Mapping Pomerania: A Journey Through History, Culture, And Landscape
Mapping Pomerania: A Journey Through History, Culture, and Landscape
Related Articles: Mapping Pomerania: A Journey Through History, Culture, and Landscape
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping Pomerania: A Journey Through History, Culture, and Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping Pomerania: A Journey Through History, Culture, and Landscape

Pomerania, a region historically spanning the southern Baltic Sea coast, boasts a rich and complex history, interwoven with vibrant cultural traditions and a captivating landscape. Understanding Pomerania requires delving into its geographical, historical, and cultural tapestry, unraveling its intricate threads to reveal a captivating narrative.
A Geographic Tapestry:
Pomerania, in its broadest sense, encompasses a region straddling the Baltic Sea coast, encompassing parts of modern-day Poland, Germany, and Denmark. The region’s northern boundary is the Baltic Sea, while the south is marked by the Oder River, which serves as a natural divide between Pomerania and Brandenburg. The western portion of Pomerania, known as Western Pomerania, lies within Germany, while the eastern part, known as Eastern Pomerania, falls within Poland.
The landscape of Pomerania is characterized by its coastal plains, rolling hills, and numerous lakes and rivers. The Baltic Sea has profoundly influenced the region’s history, culture, and economy, shaping its identity and providing a vital link to the wider world.
A History Unfolding:
Pomerania’s history is a complex tapestry woven with threads of various cultures, empires, and political entities. The region’s earliest inhabitants were the Pomeranian Slavs, who established a distinct culture and language. The region’s strategic location on the Baltic Sea drew the attention of powerful neighbors, leading to a series of conflicts and shifting alliances.
The 12th century saw the arrival of German settlers and the establishment of the Duchy of Pomerania, marking the beginning of a period of significant cultural and economic change. The Duchy, centered in Szczecin (Stettin), gradually expanded its influence, encompassing much of the region and establishing a network of towns and cities.
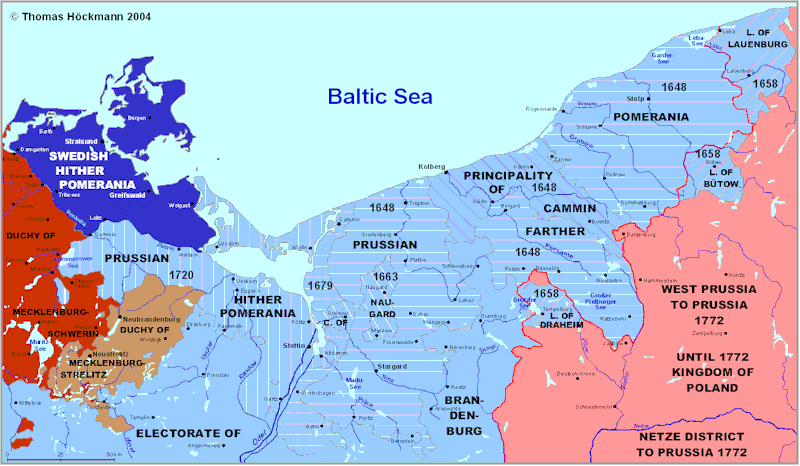
The 17th century brought a period of decline for the Duchy of Pomerania, marked by internal conflicts and the rise of Prussia. The region was subsequently divided between Prussia and Sweden, a division that would last until the 19th century.
The 19th century witnessed the rise of nationalism and the emergence of a distinct Pomeranian identity. The region was integrated into the German Empire, experiencing a period of economic growth and cultural development. However, the 20th century brought further upheaval, with the region becoming a battleground during World War II and subsequently divided between Poland and East Germany.
A Cultural Mosaic:
Pomerania’s cultural heritage is a rich blend of Slavic, Germanic, and Scandinavian influences. The region boasts a unique dialect, known as Pomeranian Low German, which has its roots in the medieval period. The region’s traditional folk music and dance traditions are characterized by a blend of Slavic and Germanic elements, reflecting the diverse cultural influences that have shaped the region.
Pomerania’s cultural heritage is also evident in its architecture, with numerous medieval churches, castles, and manor houses dotting the landscape. The region’s cities, such as Szczecin, Gdańsk (Danzig), and Koszalin, showcase a blend of architectural styles, reflecting the region’s rich history and diverse cultural influences.
The Importance of Pomerania:
Pomerania’s strategic location on the Baltic Sea has made it a vital economic and cultural hub for centuries. The region’s ports, such as Gdańsk and Szczecin, have served as gateways for trade and commerce, connecting the region to the wider world. The region’s fertile land has supported agriculture and fishing, contributing to its economic prosperity.
Pomerania’s cultural heritage is a valuable asset, attracting tourists and fostering cultural exchange. The region’s diverse historical sites, architectural landmarks, and cultural traditions offer a glimpse into its rich past and continue to inspire and captivate visitors today.
FAQs by Map Pomerania:
-
What are the main cities in Pomerania?
