural heritage, a guide to understanding its historical development, and a tool for navigating its complex political and economic landscape. Recognizing and embracing the diversity of its ethnic groups is essential for building a more inclusive, peaceful, and prosperous future for Ethiopia. By fostering mutual respect, understanding, and collaboration, the country can harness its diversity as a source of strength and resilience, ensuring a brighter future for all its citizens.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Tapestry of Cultures: Understanding Ethiopia’s Ethnic Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!