A Tapestry Of Landscapes: Exploring The Physical Geography Of North Africa And Southwest Asia
A Tapestry of Landscapes: Exploring the Physical Geography of North Africa and Southwest Asia
Related Articles: A Tapestry of Landscapes: Exploring the Physical Geography of North Africa and Southwest Asia
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Tapestry of Landscapes: Exploring the Physical Geography of North Africa and Southwest Asia. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Tapestry of Landscapes: Exploring the Physical Geography of North Africa and Southwest Asia

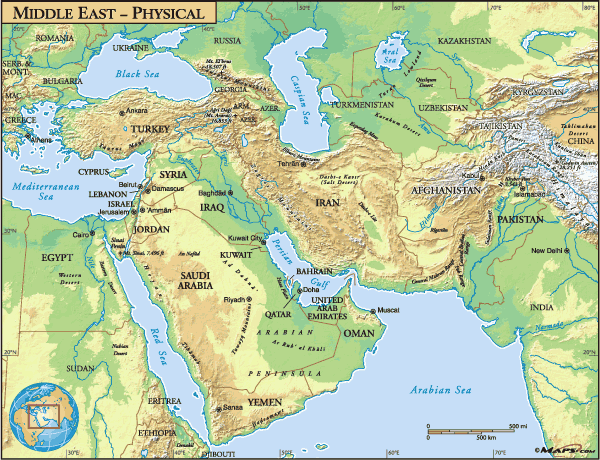
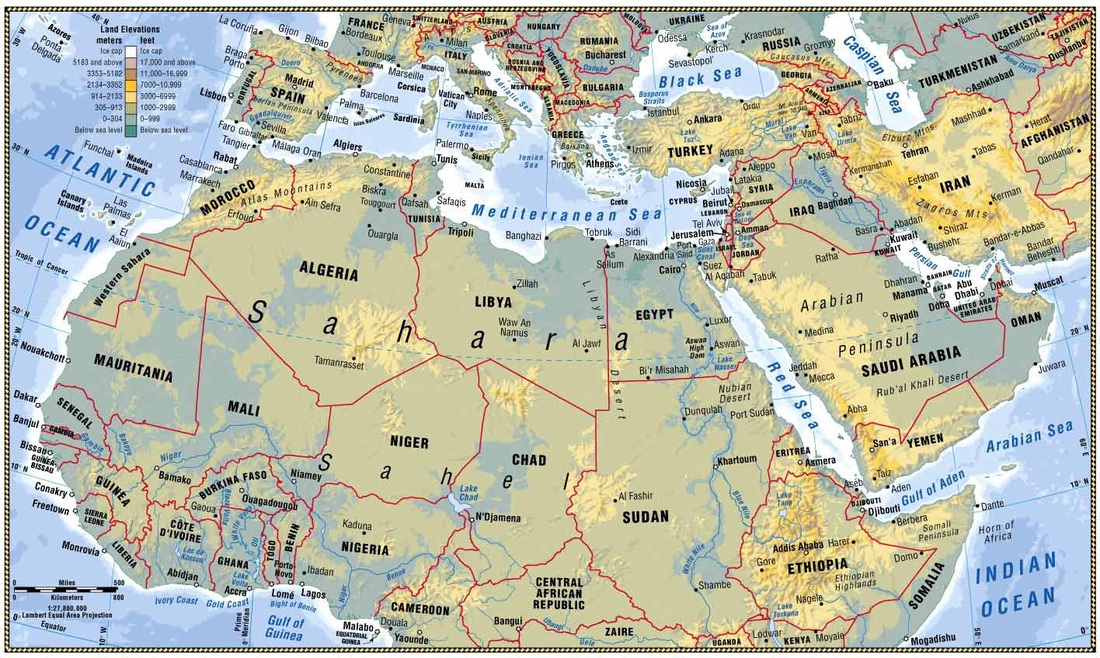
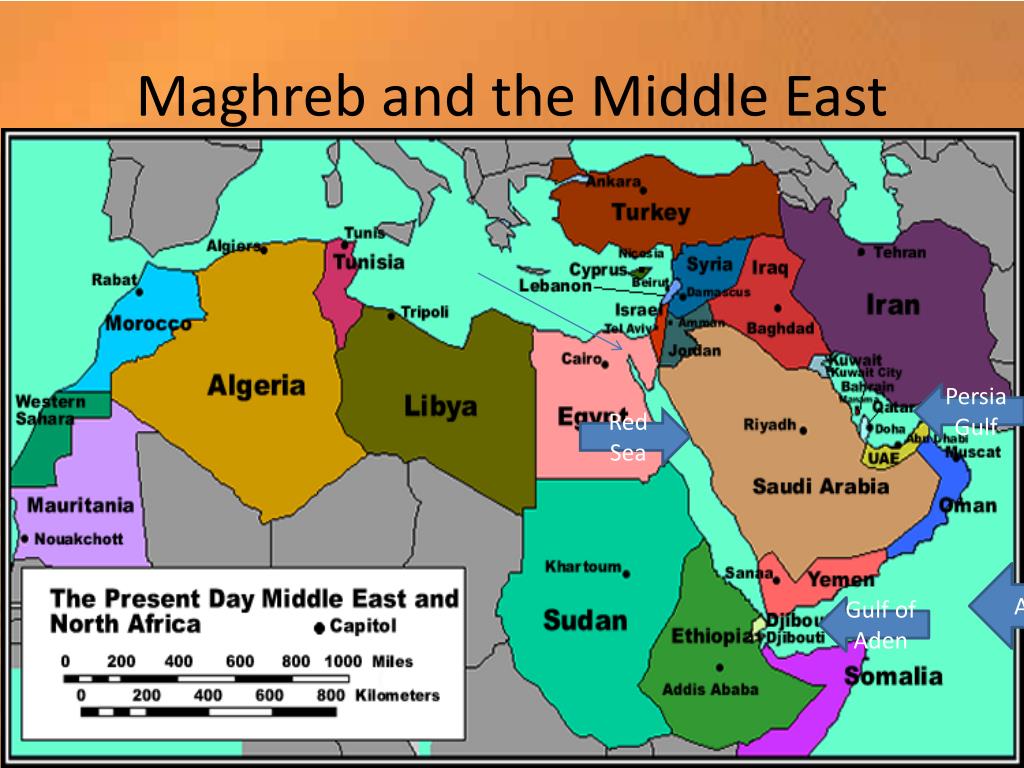
North Africa and Southwest Asia, often collectively referred to as the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region, encompass a vast and diverse expanse of land. This region, cradled between the Mediterranean Sea, the Red Sea, the Indian Ocean, and the Atlantic Ocean, boasts a remarkable array of physical features, shaping its history, culture, and the lives of its inhabitants.
