A Visual Landscape Of Pennsylvania’s Energy Future: Understanding The Fracking Map
A Visual Landscape of Pennsylvania’s Energy Future: Understanding the Fracking Map
Related Articles: A Visual Landscape of Pennsylvania’s Energy Future: Understanding the Fracking Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Visual Landscape of Pennsylvania’s Energy Future: Understanding the Fracking Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Visual Landscape of Pennsylvania’s Energy Future: Understanding the Fracking Map

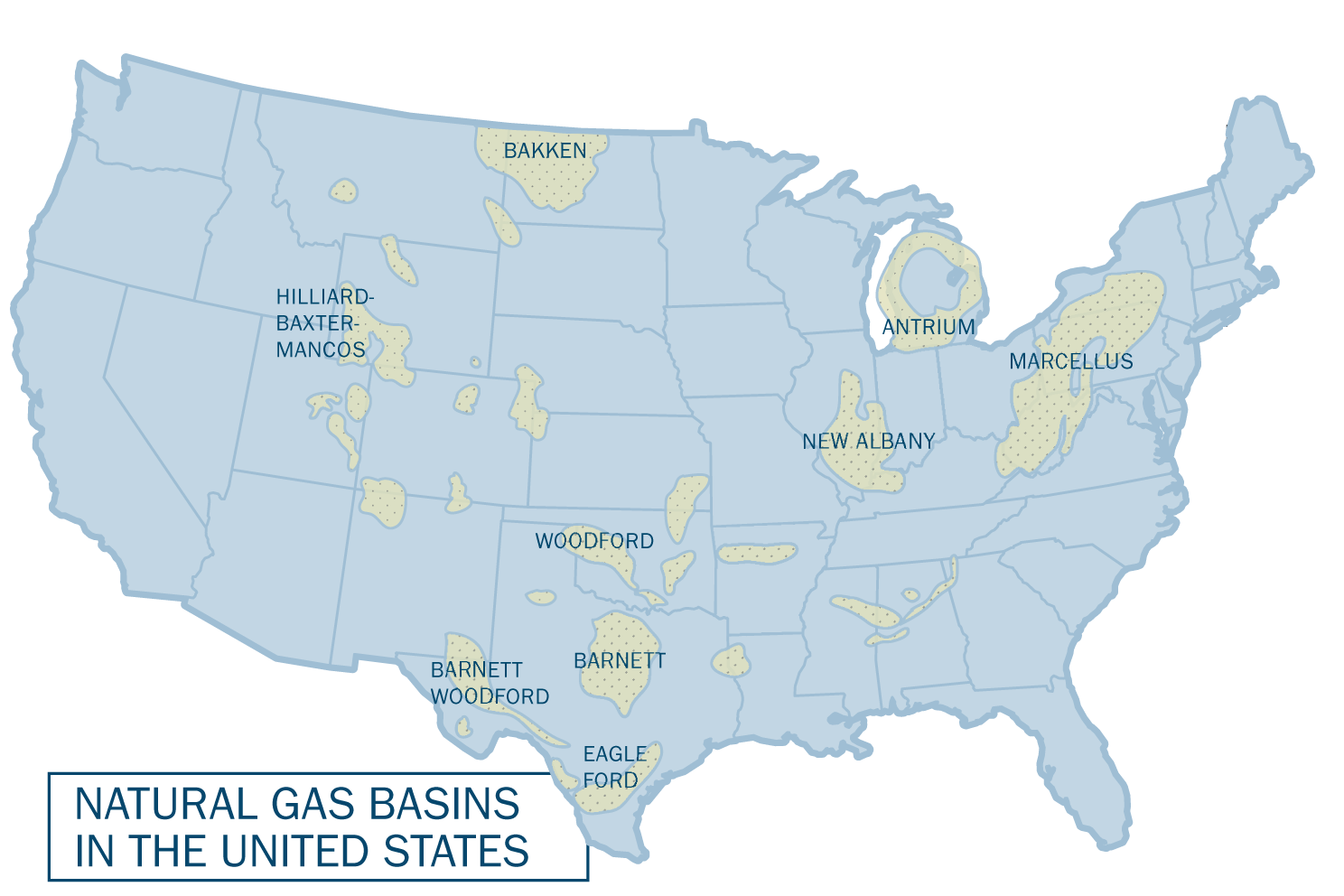
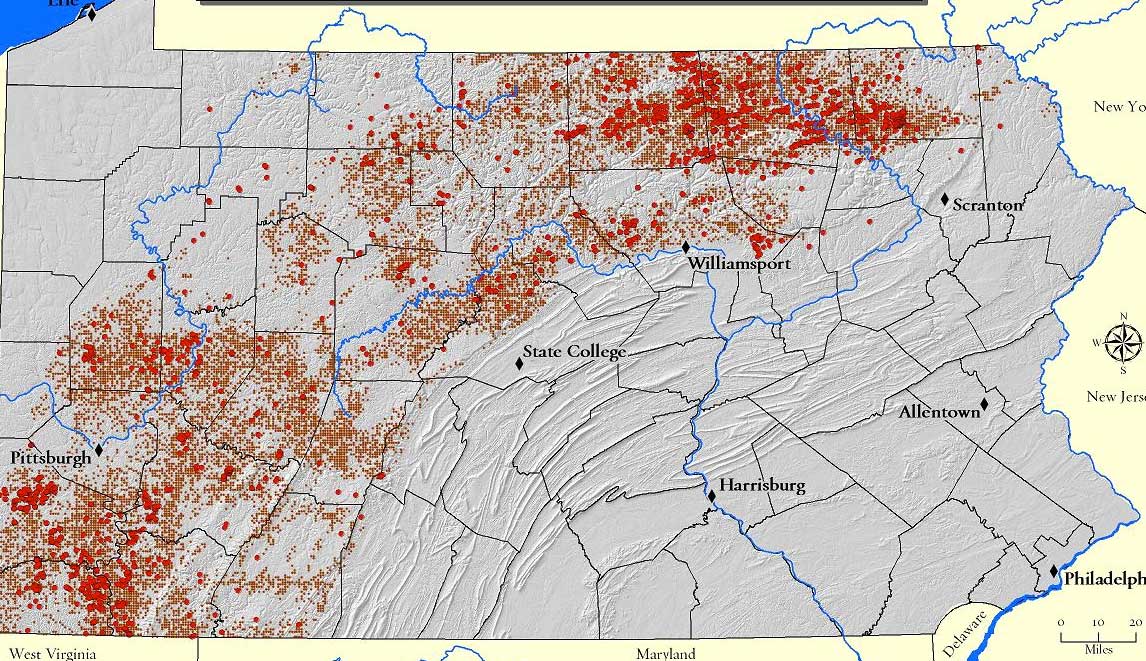
The Marcellus Shale formation, a vast underground reservoir of natural gas, stretches across much of Pennsylvania, making the state a focal point for the controversial practice of hydraulic fracturing, commonly known as fracking. This process, which involves injecting a mixture of water, sand, and chemicals into the shale to extract natural gas, has sparked heated debates about its environmental and economic impacts. A visual representation of this activity, often referred to as the "fracking map," provides a crucial tool for understanding the scope and potential consequences of this energy extraction method.
Deciphering the Map: A Window into Pennsylvania’s Energy Landscape
The fracking map of Pennsylvania is a complex and ever-evolving visual representation. It typically depicts various aspects of fracking activity, including:
- Well Locations: The map pinpoints the exact locations of active and inactive natural gas wells, offering a clear picture of the geographical distribution of fracking operations.
- Permitting and Approvals: The map may include information about permits granted for drilling, highlighting areas where fracking is legally allowed.
- Infrastructure: Pipelines, compressor stations, and processing plants, essential components of the natural gas extraction and transportation system, are often depicted on the map.
