Mapping The World From Above: The Power Of Satellite Imagery
Mapping the World from Above: The Power of Satellite Imagery
Related Articles: Mapping the World from Above: The Power of Satellite Imagery
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Mapping the World from Above: The Power of Satellite Imagery. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Mapping the World from Above: The Power of Satellite Imagery
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Mapping the World from Above: The Power of Satellite Imagery
- 3.1 Unveiling the Earth’s Surface: The Essence of Satellite Imagery
- 3.2 Beyond Traditional Maps: The Advantages of Satellite Imagery
- 3.3 Applications of Satellite Imagery Maps: A Diverse Spectrum
- 3.4 Understanding Satellite Imagery Maps: A Closer Look
- 3.5 FAQs about Satellite Imagery Maps
- 3.6 Tips for Using Satellite Imagery Maps Effectively
- 3.7 Conclusion: A Powerful Tool for Understanding and Managing Our Planet
- 4 Closure
Mapping the World from Above: The Power of Satellite Imagery
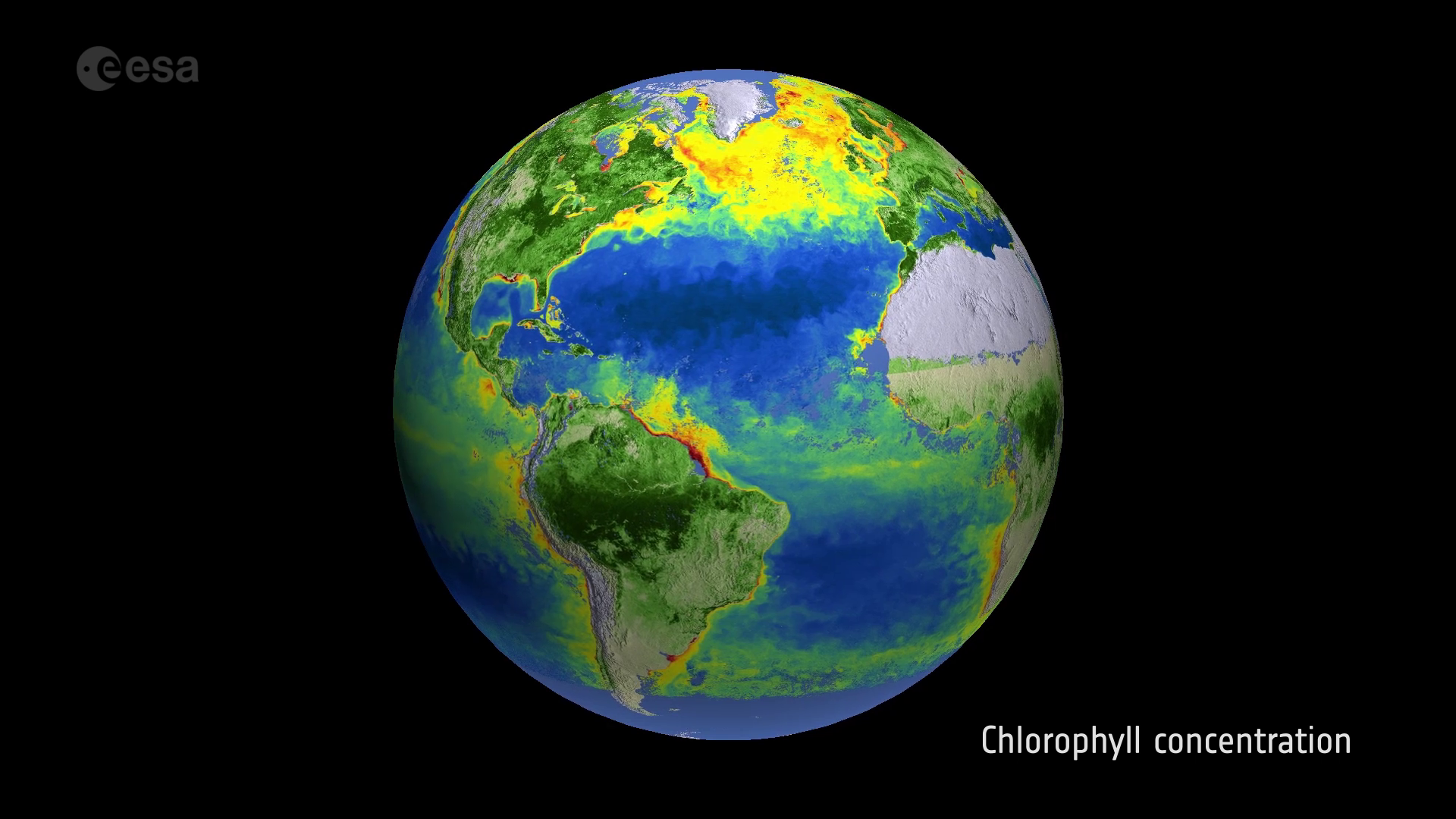
The Earth, a vibrant tapestry of land, water, and life, is a vast and complex entity. Understanding its intricate patterns and dynamics is essential for a multitude of endeavors, from urban planning and resource management to environmental monitoring and disaster response. This understanding is greatly enhanced by a powerful tool: maps generated using satellite imagery.