- Szczecin (Poland), Gdańsk (Poland), Koszalin (Poland), Greifswald (Germany), Stralsund (Germany), and Świnoujście (Poland) are some of the most prominent cities in Pomerania.
-
What languages are spoken in Pomerania?
- Polish and German are the dominant languages in Pomerania, with Pomeranian Low German still spoken in some areas.
-
What is the significance of the Baltic Sea to Pomerania?
- The Baltic Sea has been a vital waterway for trade, transportation, and cultural exchange, profoundly influencing Pomerania’s history, economy, and identity.
-
What are some of the notable historical events that have shaped Pomerania?
- The arrival of German settlers in the 12th century, the establishment of the Duchy of Pomerania, the division of the region between Prussia and Sweden in the 17th century, and the integration into the German Empire in the 19th century are some of the key historical events that have shaped Pomerania.
-
What are some of the cultural attractions in Pomerania?
- Pomerania boasts numerous historical sites, including medieval churches, castles, and manor houses, as well as museums showcasing the region’s rich history and cultural heritage. The region’s folk music and dance traditions also offer a unique glimpse into Pomeranian culture.
Tips by Map Pomerania:
- Explore the region’s historical sites: Visit medieval churches, castles, and manor houses to experience Pomerania’s rich history firsthand.
- Sample the local cuisine: Pomeranian cuisine offers a delicious blend of Slavic and Germanic influences, with dishes like "bigos" (hunter’s stew) and "kartoffelpuffer" (potato pancakes) being popular favorites.
