Navigating The Nile: Understanding The Map Of Upper And Lower Egypt
Navigating the Nile: Understanding the Map of Upper and Lower Egypt
Related Articles: Navigating the Nile: Understanding the Map of Upper and Lower Egypt
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Nile: Understanding the Map of Upper and Lower Egypt. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Nile: Understanding the Map of Upper and Lower Egypt
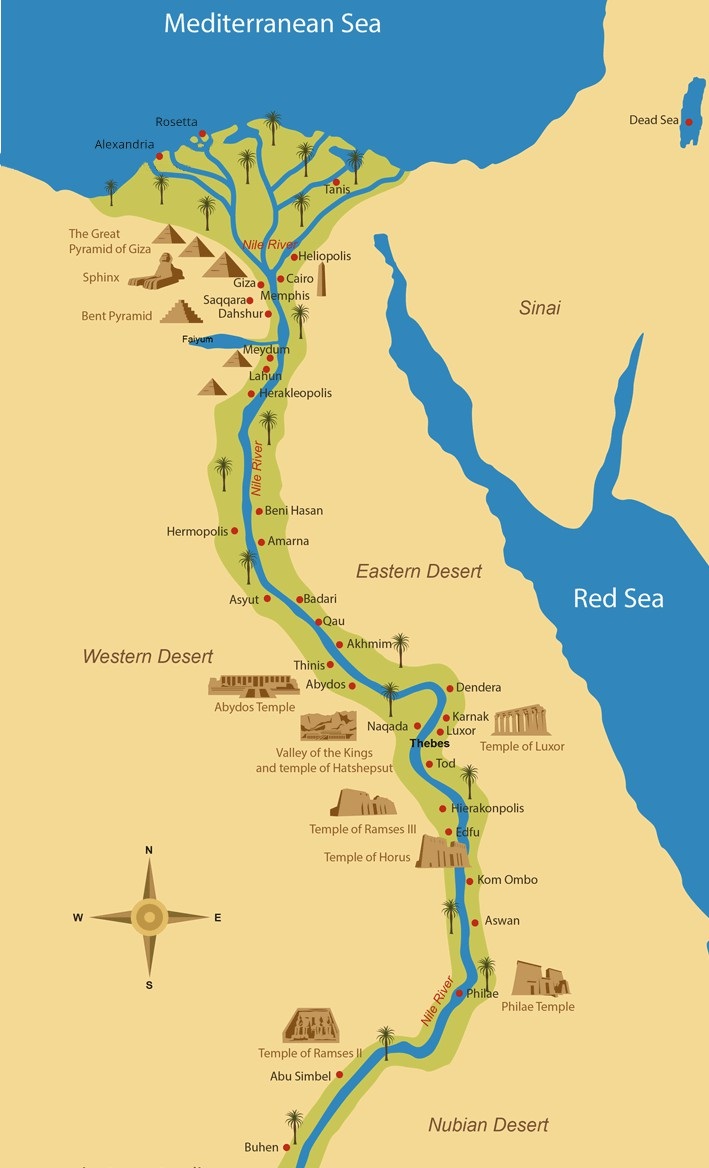
The Nile River, a lifeblood coursing through the heart of Egypt, has shaped the nation’s history, culture, and geography for millennia. This vital artery, flowing from the highlands of Ethiopia to the Mediterranean Sea, divides Egypt into two distinct regions: Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. Understanding this division is crucial for comprehending the ancient Egyptian civilization, its political structure, and its enduring legacy.
