Germany In 1939: A Nation Transformed By Aggression
Germany in 1939: A Nation Transformed by Aggression
Related Articles: Germany in 1939: A Nation Transformed by Aggression
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Germany in 1939: A Nation Transformed by Aggression. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Germany in 1939: A Nation Transformed by Aggression

The year 1939 marked a pivotal moment in European history, with Germany poised on the brink of war. The map of Germany in this year reflected not only its territorial expansion but also the ambitions and ideology of the Nazi regime. Understanding the geographical changes of this period is crucial for comprehending the events that led to World War II and the subsequent reshaping of Europe.
The Pre-War Landscape:
Prior to 1939, Germany was a nation recovering from the aftermath of World War I. The Treaty of Versailles, imposed upon Germany in 1919, had significantly reduced its territory and imposed heavy economic sanctions. The country was divided into several states, with Prussia remaining the largest and most powerful. This fragmented political structure contributed to instability and fostered a sense of national humiliation.
The Rise of the Nazis:
The rise of the Nazi Party under Adolf Hitler exploited the widespread discontent and resentment felt by many Germans. Hitler promised to restore Germany’s lost glory, dismantle the restrictions imposed by Versailles, and create a unified, powerful nation. This vision resonated with a population yearning for national pride and economic recovery.
The Aggressive Expansion:
Hitler’s ambitions were not limited to domestic affairs. He sought to expand Germany’s territory and create a vast "Greater German Reich." This expansionist policy began with the annexation of Austria in 1938, followed by the seizure of the Sudetenland region of Czechoslovakia, also in 1938. These actions were met with weak resistance from the international community, emboldening Hitler to further his ambitions.
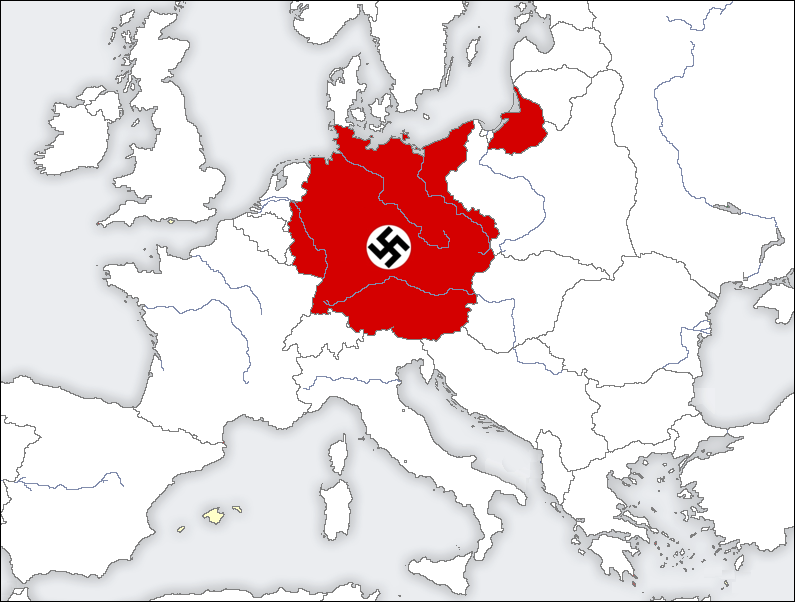
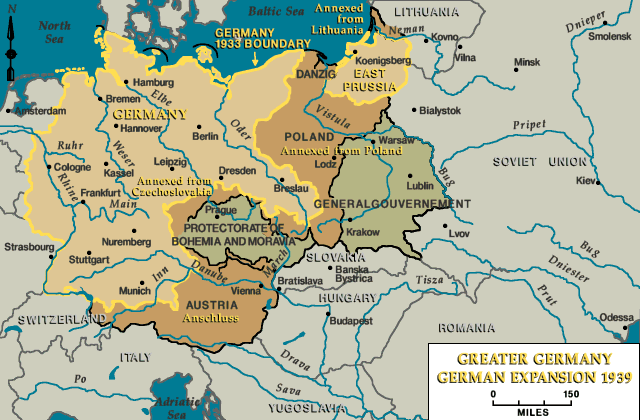
The Map of Germany in 1939:
By 1939, the map of Germany had been dramatically altered. The country had absorbed Austria, the Sudetenland, and the rest of Czechoslovakia, significantly expanding its territory and population. This territorial expansion was not achieved through peaceful means but through a combination of intimidation, military force, and diplomatic maneuvering.
The Importance of Understanding the Map:
The map of Germany in 1939 provides a visual representation of the Nazi regime’s aggressive expansionism. It highlights the extent of their territorial ambitions and the consequences of the international community’s appeasement policies. This understanding is crucial for comprehending the events leading to World War II, the subsequent devastation of Europe, and the lasting impact of the Nazi ideology.