Satellite imagery, captured by sensors orbiting the Earth, provides a unique perspective on our planet. These images, often spanning vast areas, offer a wealth of information about the Earth’s surface, revealing details invisible to the naked eye. They serve as the foundation for a new breed of maps, transforming our ability to perceive and interact with the world around us.
Unveiling the Earth’s Surface: The Essence of Satellite Imagery
Satellite imagery captures the Earth’s surface in a variety of wavelengths, encompassing the visible spectrum and extending into the infrared and microwave regions. This multispectral approach allows for the identification of distinct features and materials based on their unique spectral signatures.
Visible light imagery, similar to what we perceive with our eyes, provides a visual representation of the Earth’s surface. It is particularly useful for identifying land cover, urban areas, and natural features like forests and water bodies.
Infrared imagery, sensitive to heat radiation, reveals temperature variations. This is invaluable for monitoring vegetation health, detecting wildfires, and mapping urban heat islands.
Microwave imagery, capable of penetrating clouds and fog, allows for all-weather observation. It is instrumental in monitoring soil moisture, sea ice extent, and precipitation patterns.
These diverse data sources are combined to create detailed and informative maps, offering insights into various aspects of the Earth’s environment and human activity.
Beyond Traditional Maps: The Advantages of Satellite Imagery
Satellite imagery maps offer significant advantages over traditional maps, significantly enhancing our ability to understand and manage the Earth’s resources:
- Comprehensive Coverage: Satellites can capture images of vast areas, providing a global perspective on landscapes, urban environments, and natural phenomena.
- High Resolution: Modern satellites equipped with advanced sensors can capture images with resolutions reaching the meter level, revealing intricate details of infrastructure, vegetation, and even individual buildings.
- Regular Updates: Satellites regularly orbit the Earth, allowing for frequent image acquisition and the creation of maps that reflect dynamic changes in the environment, such as deforestation, urban expansion, and disaster impacts.
- Multispectral Analysis: The ability to capture data across multiple wavelengths provides valuable information about the composition and properties of various surface features, enabling more accurate land use classification, environmental monitoring, and resource assessment.
Applications of Satellite Imagery Maps: A Diverse Spectrum
The versatility of satellite imagery maps makes them indispensable in a wide array of fields:
Environmental Monitoring:
- Deforestation and Land Cover Change: Satellite imagery maps provide a clear picture of deforestation rates, allowing for effective monitoring and management of forest resources.
- Climate Change Impacts: Analyzing changes in vegetation cover, glacial retreat, and sea ice extent helps scientists understand and mitigate the effects of climate change.
- Pollution Monitoring: Satellite imagery maps can track pollution levels in air, water, and soil, aiding in environmental protection and policy development.
Resource Management:
- Agriculture: Satellite imagery maps assist in crop monitoring, yield prediction, and optimizing irrigation and fertilization practices.
- Water Resources: Satellite imagery maps help identify water bodies, monitor water quality, and assess groundwater resources.
- Mining and Exploration: Satellite imagery maps aid in mineral exploration, identifying potential deposits and assessing environmental impacts.
Urban Planning and Development:
- Urban Sprawl: Satellite imagery maps track urban expansion, facilitating sustainable urban planning and infrastructure development.
- Disaster Response: Satellite imagery maps provide critical information during natural disasters, aiding in rescue efforts, damage assessment, and post-disaster recovery.
- Infrastructure Management: Satellite imagery maps assist in monitoring road networks, power grids, and other critical infrastructure, ensuring efficient maintenance and repair.
