Navigating The Heart Of Italy: An Exploration Of Rome’s Geographic Significance
Navigating the Heart of Italy: An Exploration of Rome’s Geographic Significance
Related Articles: Navigating the Heart of Italy: An Exploration of Rome’s Geographic Significance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Heart of Italy: An Exploration of Rome’s Geographic Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Heart of Italy: An Exploration of Rome’s Geographic Significance
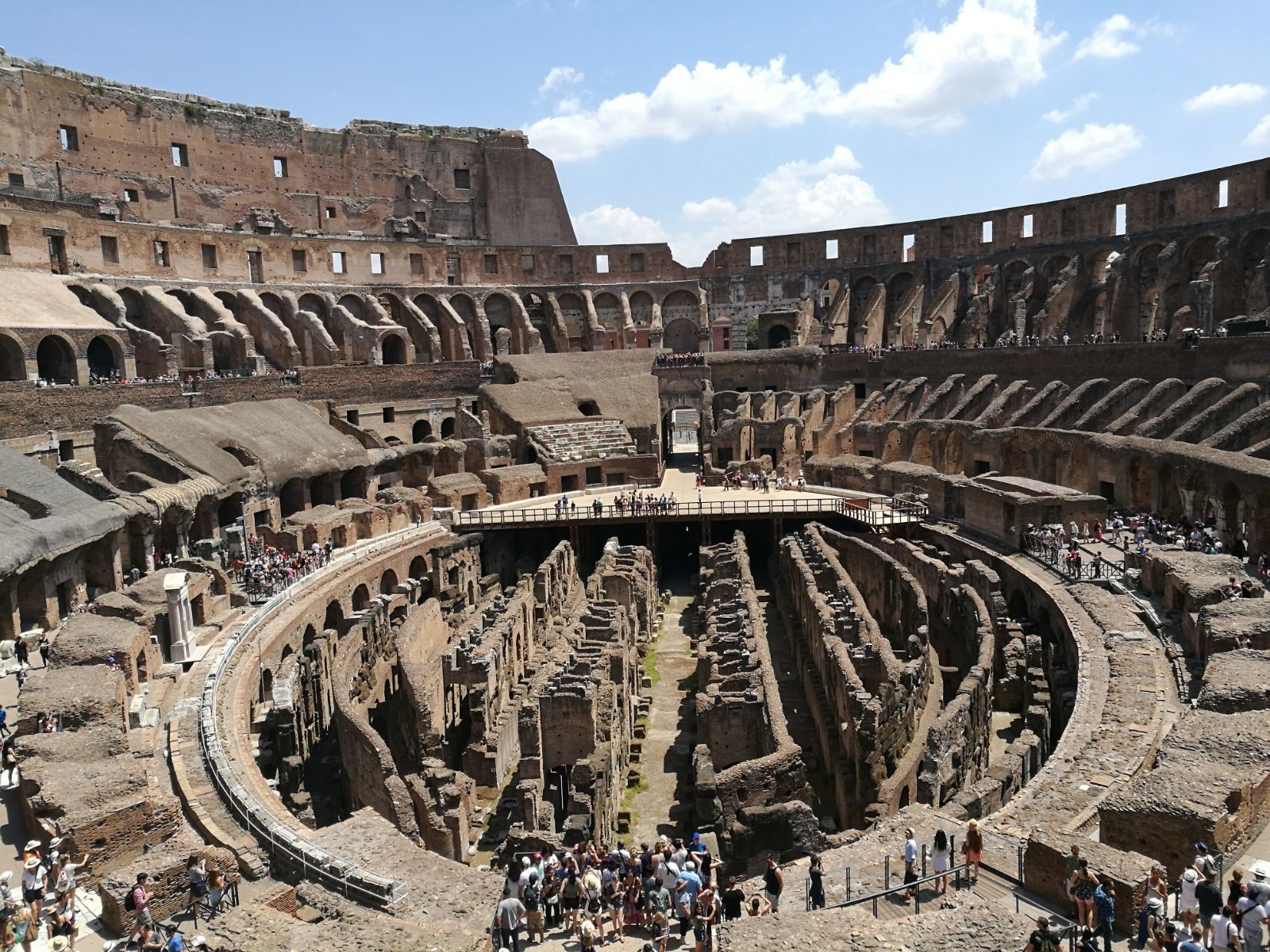

Rome, the Eternal City, holds a captivating allure for history enthusiasts, art lovers, and travelers alike. But beyond its iconic monuments and bustling streets lies a complex tapestry of geography that has shaped its past and continues to influence its present. Understanding Rome’s position within the European landscape provides a deeper appreciation for its unique character and the enduring legacy it carries.