- Environmental Data: The map might incorporate data related to water quality, air pollution, and seismic activity, allowing for a preliminary assessment of potential environmental impacts.
The Significance of the Fracking Map: A Tool for Understanding and Debate
The fracking map serves as a vital resource for various stakeholders involved in the natural gas industry and its surrounding communities:
- Policymakers and Regulators: The map provides a clear visual representation of the spatial extent of fracking activity, aiding in the development of effective regulations and policies to mitigate potential environmental and social risks.
- Environmental Groups: Environmental organizations utilize the map to identify areas of potential environmental concern, monitor the expansion of fracking operations, and advocate for responsible environmental practices.
- Local Communities: Residents can use the map to understand the proximity of fracking operations to their homes, schools, and water sources, enabling them to engage in informed discussions about potential impacts on their communities.
- Industry Representatives: The map offers valuable insights into the spatial distribution of natural gas resources, aiding in the planning and optimization of fracking operations.
Beyond the Visual: Exploring the Complexities of Fracking in Pennsylvania
While the fracking map provides a valuable snapshot of the industry’s footprint, it’s crucial to acknowledge the complexities surrounding this issue:
- Economic Benefits: Proponents of fracking highlight the significant economic benefits it brings to Pennsylvania, including job creation, increased tax revenue, and lower energy prices.
- Environmental Concerns: Opponents of fracking raise concerns about potential environmental impacts such as water contamination, air pollution, and seismic activity.
- Social Impacts: The presence of fracking operations can lead to social and community disruptions, including changes in land use patterns, increased traffic, and potential conflicts between industry and local residents.
Navigating the Debate: Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the main environmental concerns associated with fracking?
A: The primary environmental concerns include:
- Water Contamination: Fracking operations can potentially contaminate groundwater sources through leaks or spills of fracking fluids.
- Air Pollution: The burning of natural gas and the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during fracking can contribute to air pollution.
- Seismic Activity: Fracking operations can trigger minor earthquakes, particularly in areas with pre-existing fault lines.
Q: What are the economic benefits of fracking in Pennsylvania?
A: The economic benefits include:
- Job Creation: Fracking operations create jobs in various sectors, including drilling, engineering, and construction.
- Increased Tax Revenue: The industry generates significant tax revenue for state and local governments.
- Lower Energy Prices: Fracking has contributed to lower natural gas prices, benefiting consumers and businesses.
Q: What are the social impacts of fracking in Pennsylvania?
A: The social impacts include:
- Community Disruptions: Fracking operations can disrupt local communities through increased traffic, noise pollution, and changes in land use.
- Conflicts Between Industry and Residents: Fracking can lead to conflicts between industry representatives and local residents over environmental concerns and land rights.
- Health Concerns: Some residents living near fracking sites have expressed concerns about potential health impacts, such as respiratory problems and skin irritation.
Tips for Navigating the Fracking Landscape
- Research and Educate Yourself: Consult reputable sources of information about fracking, including scientific studies, government reports, and independent organizations.
- Engage in Informed Dialogue: Participate in discussions about fracking, expressing your concerns and perspectives respectfully.
- Support Responsible Regulation: Advocate for policies that promote environmental protection and ensure the safety of communities.
- Consider the Long-Term Impacts: Evaluate the potential long-term consequences of fracking on the environment, economy, and society.
Conclusion: A Complex Landscape with No Easy Answers
The fracking map of Pennsylvania offers a crucial visual aid for understanding the spatial extent of this controversial industry. However, it’s essential to recognize that the map alone cannot provide a comprehensive picture of the complex environmental, economic, and social implications of fracking. Navigating this landscape requires a nuanced understanding of the various perspectives and a commitment to informed and respectful dialogue. Ultimately, the future of fracking in Pennsylvania will depend on a careful balancing of economic benefits, environmental protection, and social considerations.



![]()


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Visual Landscape of Pennsylvania’s Energy Future: Understanding the Fracking Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!