A Tapestry Of Cultures: Understanding The Indigenous Tribes Of Mexico
A Tapestry of Cultures: Understanding the Indigenous Tribes of Mexico
Related Articles: A Tapestry of Cultures: Understanding the Indigenous Tribes of Mexico
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Tapestry of Cultures: Understanding the Indigenous Tribes of Mexico. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Tapestry of Cultures: Understanding the Indigenous Tribes of Mexico
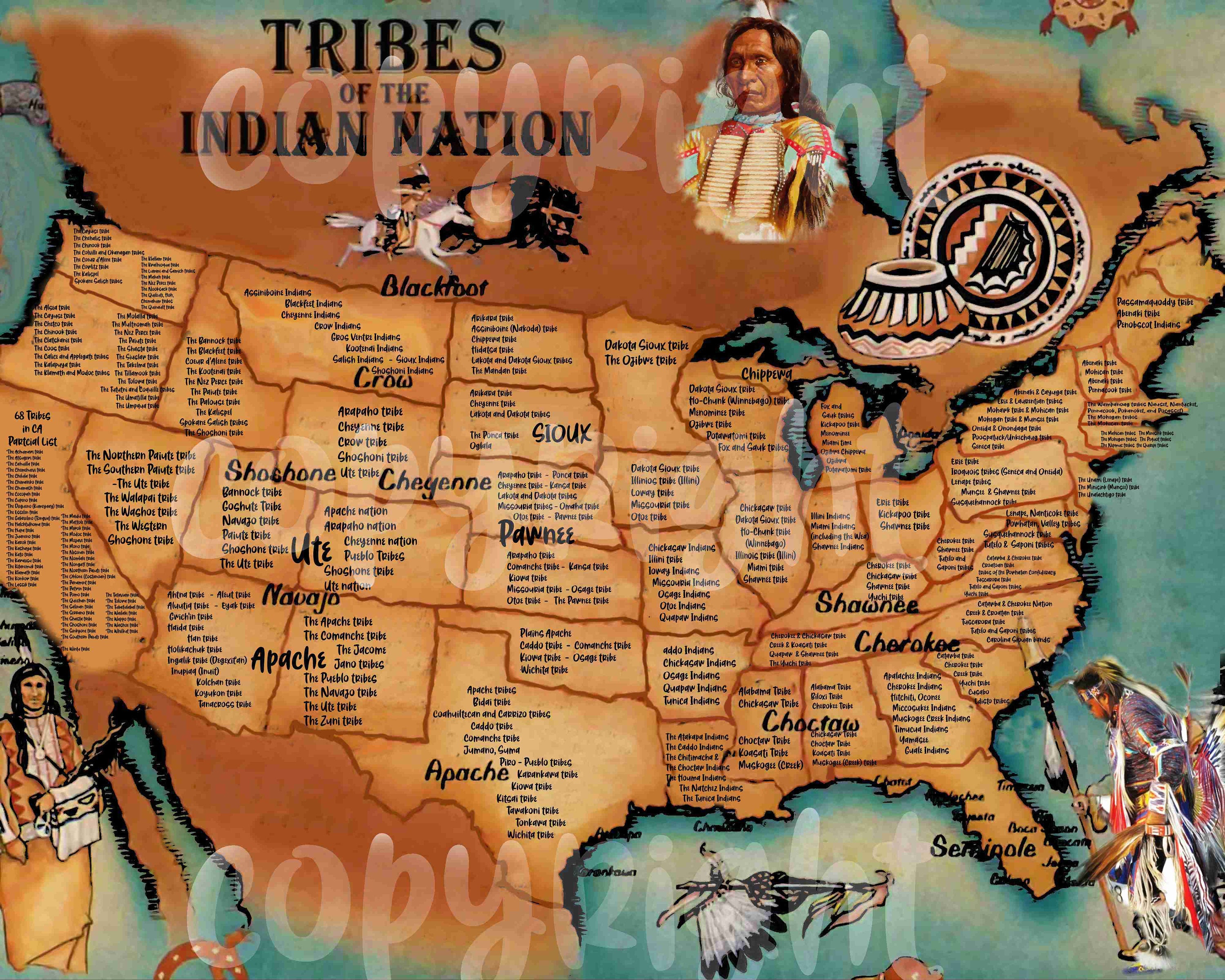
Mexico, a land of vibrant colors, rich history, and diverse landscapes, is also home to a tapestry of indigenous cultures that have thrived for millennia. The country’s indigenous population, representing over 10% of the total, is a testament to the enduring legacy of pre-Hispanic civilizations. Understanding the distribution and cultural nuances of these tribes is crucial for appreciating the complexity and richness of Mexican heritage.
A Geographic Overview: Navigating the Map of Indigenous Mexico
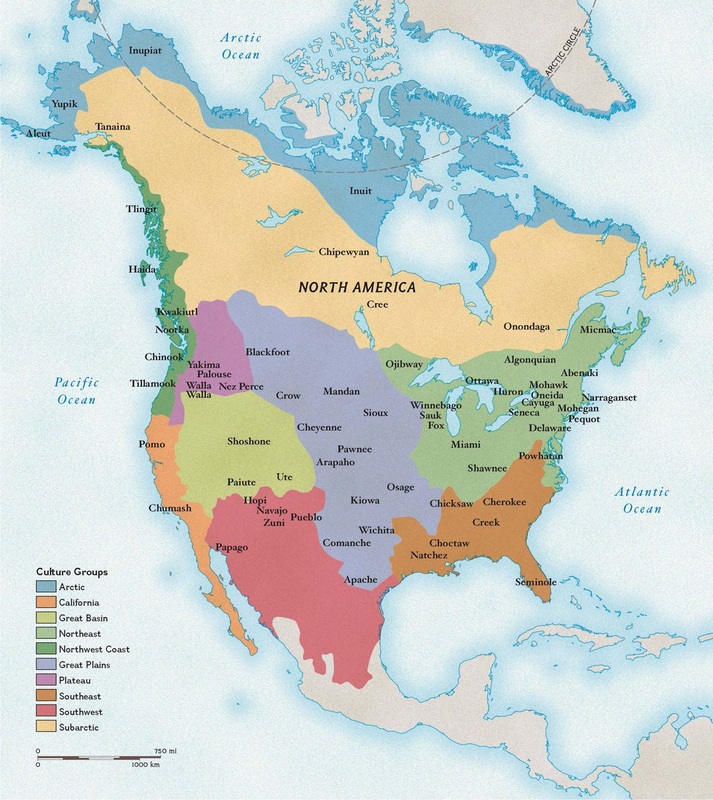
A map depicting the indigenous tribes of Mexico reveals a fascinating mosaic of cultural identities. Each region boasts a unique blend of languages, traditions, and artistic expressions, reflecting the diverse environments and historical experiences that shaped their development.