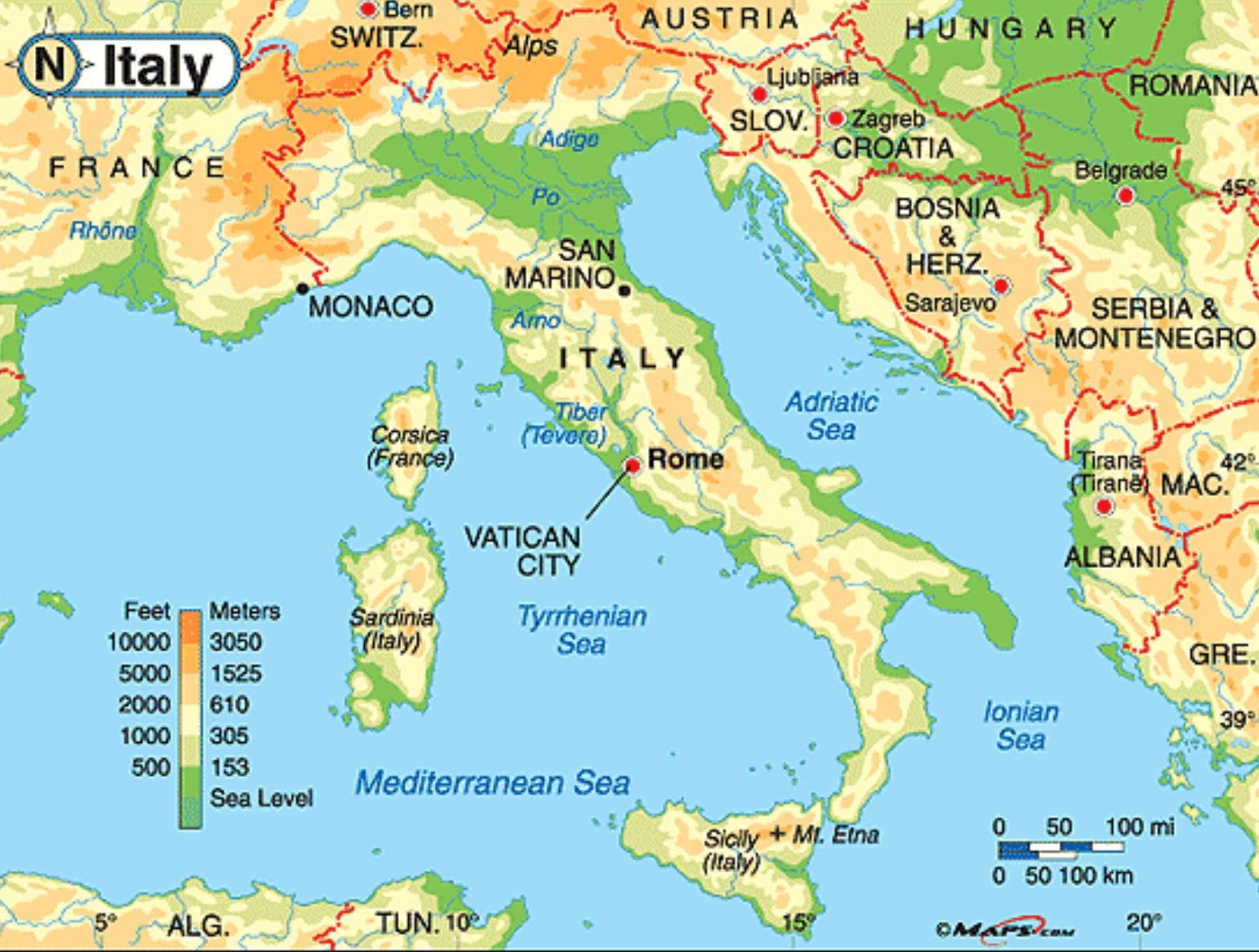
Rome’s Position on the European Map
Rome sits nestled in the heart of Italy, strategically positioned in the Lazio region, on the western coast of the Italian peninsula. Its location offers a blend of advantages:
- Central Location: Situated in the center of Italy, Rome acts as a natural hub, connecting the northern and southern regions of the country. This central location facilitated the spread of Roman influence throughout the Italian peninsula and beyond.
