Sculpting With Light: A Comprehensive Guide To Displacement Maps In Blender
Sculpting with Light: A Comprehensive Guide to Displacement Maps in Blender
Related Articles: Sculpting with Light: A Comprehensive Guide to Displacement Maps in Blender
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Sculpting with Light: A Comprehensive Guide to Displacement Maps in Blender. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Sculpting with Light: A Comprehensive Guide to Displacement Maps in Blender

In the realm of 3D modeling, the pursuit of realistic and detailed surfaces often necessitates advanced techniques. Among these, displacement mapping emerges as a powerful tool, enabling artists to imbue their models with intricate surface variations without compromising performance. This technique, widely employed in Blender, leverages grayscale images to manipulate the geometry of a 3D object, adding depth, texture, and a sense of realism that would be impossible to achieve through traditional modeling alone.
Understanding the Mechanics of Displacement Mapping
At its core, displacement mapping functions by interpreting the grayscale values of a designated image, known as the displacement map. Each pixel within this image corresponds to a specific point on the 3D object’s surface. The brightness of each pixel dictates how much the corresponding point on the object is displaced.
Imagine a flat plane as the base of your model. The displacement map, when applied, acts as a set of instructions, pushing and pulling the plane’s surface in accordance with the image’s grayscale values. Darker areas in the displacement map cause the surface to sink inwards, while brighter areas push the surface outwards. This process creates intricate surface details, ranging from subtle imperfections to dramatic, sculpted formations.
The Power of Displacement Maps: Benefits and Applications
The benefits of displacement mapping extend beyond mere aesthetic enhancement. Its versatility makes it a valuable tool for artists across various disciplines:
-
Detailed Surface Textures: Displacement maps excel at replicating intricate surface details, such as the rough texture of bark, the porous surface of stone, or the delicate veins of a leaf. This eliminates the need for painstaking manual modeling, allowing artists to focus on artistic expression.
-
High-Resolution Geometry: By leveraging displacement maps, artists can achieve high-resolution geometry without incurring the computational burden of modeling every detail. This is particularly beneficial for large-scale environments or models with complex surface variations, significantly improving rendering performance.
-
Procedural Generation: Displacement maps can be procedurally generated, allowing for dynamic and randomized surface variations. This opens up possibilities for creating unique, organic, and unpredictable textures that would be challenging to achieve manually.
-
Efficient Workflow: Displacement mapping streamlines the modeling process, allowing artists to quickly and easily create highly detailed models without the need for complex manual sculpting. This translates to increased productivity and reduced development time.
-
Non-Destructive Modification: Displacement maps are non-destructive, meaning they do not alter the original geometry of the model. This allows for easy adjustments and experimentation without permanently affecting the underlying mesh.
Harnessing the Power of Displacement Maps in Blender
Blender, a free and open-source 3D creation suite, provides a robust environment for implementing displacement mapping. The process involves several key steps:
-
Preparing the Displacement Map: The first step involves creating or acquiring a displacement map. This can be achieved through various methods, including:
-
Sculpting in Blender: Artists can directly sculpt displacement maps within Blender using tools like the "Sculpt" mode. This provides a highly customizable and intuitive approach to creating detailed surface variations.
-
Utilizing External Software: External software like ZBrush or Mudbox can be used to create high-resolution displacement maps that can be imported into Blender.
-
Generating Displacement Maps: Various software and online resources offer tools for procedurally generating displacement maps based on user-defined parameters.
-
-
Importing the Displacement Map: Once the displacement map is ready, it needs to be imported into Blender. This can be achieved through the "Image" menu or by directly dragging the image file into the Blender scene.