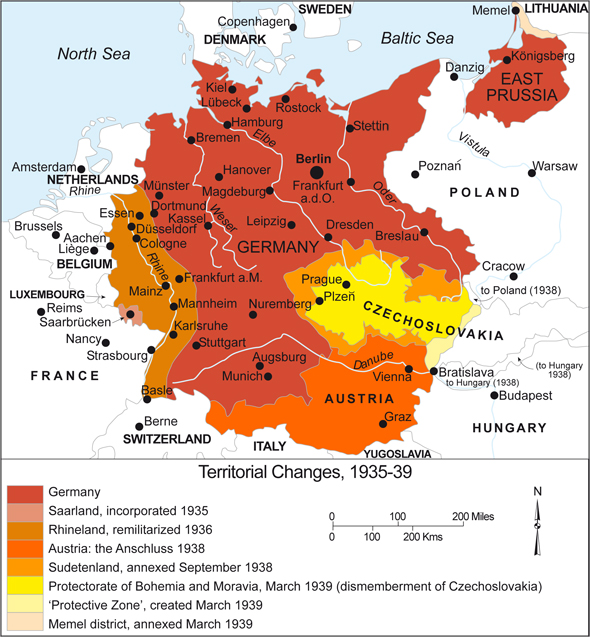
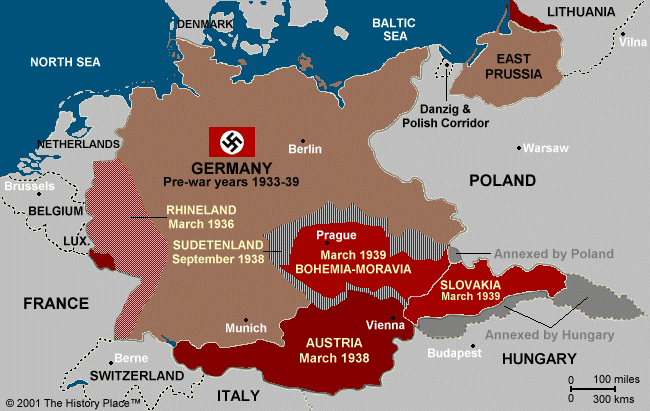
Examining the Changes in Detail:
- Austria: The annexation of Austria, known as the Anschluss, was a significant step towards creating a unified "Greater German Reich." Austria’s strategic location, bordering Germany and Italy, made it a valuable addition to Hitler’s plans.
- Sudetenland: The Sudetenland region of Czechoslovakia was predominantly inhabited by ethnic Germans. Hitler used this fact to justify his claim to the region, arguing for the reunification of German people. The Munich Agreement, signed in 1938, allowed Germany to annex the Sudetenland, despite Czechoslovakia’s opposition.
- Czechoslovakia: Following the annexation of the Sudetenland, the rest of Czechoslovakia was forced to submit to German domination. The country was effectively dismembered, with parts of its territory being annexed by Hungary and Poland. This act demonstrated the ruthlessness of the Nazi regime and its disregard for international law.
- Memel Territory: The Memel Territory, a small region on the Baltic coast, was returned to Germany in 1939. This territory had been annexed by Lithuania after World War I, but Hitler used a fabricated "crisis" to force its return.
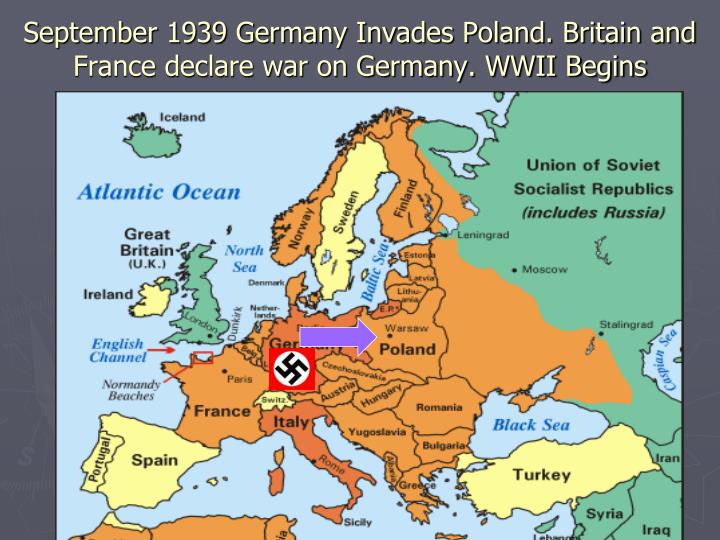
The Consequences of Expansion:
Germany’s aggressive expansion had significant consequences for Europe and the world. It led to the outbreak of World War II, a conflict that resulted in millions of deaths and widespread devastation. The war also resulted in the collapse of empires, the rise of new superpowers, and the creation of new political and economic structures.
FAQs about the Map of Germany in 1939:
Q: What were the main factors that contributed to Germany’s expansion in 1939?
A: The main factors were the rise of the Nazi Party, Hitler’s aggressive ambitions, and the appeasement policies of the international community.
Q: What were the consequences of Germany’s territorial expansion?
A: The consequences were far-reaching and devastating, leading to the outbreak of World War II, millions of deaths, and the reshaping of the geopolitical landscape.
Q: How did the map of Germany in 1939 differ from the map before the Nazi takeover?
A: The map of Germany in 1939 was significantly larger, incorporating Austria, the Sudetenland, and the rest of Czechoslovakia. It also included the Memel Territory, which had been annexed from Lithuania.
Q: Why is it important to understand the map of Germany in 1939?
A: It is crucial to understand the map to comprehend the events leading to World War II, the Nazi regime’s ambitions, and the consequences of their actions.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Germany in 1939:
- Use historical maps: Refer to maps from the period to visualize the territorial changes and the extent of Germany’s expansion.
- Research key events: Explore the historical context surrounding the annexation of Austria, the Sudetenland, and Czechoslovakia.
- Analyze the political situation: Understand the role of the Nazi Party, the international community’s response, and the impact of appeasement policies.
- Consider the consequences: Reflect on the long-term effects of Germany’s aggressive expansion, including the outbreak of World War II and the subsequent reshaping of Europe.
Conclusion:
The map of Germany in 1939 is a stark reminder of the dangers of unchecked aggression and the importance of international cooperation. It represents a period of profound political and territorial upheaval, shaping the course of European history for decades to come. By understanding the map, we can gain valuable insights into the causes and consequences of war, the impact of ideology, and the importance of upholding international law and order.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Germany in 1939: A Nation Transformed by Aggression. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!