- Coastal Proximity: Located on the coast of the Tyrrhenian Sea, Rome enjoyed access to maritime trade routes, fostering economic growth and cultural exchange. This maritime connection played a vital role in the development of the Roman Empire, enabling trade with distant lands and the transportation of goods and resources.
- River Access: The Tiber River, flowing through Rome, provided a crucial transportation route, connecting the city to the interior of Italy and facilitating trade and communication. This river access was instrumental in the city’s growth and its ability to sustain a large population.
- Geographic Features: The surrounding landscape offers a mix of rolling hills, fertile plains, and volcanic areas. This diverse terrain provided fertile land for agriculture, while the volcanic soils enriched the surrounding area, creating a rich and varied ecosystem.
Rome’s Historical and Cultural Significance
Rome’s strategic location has played a pivotal role in its historical and cultural development. The city’s central position within Italy allowed it to exert significant influence over the peninsula, leading to the rise of the Roman Republic and subsequently the Roman Empire.
- The Birthplace of an Empire: Rome’s location, coupled with its access to resources and trade routes, provided the necessary foundation for the emergence of a powerful empire. Its influence extended across Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East, leaving a lasting mark on the world.
- A Crossroads of Cultures: Rome’s position on the Mediterranean Sea facilitated the exchange of ideas, goods, and cultures. This cultural fusion enriched the city’s artistic, architectural, and intellectual development, leaving behind a legacy of magnificent monuments, intricate mosaics, and influential philosophies.
- A Center of Religious Influence: Rome’s location played a significant role in the development of Christianity. The city became a center of Christian pilgrimage and the seat of the papacy, making it a focal point for the spread of Christianity throughout Europe.
Exploring the City’s Geographic Features
Rome’s geographic landscape contributes to its unique character and charm:
- The Seven Hills: Rome is built upon seven hills, each with its own distinct history and character. These hills, including the Palatine Hill, the Capitoline Hill, and the Aventine Hill, provided natural defenses and shaped the city’s urban development.
- The Tiber River: The Tiber River, flowing through the city, offers a picturesque backdrop and serves as a vital artery for transportation and recreation. The river has played a significant role in Rome’s history, providing access to trade routes and shaping the city’s development.
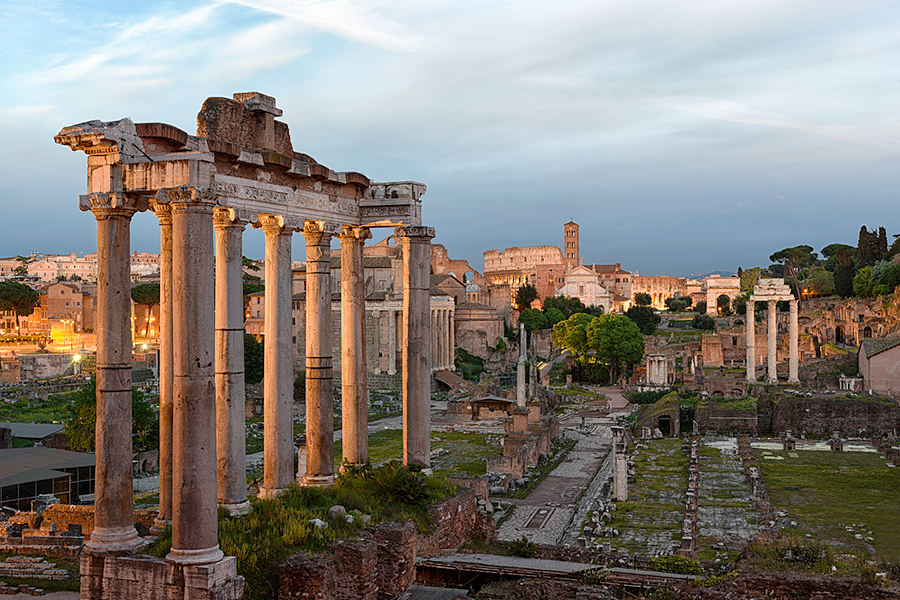
- The Roman Forum: This ancient forum, located in the heart of Rome, was once the center of political, social, and economic life. The Forum’s location on the Palatine Hill provided a strategic vantage point for the city’s leaders.
