Mapping The Shadows: Understanding Human Trafficking Through Data Visualization
Mapping the Shadows: Understanding Human Trafficking Through Data Visualization
Related Articles: Mapping the Shadows: Understanding Human Trafficking Through Data Visualization
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Shadows: Understanding Human Trafficking Through Data Visualization. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Shadows: Understanding Human Trafficking Through Data Visualization
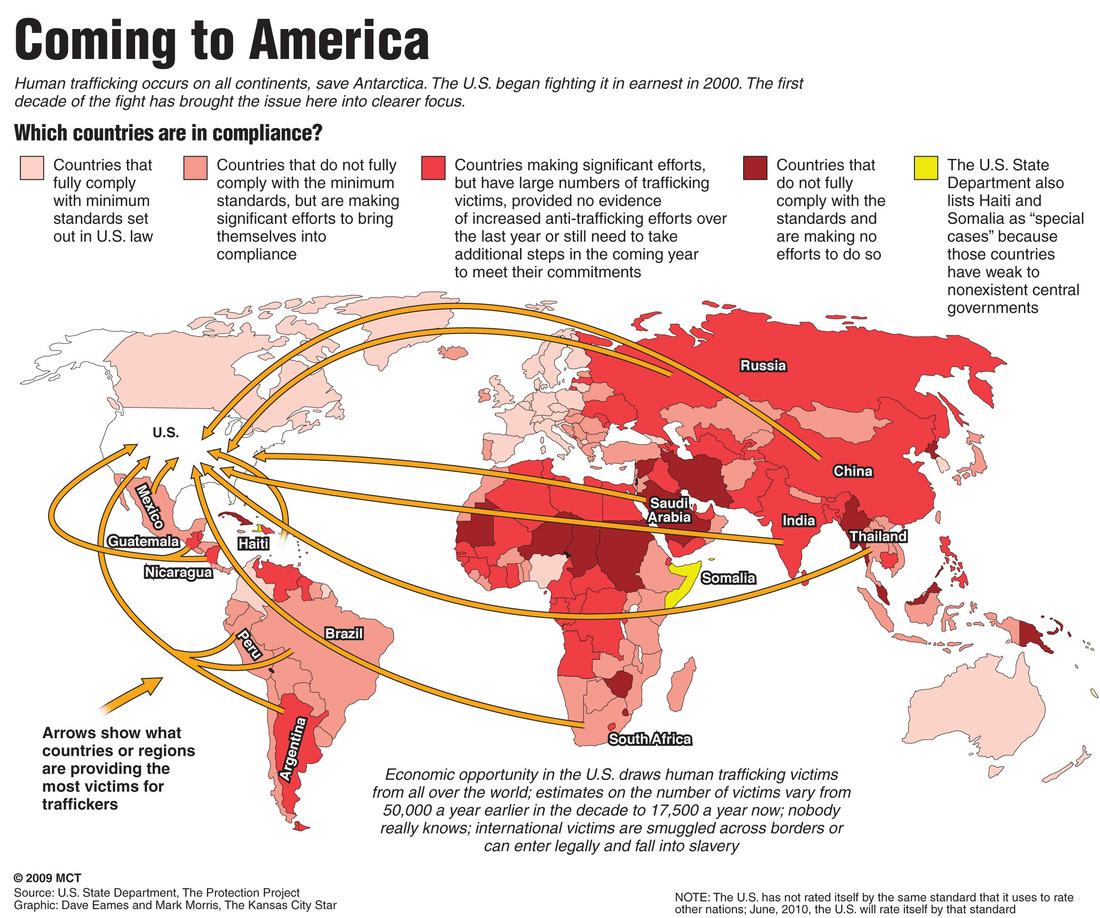
Human trafficking, a modern-day form of slavery, thrives in the shadows, exploiting vulnerable individuals for profit. While the crime itself is hidden, its impact is vast and devastating. To effectively combat this insidious trade, a crucial tool has emerged: the human trafficking map. These maps, utilizing data visualization techniques, offer a powerful means to understand the complex dynamics of human trafficking, revealing patterns, hotspots, and trends.