- Attend a cultural event: Immerse yourself in Pomeranian culture by attending a folk music concert, dance performance, or traditional festival.
- Learn about the region’s history: Visit museums and historical sites to deepen your understanding of Pomerania’s fascinating past.
- Enjoy the region’s natural beauty: Explore the Baltic Sea coast, visit the region’s numerous lakes and forests, and experience the tranquility of Pomerania’s natural landscapes.
Conclusion by Map Pomerania:
Pomerania, with its rich history, vibrant culture, and captivating landscape, stands as a testament to the enduring power of human resilience and cultural exchange. Its strategic location on the Baltic Sea has shaped its destiny, connecting it to the wider world and fostering a unique blend of cultural influences. Whether exploring its historical sites, indulging in its culinary delights, or simply enjoying its natural beauty, Pomerania offers a captivating journey through time and culture, leaving a lasting impression on all who visit.




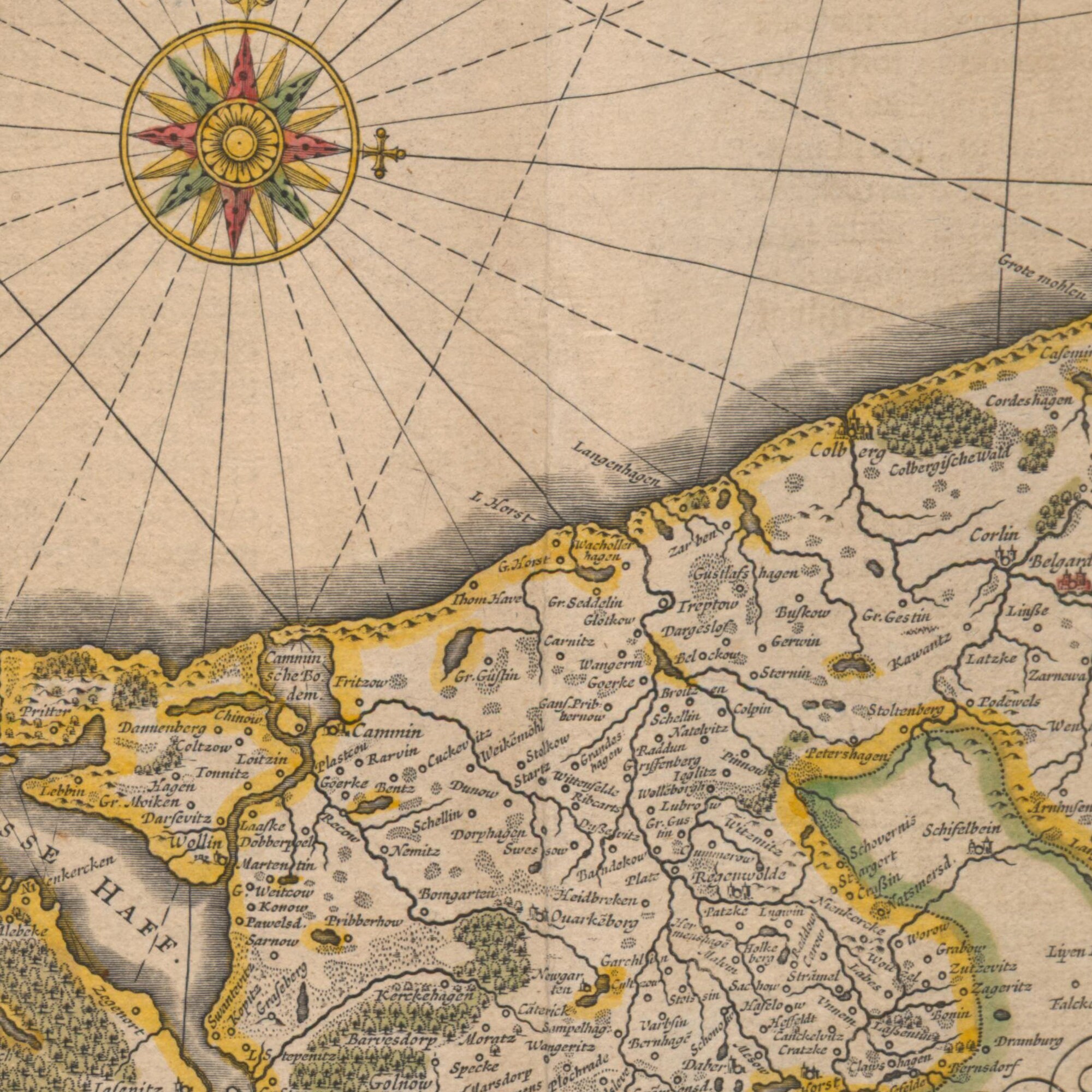
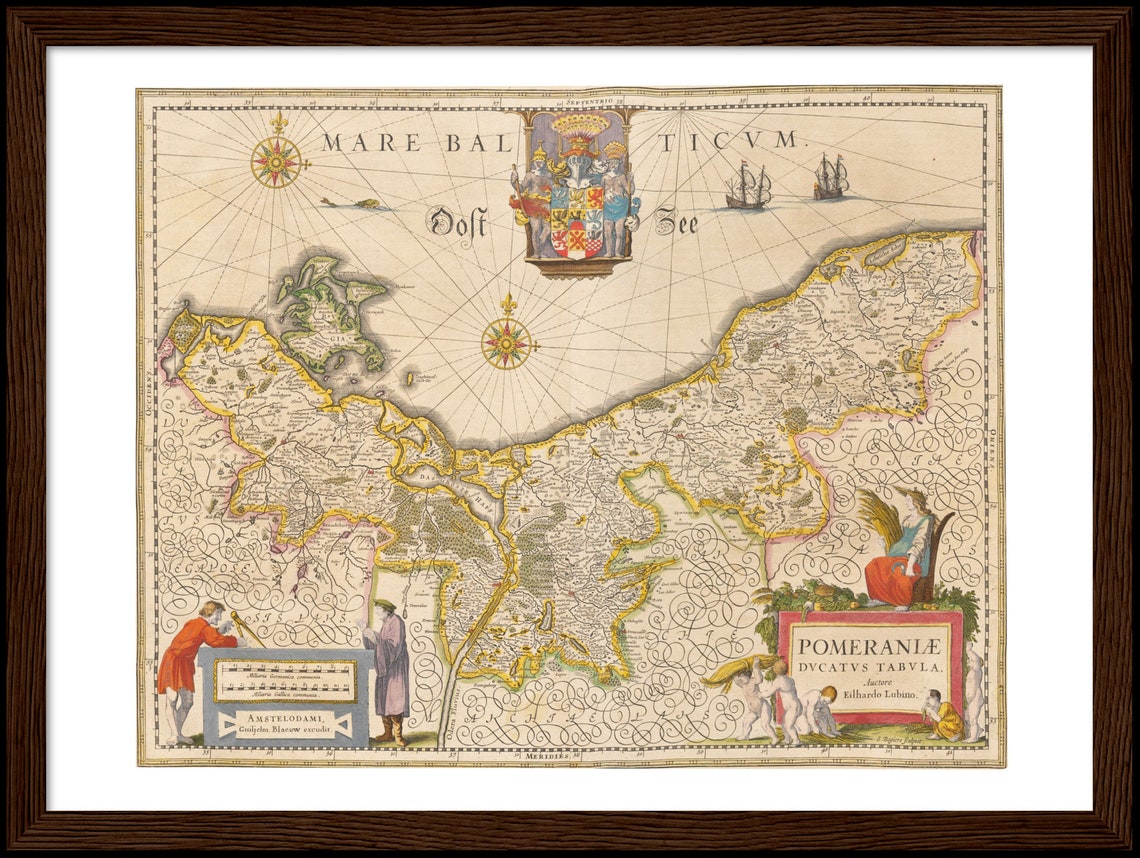
![The Duchy of Pomerania, a detailed map from 1794 [5540x3372] : MapPorn](https://external-preview.redd.it/DbeR2dRvxnEQsneYgpwCU09cIr69RF98zMEvzdoC6yA.jpg?width=960u0026crop=smartu0026auto=webpu0026s=1a027b86bb1c03b23ca5c8b1dec9a285e224d899)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping Pomerania: A Journey Through History, Culture, and Landscape. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!