- The Colosseum: This iconic amphitheater, built in the 1st century AD, stands as a testament to the Romans’ architectural prowess. Its location near the Roman Forum facilitated access for large crowds and its impressive size and grandeur reflected the power and influence of the Roman Empire.
Rome’s Modern Significance
Today, Rome remains a vibrant and influential city, attracting millions of visitors each year. Its strategic location and rich history continue to shape its modern identity:
- A Cultural Hub: Rome remains a center of culture and art, hosting numerous museums, galleries, and theaters. The city’s rich history and heritage continue to inspire artists and performers, making it a thriving cultural hub.
- A Tourism Destination: Rome’s iconic monuments, historical sites, and charming streets draw visitors from all corners of the globe. The city’s tourism industry plays a vital role in its economy, providing employment opportunities and contributing to its cultural vibrancy.
- A Political and Economic Center: As the capital of Italy, Rome remains a significant political and economic center. The city houses the Italian government, major corporations, and international organizations, making it a vital hub for business and diplomacy.
FAQs about Rome’s Geographic Significance
Q: What is the geographical location of Rome?
A: Rome is located in the Lazio region of Italy, on the western coast of the Italian peninsula. It sits on the Tiber River and is close to the Tyrrhenian Sea.
Q: Why is Rome’s location important?
A: Rome’s central location in Italy, its proximity to the sea, and its access to the Tiber River made it a strategic hub for trade, communication, and military expansion, contributing to the rise of the Roman Empire.
Q: What are the main geographic features of Rome?
A: Rome is built on seven hills, including the Palatine Hill, the Capitoline Hill, and the Aventine Hill. The Tiber River flows through the city, and the surrounding landscape includes fertile plains and volcanic areas.
Q: How has Rome’s geography influenced its history and culture?
A: Rome’s location facilitated the development of the Roman Empire, its connection to the Mediterranean Sea fostered cultural exchange, and its central position within Italy made it a center of political and religious influence.
Q: What is the significance of Rome’s location today?
A: Rome’s central location within Italy, its rich history, and its cultural heritage continue to make it a vital economic, political, and cultural hub, attracting millions of visitors each year.
Tips for Understanding Rome’s Geography
- Explore the City on Foot: Walking through the city allows you to experience its unique character and appreciate the role of geography in shaping its urban layout.
- Visit the Seven Hills: Each hill offers a different perspective of the city and provides insight into its history and development.
- Take a Boat Trip on the Tiber River: A boat tour offers a unique perspective of the city and allows you to appreciate the river’s role in Rome’s history.
- Learn about Roman History: Understanding Rome’s past helps to appreciate the city’s present and the role of geography in its development.
Conclusion
Rome’s geographic location has been instrumental in shaping its rich history, vibrant culture, and enduring legacy. From its strategic position within Italy to its proximity to the Mediterranean Sea, Rome’s geography has played a vital role in its rise to prominence and its continued influence on the world. By understanding the city’s unique geographic features and their impact on its past and present, we gain a deeper appreciation for the enduring power of the Eternal City.




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/map-of-italy--150365156-59393b0d3df78c537b0d8aa6.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Heart of Italy: An Exploration of Rome’s Geographic Significance. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!