Visualizing the Invisible: The Power of Data in Human Trafficking Maps
Human trafficking maps serve as visual representations of data related to the crime, providing insights that are often obscured by the clandestine nature of the trade. They can depict a range of information, including:
- Geographic Distribution: Identifying regions with high prevalence of trafficking, revealing areas where resources and interventions are most needed.
- Trafficking Routes: Mapping the flow of victims, from source countries to transit points and destination locations, highlighting key transit hubs and smuggling networks.
- Types of Trafficking: Depicting the various forms of exploitation, including sexual exploitation, forced labor, and organ harvesting, allowing for targeted interventions.
- Victim Demographics: Revealing the profiles of vulnerable individuals most at risk, such as women, children, and migrants, aiding in tailored prevention and protection strategies.
- Perpetrator Networks: Identifying key players and organizations involved in trafficking, facilitating investigations and disrupting criminal operations.
- Trends and Patterns: Analyzing data over time to identify emerging trends and patterns, enabling proactive responses to evolving trafficking tactics.
Benefits of Human Trafficking Maps: A Powerful Tool for Action
The use of human trafficking maps offers significant benefits for combating this global scourge:
- Enhanced Awareness: Visualizing the scope and impact of human trafficking raises awareness among policymakers, law enforcement, and the public, fostering a greater understanding of the issue.
- Targeted Intervention: Maps facilitate the identification of hotspots and vulnerable populations, allowing for targeted resource allocation and interventions where they are most needed.
- Improved Law Enforcement: Maps aid in investigations by providing valuable insights into trafficking routes, networks, and modus operandi, enabling more effective law enforcement strategies.
- Prevention Strategies: Understanding the factors driving trafficking allows for the development of tailored prevention programs, targeting vulnerable populations and addressing root causes.
- Victim Protection: Identifying trafficking routes and hotspots enables the establishment of safe passage routes and support services for rescued victims.
- Data-Driven Policy: Maps provide valuable data for policymakers, informing the development of effective anti-trafficking legislation and policies.
- International Collaboration: Sharing mapping data across borders facilitates international cooperation in combating trafficking, enabling a more coordinated global response.
Types of Human Trafficking Maps: A Diverse Landscape of Data Visualization
Human trafficking maps encompass a variety of approaches, each offering unique insights:
- Static Maps: These maps depict data at a specific point in time, offering a snapshot of the trafficking landscape. They are typically used to illustrate geographic distribution, trafficking routes, and victim demographics.
- Dynamic Maps: These maps visualize data over time, showcasing trends and patterns in trafficking activities. They are particularly useful for identifying emerging hotspots, changes in trafficking routes, and shifts in perpetrator tactics.
- Interactive Maps: These maps allow users to explore data interactively, zooming in on specific regions, filtering data by criteria, and accessing detailed information about individual cases. They provide a more user-friendly and engaging experience, facilitating data exploration and analysis.
- Heatmaps: These maps use color gradients to represent the intensity of trafficking activity in different areas, providing a visual representation of hotspots and areas requiring urgent attention.
- Network Maps: These maps visualize the relationships between individuals and organizations involved in trafficking, revealing the structure of criminal networks and facilitating investigations.
Challenges and Considerations: Navigating the Ethical and Practical Landscape
While human trafficking maps offer invaluable insights, their development and use present certain challenges:
- Data Availability: Accurate and comprehensive data is essential for effective mapping. However, the clandestine nature of human trafficking often makes data collection difficult, requiring collaboration between various stakeholders.
- Data Privacy: Ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of victims’ information is paramount. Maps should be designed to anonymize data and protect the identities of vulnerable individuals.