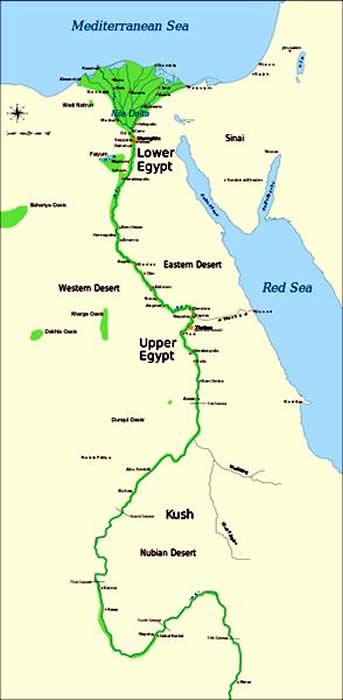
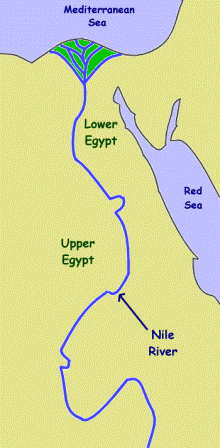
Upper Egypt: The Cradle of Civilization
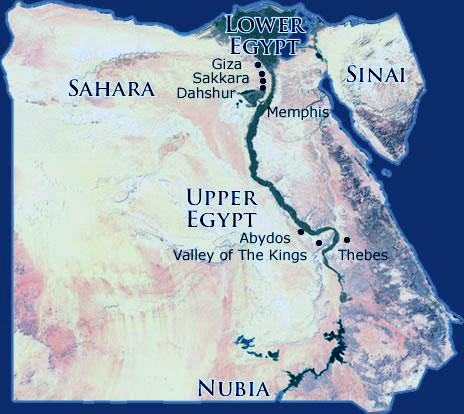
Upper Egypt, located south of modern-day Cairo, encompasses the Nile’s upper reaches, stretching from the First Cataract at Aswan to the southern border. This region is characterized by its rugged terrain, encompassing the fertile Nile Valley and the desolate Western Desert.
A Closer Look at Upper Egypt:
- Fertile Nile Valley: This narrow strip of land along the riverbank, a testament to the Nile’s annual floods, has been a crucial agricultural hub since ancient times. Its fertile soil allowed for the development of a flourishing agricultural society, laying the foundation for Egyptian civilization.
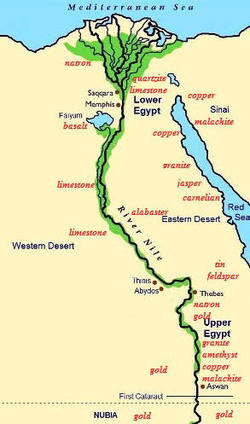
- Western Desert: This vast expanse of arid landscape, bordering the Nile Valley, was home to ancient oases and served as a source of raw materials.
- The First Cataract: This natural barrier at Aswan, marking the southernmost point of navigable waters, served as a natural border and a strategic location for trade and defense.
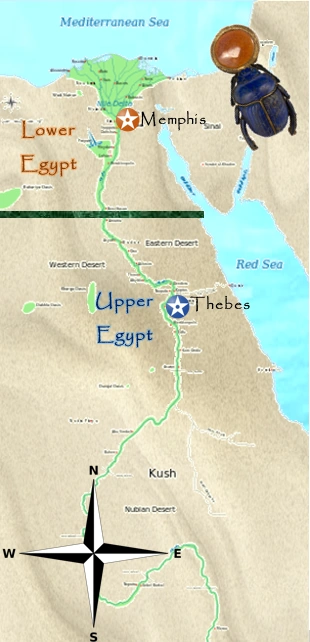