Mountains and Plateaus: The Backbone of the Region
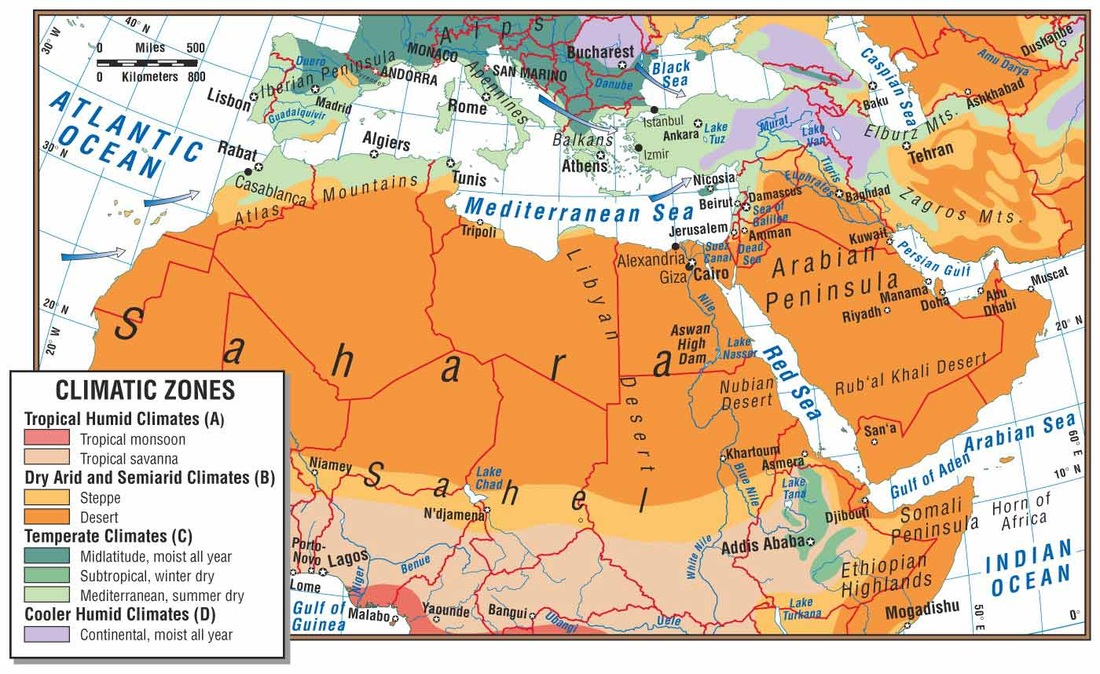
The region’s topography is characterized by a dominant presence of mountains and plateaus. The Atlas Mountains, a formidable range traversing North Africa, are home to the highest peak in North Africa, Mount Toubkal in Morocco. These mountains, along with the Anti-Atlas and Saharan Atlas, act as a natural barrier, influencing rainfall patterns and creating distinct climatic zones.
Further east, the Zagros Mountains, a dramatic range spanning Iran and Iraq, are a vital water source, feeding rivers like the Tigris and Euphrates. The Taurus Mountains in Turkey, known for their rugged beauty and diverse ecosystems, have played a pivotal role in shaping the history and culture of Anatolia.
The vast Iranian Plateau, a high and arid expanse, dominates the eastern part of the region. Its elevation and location in a rain shadow zone contribute to its dry and sparsely populated nature. The Arabian Peninsula, the largest in the world, is dominated by the vast Empty Quarter, a desert plateau of sand dunes and wind-swept plains.