- Data Accuracy: The accuracy of data used in mapping is crucial to avoid misinterpretations and misleading conclusions. Data validation and quality control are essential steps in the mapping process.
- Ethical Considerations: Mapping can raise ethical concerns, particularly regarding the potential for stigmatization of certain regions or communities. Careful consideration should be given to the potential impact of map visualizations on public perception and the risk of discrimination.
- Data Accessibility: Maps should be accessible to a wide range of stakeholders, including law enforcement, policymakers, NGOs, and the public. This requires ensuring that maps are developed in user-friendly formats and languages, with clear and concise explanations of the data represented.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Human Trafficking Maps
Q: How are human trafficking maps created?
A: Human trafficking maps are created using various data sources, including law enforcement reports, victim testimonies, NGO data, and public records. Data is then analyzed, processed, and visualized using Geographic Information Systems (GIS) software or other data visualization tools.
Q: What are the limitations of human trafficking maps?
A: Human trafficking maps are only as good as the data they are based on. Data availability, accuracy, and reliability can influence the effectiveness of maps. Additionally, the clandestine nature of the crime can make it difficult to capture all trafficking activities, resulting in an incomplete picture.
Q: Can human trafficking maps be used to identify victims?
A: Human trafficking maps are not designed to identify individual victims. They are used to visualize trends, patterns, and hotspots, providing insights into the broader trafficking landscape.
Q: How can I contribute to the development of human trafficking maps?
A: Individuals can contribute to the development of human trafficking maps by supporting organizations working to collect and analyze data on the crime. Additionally, raising awareness about the issue and advocating for increased data transparency can help improve the accuracy and comprehensiveness of mapping efforts.
Tips for Utilizing Human Trafficking Maps Effectively
- Understand the context: Consider the data sources, methodologies, and limitations of the map before drawing conclusions.
- Interpret data cautiously: Maps can provide valuable insights, but they should not be interpreted as definitive representations of reality.
- Use maps for informed decision-making: Maps can be valuable tools for allocating resources, targeting interventions, and developing prevention strategies.
- Engage with stakeholders: Involve diverse stakeholders in the development and use of maps to ensure their relevance and impact.
Conclusion: A Collaborative Effort to Illuminate the Shadows
Human trafficking maps offer a powerful tool for illuminating the shadows of this complex crime. By visualizing data and revealing patterns, they provide crucial insights for combating trafficking, protecting victims, and promoting justice. However, their effectiveness hinges on a collaborative effort involving governments, law enforcement, NGOs, and the public. By working together to improve data collection, enhance data quality, and promote ethical map development, we can leverage this valuable tool to create a more effective and informed response to the global challenge of human trafficking.


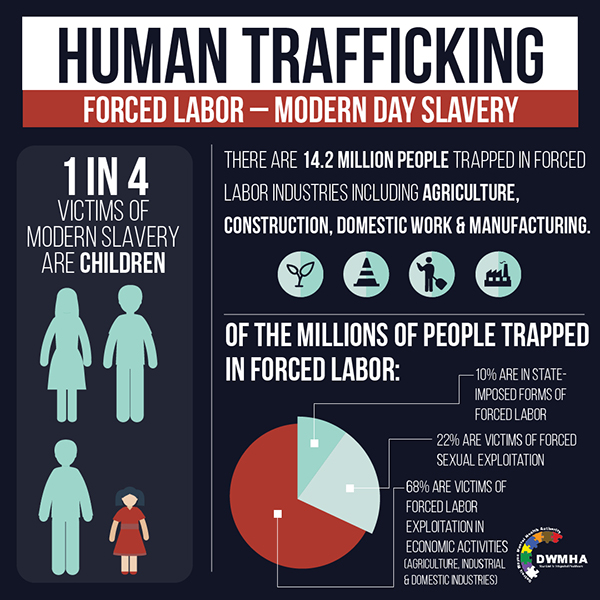





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Shadows: Understanding Human Trafficking Through Data Visualization. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!