Lower Egypt: The Delta and the Sea
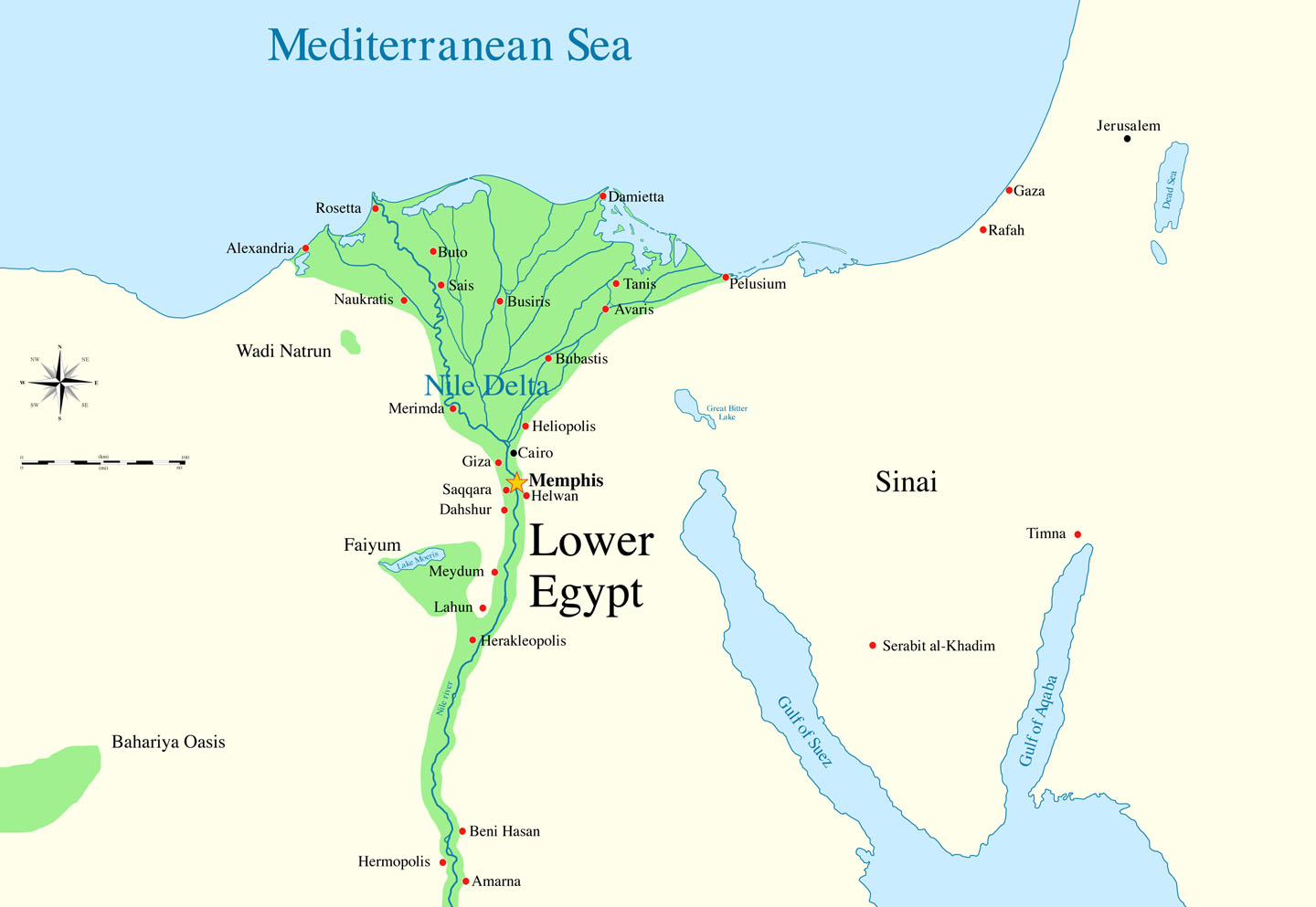
Lower Egypt, situated north of Cairo, encompasses the Nile Delta, a fertile region created by the river’s branching tributaries as it flows towards the Mediterranean Sea. This region is characterized by its flat landscape, fertile soil, and proximity to the sea, making it a crucial hub for trade and cultural exchange.
Exploring Lower Egypt:
- The Nile Delta: This fertile delta, formed by the Nile’s branching tributaries, is a fertile agricultural region, supporting a dense population and contributing significantly to Egypt’s economy.
- The Mediterranean Sea: This body of water provided access to trade routes, connecting Egypt to other civilizations and facilitating cultural exchange.
- The Red Sea: Although not directly connected to the Nile Delta, the Red Sea provided access to vital trade routes, connecting Egypt to the Arabian Peninsula and the Indian Ocean.
The Significance of the Division: Political and Social Implications
The division of Egypt into Upper and Lower Egypt was not merely geographical but also had profound political and social implications.