Major Linguistic Families: A Linguistic Landscape
Mexico is home to a vast array of languages, with the majority belonging to four major linguistic families:
- Nahuatl: The most widely spoken indigenous language, Nahuatl, is primarily found in central Mexico, particularly in the states of Puebla, Veracruz, and Guerrero. It is closely associated with the Aztec civilization and its legacy.
- Maya: This family encompasses a wide range of languages spoken in the Yucatan Peninsula, Chiapas, and Guatemala. Maya languages are known for their complex writing systems and intricate mythology.
- Otomanguean: This family, found in central and southern Mexico, includes languages like Otomi, Zapotec, and Mixtec. These languages are characterized by their tonal systems and unique phonological features.
- Uto-Aztecan: Extending beyond Mexico into the southwestern United States, this family includes languages like Tarahumara, Huichol, and Yaqui. Uto-Aztecan languages often feature complex verb conjugations and grammatical structures.
Regional Diversity: A Glimpse into Cultural Landscapes
Exploring the map reveals distinct regional clusters of indigenous communities, each with its own unique cultural identity:
- Mesoamerica: The heartland of pre-Hispanic civilizations, Mesoamerica encompasses central and southern Mexico. Here, the influence of the Aztecs, Maya, and Zapotecs is evident in the architecture, art, and religious practices of present-day communities.
- Northern Mexico: This region, encompassing the states of Sonora, Chihuahua, and Baja California, is home to indigenous communities with a strong connection to the desert environment. The Tarahumara, Yaqui, and Seri tribes are known for their resilience and adaptation to harsh conditions.
- Oaxaca: This state is renowned for its rich indigenous heritage, with over 16 distinct indigenous groups. The Zapotec and Mixtec civilizations left behind a legacy of intricate textiles, pottery, and archaeological sites.
- Yucatan Peninsula: The Mayan civilization flourished in this region, leaving behind a legacy of impressive archaeological sites like Chichén Itzá and Uxmal. The Maya languages and traditions continue to thrive in communities throughout the peninsula.
Cultural Preservation: A Vital Legacy
The indigenous tribes of Mexico are not merely historical remnants; they are vibrant communities actively preserving their cultural heritage. Their languages, traditions, and artistic expressions are a testament to their resilience and enduring spirit.
Importance of Mapping Indigenous Tribes:
- Understanding Cultural Diversity: The map provides a visual representation of the diverse cultural landscape of Mexico, highlighting the richness and complexity of its indigenous heritage.
- Preserving Languages: Mapping indigenous communities helps identify areas where language revitalization efforts are needed, promoting the preservation of these valuable cultural resources.
- Promoting Cultural Tourism: The map can guide travelers to communities that are actively sharing their cultural traditions, fostering cultural exchange and appreciation.
- Advocating for Indigenous Rights: By highlighting the geographical distribution of indigenous communities, the map helps raise awareness of their needs and rights, facilitating efforts to address historical injustices.
FAQs About Indigenous Tribes of Mexico:
Q: What is the largest indigenous group in Mexico?
A: The Nahua people, speaking the Nahuatl language, are the largest indigenous group in Mexico, with a population estimated to be over 1.5 million.
Q: Are all indigenous tribes in Mexico recognized by the government?
A: While the Mexican government recognizes the rights of indigenous peoples, the process of official recognition varies depending on the specific tribe and its history. Some communities have achieved official recognition, while others are still advocating for their rights.
Q: How can I learn more about indigenous cultures in Mexico?
A: Visit museums and cultural centers dedicated to indigenous art and history, attend cultural events and festivals, and interact with indigenous communities through responsible tourism.
Tips for Interacting with Indigenous Communities:
- Respect Cultural Practices: Be mindful of local customs and traditions, and ask for permission before taking photographs or recording videos.
- Support Indigenous Businesses: Patronize indigenous-owned businesses and crafts, contributing to their economic well-being.
- Learn Basic Phrases: Even a few basic phrases in the local language can demonstrate respect and foster meaningful connections.
- Engage in Cultural Exchange: Participate in cultural activities and workshops, and learn about the history and traditions of the community.
Conclusion: A Tapestry of Cultures
The map of indigenous tribes in Mexico is a powerful tool for understanding the cultural richness and historical significance of this diverse nation. It is a reminder that the legacy of pre-Hispanic civilizations continues to thrive in the vibrant communities that call Mexico home. By appreciating the diversity of these cultures, we can foster a deeper understanding of Mexico’s complex history and its enduring cultural legacy.
![Natives of Mexico [1200 x 800] : r/MapPorn](https://i.redd.it/fj9vj92csm211.jpg)






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Tapestry of Cultures: Understanding the Indigenous Tribes of Mexico. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!