A Tapestry Of Time: Exploring The Historical Maps Of Texas
A Tapestry of Time: Exploring the Historical Maps of Texas
Related Articles: A Tapestry of Time: Exploring the Historical Maps of Texas
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Tapestry of Time: Exploring the Historical Maps of Texas. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Tapestry of Time: Exploring the Historical Maps of Texas
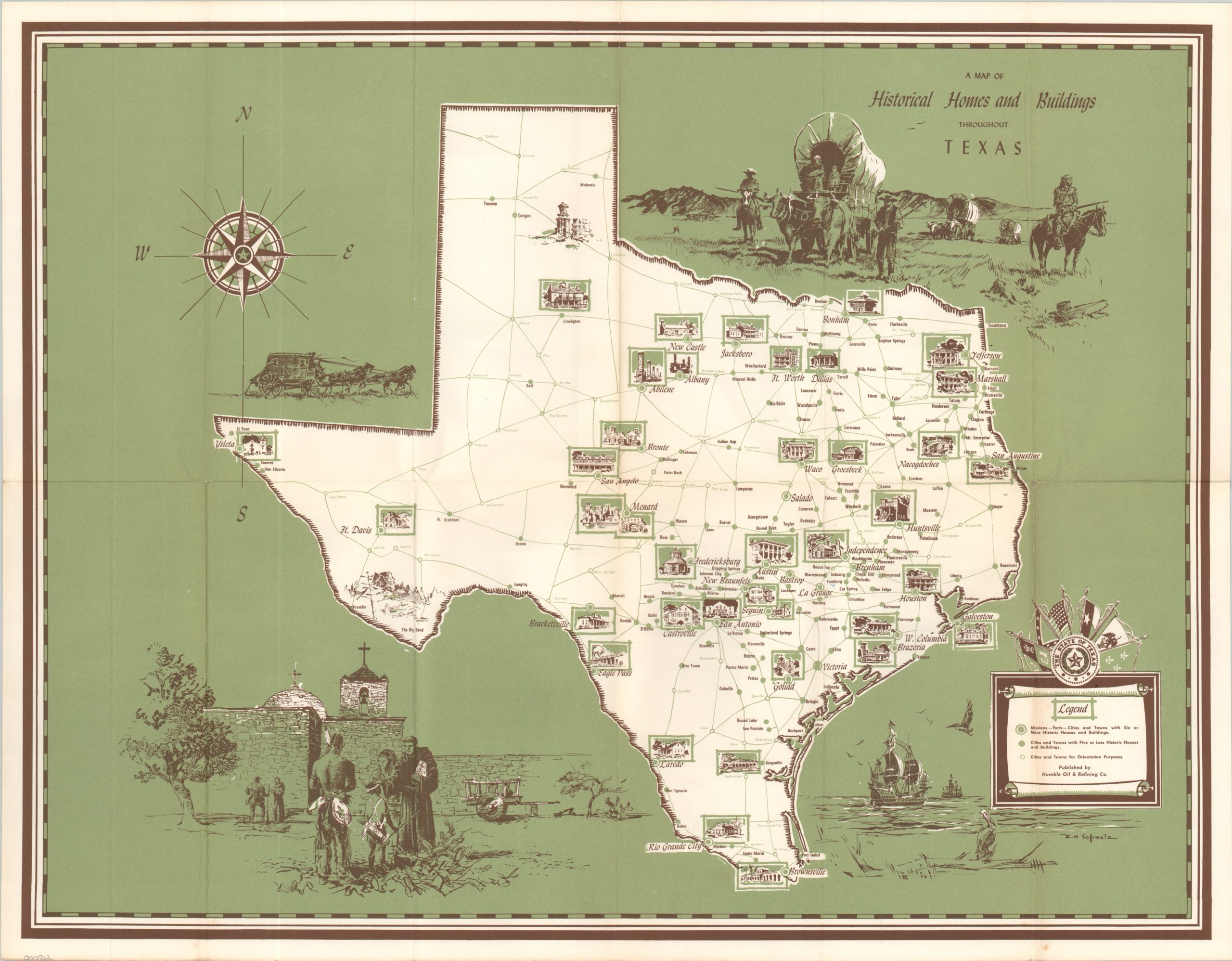
The Lone Star State, with its vast landscapes and rich history, offers a captivating narrative woven through the threads of time. Historical maps of Texas, like ancient scrolls, unveil this story, providing a visual chronicle of its evolution from a sparsely populated frontier to a vibrant, modern state. These maps are not merely static representations of land; they are dynamic documents that illuminate the changing political, economic, and social landscapes of Texas.
From Early Explorations to Spanish Dominance:
The earliest maps of Texas, dating back to the 16th century, were primarily the work of European explorers seeking new trade routes and claiming new territories. These rudimentary maps often depicted Texas as a mysterious land of vast prairies, dense forests, and indigenous populations. Spanish conquistadors, like Álvar Núñez Cabeza de Vaca and Francisco Vázquez de Coronado, ventured into the region, charting their journeys and adding valuable information to existing cartographic knowledge.
The Spanish colonial period, which lasted for nearly three centuries, saw the establishment of missions, presidios, and settlements along the Rio Grande and the Gulf Coast. Spanish cartographers meticulously documented these settlements, creating maps that reflected the growing influence of Spanish rule. Maps from this era showcase the strategic locations of missions, the intricate network of trade routes, and the distribution of indigenous communities.