- Political Structure: The pharaohs, the rulers of ancient Egypt, were seen as the unifiers of Upper and Lower Egypt. The double crown, symbolizing the unification of both regions, became a symbol of royal power and legitimacy.
- Cultural Identity: Each region developed its own distinct cultural identity, reflected in their art, architecture, and religious practices. This cultural exchange, however, was also a source of unity, fostering a shared Egyptian identity.
- Economic Exchange: The two regions were economically interdependent, with Upper Egypt providing agricultural produce and raw materials, while Lower Egypt served as a center for trade and manufacturing.
A Visual Guide to Understanding the Map:
The map of Upper and Lower Egypt is more than just a geographical representation; it’s a window into the past, showcasing the historical, cultural, and political evolution of ancient Egypt. Studying the map allows us to:
- Trace the Nile’s Flow: By observing the river’s course, we can understand how it shaped the landscape, influenced agriculture, and facilitated communication and trade.
- Identify Major Cities: Examining the map reveals the location of key ancient cities, such as Thebes (modern Luxor) in Upper Egypt and Memphis in Lower Egypt, providing insights into the distribution of power and cultural centers.
- Recognize Historical Boundaries: The map clearly shows the division between Upper and Lower Egypt, highlighting the importance of the First Cataract as a natural boundary and the Nile Delta as a crucial geographical feature.
- Visualize the Spread of Civilization: By tracing the spread of ancient Egyptian settlements and monuments along the Nile Valley, the map reveals the gradual expansion of civilization from Upper Egypt to Lower Egypt.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
1. Why was the division of Upper and Lower Egypt significant?
The division was significant for its political, social, and economic implications. It shaped the political structure, with the pharaohs symbolizing unity, and influenced the cultural identity of each region. The economic interdependence of the two regions also played a crucial role in the development of ancient Egypt.
2. What are the key differences between Upper and Lower Egypt?
Upper Egypt is characterized by its rugged terrain, including the fertile Nile Valley and the Western Desert, while Lower Egypt encompasses the flat, fertile Nile Delta and the Mediterranean Sea. These geographical differences influenced the development of distinct cultural identities and economic activities in each region.
3. How did the Nile River influence the development of Egypt?
The Nile River was the lifeblood of ancient Egypt, providing fertile land for agriculture, water for irrigation, and a means of transportation and communication. Its annual floods, while challenging, also provided the fertile soil that sustained Egyptian civilization.
4. What are some of the important cities in Upper and Lower Egypt?
Important cities in Upper Egypt include Thebes (Luxor), Abydos, and Aswan. Key cities in Lower Egypt include Memphis, Saqqara, and Alexandria. These cities served as centers of political power, religious worship, and economic activity.
5. How did the map of Upper and Lower Egypt contribute to our understanding of ancient Egypt?
The map provides a visual representation of the geographical and political landscape of ancient Egypt, helping us understand the importance of the Nile River, the division of the country into Upper and Lower Egypt, and the location of key cities and monuments. It offers valuable insights into the development of ancient Egyptian civilization.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Upper and Lower Egypt:
- Start with the Nile River: Focus on the river’s course and its impact on the surrounding landscape.
- Identify Key Cities: Locate major cities and understand their historical significance.
- Recognize Geographical Features: Pay attention to the Nile Delta, the First Cataract, and the Western Desert.
- Explore Historical Boundaries: Understand the division between Upper and Lower Egypt and its implications.
- Relate the Map to Historical Events: Use the map to visualize historical events and their geographical context.
Conclusion:
The map of Upper and Lower Egypt is a powerful tool for understanding the ancient Egyptian civilization. It reveals the geographical context that shaped the nation’s history, culture, and political structure. By studying the map, we can gain valuable insights into the Nile’s influence, the division of the country, and the location of key cities and monuments. The map serves as a visual reminder of the enduring legacy of ancient Egypt and its profound connection to the life-giving Nile River.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Nile: Understanding the Map of Upper and Lower Egypt. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!