Deserts: A Defining Feature
Deserts, a defining characteristic of the region, cover a significant portion of North Africa and Southwest Asia. The Sahara Desert, the largest hot desert in the world, stretches across North Africa, a vast expanse of sand dunes, rocky plateaus, and oases. The Arabian Desert, encompassing the Empty Quarter and other vast desert regions, is another prominent feature, characterized by its harsh conditions and limited water resources.
The presence of deserts has had a profound impact on the region’s history, shaping its nomadic cultures, influencing settlement patterns, and driving the development of innovative water management systems.
Rivers and Waterways: Lifeblood of the Region
Despite the prevalence of arid landscapes, the region is traversed by several major rivers, acting as vital lifelines for its inhabitants. The Nile River, the longest river in the world, flows through Egypt, providing fertile land for agriculture and supporting a rich biodiversity. The Tigris and Euphrates Rivers, originating in the Taurus Mountains, have nurtured ancient civilizations in Mesopotamia and continue to be crucial for irrigation and water supply in Iraq and Syria.
The Jordan River, flowing through Israel, Jordan, and the West Bank, is another significant waterway, though its flow has been affected by water management disputes. The Red Sea, a narrow body of water connecting the Indian Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea, is a vital shipping route and a haven for diverse marine life.
Coastal Zones: Connecting to the World
The Mediterranean Sea, bordering North Africa and Southwest Asia, has played a pivotal role in the region’s history, facilitating trade, cultural exchange, and migration. Its coastal areas, characterized by their fertile lands and pleasant climate, have been centers of civilization for millennia. The Red Sea, with its strategic location and diverse marine life, is a significant economic and ecological resource.
The Persian Gulf, an extension of the Indian Ocean, is a vital source of oil and natural gas, contributing significantly to the economies of the Gulf States. The Indian Ocean, bordering the southern part of the region, has been a major trading route for centuries, connecting the region to the East.
Volcanic Activity and Earthquakes: Shaping the Landscape
The region is situated in a seismically active zone, where the collision of tectonic plates has resulted in volcanic activity and frequent earthquakes. Mount Ararat in Turkey, believed to be the resting place of Noah’s Ark, is a dormant volcano, a testament to the region’s geological history. The Dead Sea, a salt lake bordering Israel and Jordan, is located in a rift valley formed by tectonic activity.
The Importance of Physical Geography
The physical geography of North Africa and Southwest Asia is more than just a collection of mountains, deserts, and rivers. It is a dynamic force that has shaped the region’s history, culture, and the lives of its people. The arid climate, the presence of deserts, and the availability of water resources have all played a significant role in shaping settlement patterns, agricultural practices, and the development of water management systems.
The region’s diverse landscapes have also fostered unique cultures and traditions. The mountains, with their rugged terrain and isolation, have often been home to distinct ethnic groups and languages. The coastal areas, with their access to trade and cultural exchange, have developed vibrant urban centers and diverse societies.
FAQs
Q1: What are the major mountain ranges in North Africa and Southwest Asia?
A: The major mountain ranges include the Atlas Mountains in North Africa, the Zagros Mountains in Iran and Iraq, the Taurus Mountains in Turkey, and the Lebanon Mountains in Lebanon.
Q2: What are the main desert regions in the region?
A: The main desert regions include the Sahara Desert in North Africa, the Arabian Desert in the Arabian Peninsula, and the Syrian Desert in Syria and Iraq.
Q3: What are the most important rivers in the region?
A: The most important rivers include the Nile River in Egypt, the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers in Iraq and Syria, the Jordan River in Israel, Jordan, and the West Bank, and the Indus River in Pakistan.
Q4: What are the major coastal zones in the region?
A: The major coastal zones include the Mediterranean Sea, the Red Sea, the Persian Gulf, and the Indian Ocean.
Q5: What are the major environmental challenges facing the region?
A: The major environmental challenges include desertification, water scarcity, pollution, and climate change.
Tips for Understanding the Physical Geography of the Region
- Use a physical map: A physical map is an essential tool for understanding the region’s geography. It shows the major landforms, water bodies, and elevations, providing a visual representation of the landscape.
- Read about the region’s history: The region’s history is inextricably linked to its physical geography. Understanding the historical context can help you appreciate the impact of the landscape on human societies.
- Explore the region’s cultures: The region’s diverse cultures are shaped by its physical geography. Learn about the different ways people have adapted to the challenges and opportunities presented by the landscape.
- Consider the impact of climate change: Climate change is a major threat to the region’s environment and its people. Understanding the potential impacts of climate change can help you appreciate the importance of sustainable practices.
Conclusion
The physical geography of North Africa and Southwest Asia is a tapestry of landscapes, a complex and fascinating interplay of mountains, deserts, rivers, and coastlines. This region’s diverse topography has shaped its history, culture, and the lives of its people. Understanding the region’s physical geography is crucial for appreciating its rich history, its diverse cultures, and the challenges it faces in the 21st century.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Tapestry of Landscapes: Exploring the Physical Geography of North Africa and Southwest Asia. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!