Security and Defense:
- Military Intelligence: Satellite imagery maps provide valuable information for military operations, target identification, and situational awareness.
- Border Security: Satellite imagery maps aid in monitoring border activity, identifying potential threats, and securing national borders.
- Disaster Relief: Satellite imagery maps support disaster relief efforts by providing real-time information on affected areas and facilitating efficient distribution of aid.
Understanding Satellite Imagery Maps: A Closer Look
While satellite imagery maps offer a wealth of information, it is crucial to understand the nuances of their interpretation:
- Resolution: The resolution of satellite imagery determines the level of detail that can be observed. Higher resolution images provide a clearer picture of smaller features, while lower resolution images are better suited for analyzing large-scale patterns.
- Spectral Bands: The specific wavelengths captured by a satellite sensor influence the type of information that can be extracted. Different spectral bands highlight different features, requiring specialized knowledge for accurate interpretation.
- Data Processing: Raw satellite imagery data needs to be processed and analyzed to generate meaningful maps. This involves various techniques, including image enhancement, geometric correction, and classification.
Navigating Satellite Imagery Data:
Several platforms and tools facilitate the access and analysis of satellite imagery data, including:
- Google Earth: A widely accessible platform that provides a user-friendly interface for exploring satellite imagery maps.
- NASA EarthData Search: A comprehensive repository of satellite imagery data from various NASA missions.
- USGS EarthExplorer: A platform for accessing and downloading satellite imagery data from the United States Geological Survey.
- GIS Software: Geographic Information Systems (GIS) software provides advanced tools for analyzing, visualizing, and integrating satellite imagery data with other spatial datasets.
FAQs about Satellite Imagery Maps
1. What are the limitations of satellite imagery maps?
While satellite imagery maps offer significant advantages, they also have limitations:
- Cloud Cover: Cloud cover can obstruct the view of the Earth’s surface, limiting the availability of data for certain areas.
- Atmospheric Effects: Atmospheric conditions can affect the quality of satellite imagery, introducing distortions or blurring.
- Data Availability: Access to high-resolution satellite imagery data can be restricted due to security concerns or commercial interests.
2. How accurate are satellite imagery maps?
The accuracy of satellite imagery maps depends on various factors, including sensor resolution, data processing techniques, and the specific application. Modern satellite imagery maps can achieve high levels of accuracy, especially when combined with ground truth data and advanced analysis techniques.
3. What are the ethical considerations associated with satellite imagery maps?
The use of satellite imagery maps raises ethical concerns related to privacy, security, and potential misuse. It is crucial to ensure responsible data collection, storage, and dissemination practices to protect individual privacy and prevent unauthorized access.
4. What is the future of satellite imagery maps?
The future of satellite imagery maps is bright, with advancements in sensor technology, data processing techniques, and artificial intelligence leading to:
- Higher Resolution and Accuracy: Increased sensor resolution and advanced image processing algorithms will enable the creation of even more detailed and accurate maps.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Real-time data acquisition and processing will provide up-to-the-minute information about dynamic events, facilitating faster response times and improved decision-making.
- Integrated Data Analysis: Combining satellite imagery data with other sources, such as sensor networks and social media data, will enable more comprehensive and insightful analyses.
Tips for Using Satellite Imagery Maps Effectively
- Choose the right resolution: Select a resolution appropriate for the scale of analysis and the level of detail required.
- Consider the spectral bands: Analyze the data in relevant spectral bands to extract specific information about the surface features.
- Use appropriate data processing techniques: Employ suitable image enhancement, geometric correction, and classification methods to enhance data quality and accuracy.
- Validate data with ground truth: Verify the accuracy of satellite imagery maps by comparing them with ground truth data, such as field measurements or aerial photographs.
- Integrate with other data sources: Combine satellite imagery maps with other spatial datasets, such as topographic maps, demographic data, and economic indicators, for a more comprehensive analysis.
Conclusion: A Powerful Tool for Understanding and Managing Our Planet
Satellite imagery maps have revolutionized our ability to understand and manage the Earth’s resources, providing a global perspective on our planet’s intricate dynamics. From monitoring environmental changes and managing natural resources to supporting urban planning and disaster response, satellite imagery maps play a vital role in addressing critical challenges facing humanity. As technology continues to advance, satellite imagery maps will become even more powerful and essential for shaping a sustainable future.




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-155439194-58b73fd35f9b5880804c1963.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the World from Above: The Power of Satellite Imagery. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!