The Birth of a Republic:
The 19th century witnessed a dramatic shift in Texas’s destiny. The Mexican War of Independence in 1821 opened the door for Anglo-American settlers to claim land in Texas. The influx of new settlers, spurred by land grants and the promise of freedom, led to a burgeoning population and a growing sense of independence. Maps of this period depict the expansion of Anglo-American settlements, the establishment of new towns, and the emergence of distinct cultural and economic zones.
The Texas Revolution (1835-1836), a pivotal moment in the state’s history, saw the declaration of independence from Mexico. Maps from this era highlight the key battle sites, the movement of armies, and the evolving territorial boundaries of the newly formed Republic of Texas.
Statehood and Expansion:
Texas’s annexation into the United States in 1845 marked a new chapter in its history. The subsequent Mexican-American War (1846-1848) resulted in significant territorial gains for the United States, including the annexation of vast tracts of land from Mexico. Maps from this period reflect the shifting political landscape, showcasing the newly acquired territories, the establishment of military outposts, and the expansion of American influence westward.
The latter half of the 19th century saw the rapid development of Texas’s infrastructure. Railroads, connecting distant towns and cities, transformed the state’s economy, and the discovery of oil in the early 20th century further propelled its growth. Maps from this era illustrate the construction of railroads, the emergence of new industries, and the changing demographics of the state.
The 20th Century and Beyond:
The 20th century brought about significant changes in Texas, including the rise of urbanization, the development of major cities like Houston, Dallas, and San Antonio, and the increasing influence of the oil and gas industry. Maps from this era showcase the urban sprawl, the growth of transportation networks, and the development of new industries.
Contemporary maps of Texas continue to evolve, reflecting the state’s ongoing transformation. These maps incorporate advanced technologies, incorporating detailed data on population density, economic activity, environmental conditions, and infrastructure. They provide valuable insights into the present and future of the Lone Star State.
Importance of Historical Maps:
Historical maps of Texas serve as invaluable resources for understanding the state’s past, present, and future. They offer a unique perspective on:
- Spatial Relationships: Maps reveal the spatial relationships between different settlements, natural features, and infrastructure, providing a visual understanding of how the state developed and evolved over time.
- Historical Events: Maps document key historical events, such as battles, migrations, and political changes, offering a tangible record of the past.
- Cultural Landscapes: Maps depict the cultural landscapes of Texas, showcasing the distribution of different ethnic groups, religious practices, and economic activities.
- Environmental Change: Maps can track changes in the environment, such as deforestation, urbanization, and the effects of climate change, providing a visual record of the state’s evolving landscape.
- Economic Development: Maps illustrate the growth of industries, the development of transportation networks, and the changing economic landscape of Texas.
FAQs:
Q: Where can I find historical maps of Texas?
A: Historical maps of Texas can be found in various repositories, including:
- Libraries: University libraries, state archives, and local historical societies often house collections of historical maps.
- Museums: Historical museums and art museums may display or have collections of maps related to Texas history.
- Online Archives: Digital archives, such as the Library of Congress, the Texas State Library and Archives Commission, and the University of Texas at Austin’s Center for American History, offer online access to digitized maps.
- Private Collections: Individuals and organizations may have private collections of historical maps.
Q: How can I use historical maps to learn about Texas history?
A: Historical maps can be used to:
- Trace the movement of people and goods: Maps can show the routes taken by explorers, settlers, and traders, providing insights into the patterns of migration and trade in Texas.
- Identify key settlements and landmarks: Maps can reveal the locations of early settlements, missions, forts, and other significant landmarks, offering a glimpse into the state’s early history.
- Understand the impact of historical events: Maps can document the locations of battles, the movement of armies, and the effects of natural disasters, offering a visual understanding of the impact of historical events on the state.
- Analyze the changing landscape: Maps can show the evolution of the landscape, including the growth of cities, the expansion of agriculture, and the development of transportation networks.
Q: What are some of the most important historical maps of Texas?
A: Some of the most important historical maps of Texas include:
- The "Carta del Rio Bravo" (1749): This map, created by Spanish cartographer José Antonio de Alzate y Ramírez, depicts the Rio Grande River and the surrounding territory, providing valuable information about the Spanish colonial period.
- The "Map of Texas" (1840): Created by the Republic of Texas, this map shows the boundaries of the newly formed republic, outlining its claims to territory that would later become part of the United States.
- The "Map of Texas" (1845): This map, published shortly after Texas’s annexation into the United States, reflects the newly established state boundaries and the expansion of American influence in the region.
- The "Map of Texas" (1872): This map, created by the Texas Railroad Commission, showcases the rapidly growing network of railroads that transformed the state’s economy and connected distant communities.
Tips for Using Historical Maps:
- Analyze the map’s scale and date: The scale of the map will determine the level of detail, while the date of creation will provide context for the information it depicts.
- Consider the map’s purpose and creator: The map’s purpose, whether it was for navigation, exploration, or political purposes, will influence its content and accuracy.
- Compare different maps: Comparing maps from different periods can reveal how the landscape and political boundaries have changed over time.
- Use maps in conjunction with other sources: Maps can be combined with other historical sources, such as diaries, letters, and government documents, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the past.
Conclusion:
Historical maps of Texas are more than just static representations of land; they are windows into the past, offering a unique perspective on the state’s evolution. By studying these maps, we gain a deeper understanding of the historical forces that shaped Texas, the challenges it faced, and the triumphs it achieved. These maps serve as valuable resources for researchers, historians, and anyone seeking to explore the rich tapestry of Texas’s history. They remind us that the land we inhabit today is the product of countless journeys, struggles, and triumphs, a legacy that continues to shape the Lone Star State.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Tapestry of Time: Exploring the Historical Maps of Texas. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!