-
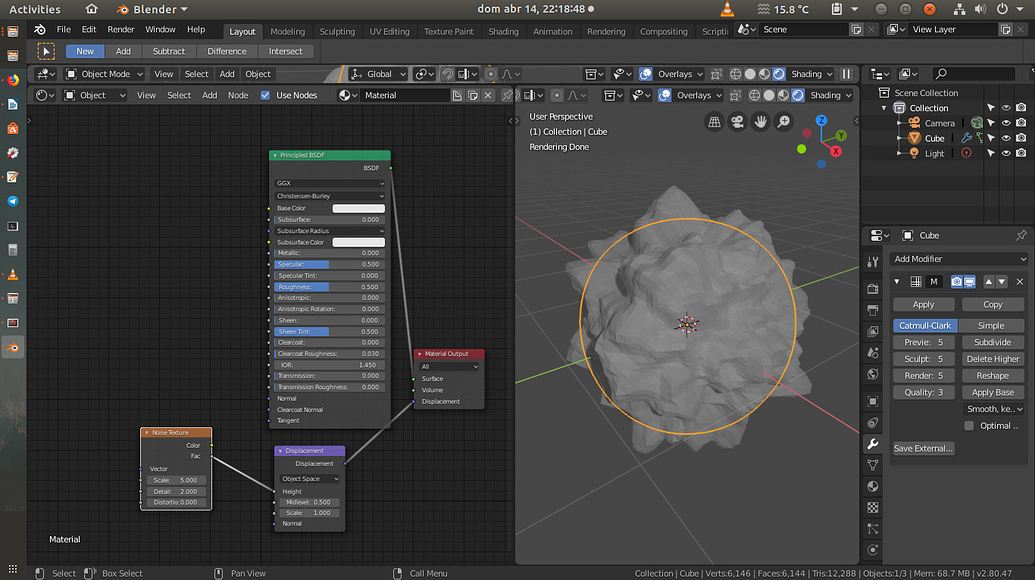
Applying the Displacement Map: The displacement map is applied to the desired object using the "Displacement" modifier within the "Modifiers" panel. This modifier allows for various settings, including:
-
Strength: Controls the intensity of the displacement effect.
-
Midlevel: Defines the midpoint of the displacement range, allowing for fine-tuning the overall effect.
-
Coordinates: Determines how the displacement map is mapped onto the object’s surface.
-
-
Rendering with Displacement: Once the displacement map is applied, the object can be rendered using the "Cycles" render engine. This engine is capable of accurately interpreting and rendering displacement maps, resulting in highly realistic and detailed surfaces.
FAQs about Displacement Mapping in Blender
Q: What are the best image formats for displacement maps?
A: The most commonly used image formats for displacement maps are grayscale 16-bit or 32-bit PNG or EXR files. These formats provide the necessary dynamic range to accurately capture the details of the displacement map.
Q: How do I create a displacement map for a specific material?
A: The creation of a displacement map for a specific material depends on the desired level of detail and the chosen method. For example, a displacement map for a rough stone surface might involve sculpting in Blender, while a displacement map for a complex organic texture might require procedural generation or external software.
Q: What are the limitations of displacement mapping?
A: Displacement mapping, while powerful, does have certain limitations:
* **Performance:** High-resolution displacement maps can significantly impact rendering time, especially for complex scenes.
* **Geometric Detail:** Displacement maps primarily affect surface detail and cannot create new geometry. This means that they cannot be used to add new features or change the overall shape of an object.
* **Sharp Edges:** Displacement maps can sometimes create sharp edges or artifacts, especially when used with high displacement values.Tips for Effective Displacement Mapping in Blender
-
Optimize Resolution: Use the appropriate resolution for your displacement map, balancing detail with performance.
-
Experiment with Settings: Adjust the "Strength," "Midlevel," and "Coordinates" settings of the "Displacement" modifier to fine-tune the effect.
-
Utilize Normal Maps: Combine displacement maps with normal maps to enhance surface details and create a more realistic appearance.
-
Bake Displacement: Bake the displacement map onto the object’s geometry to create a permanent, high-resolution model for faster rendering.
Conclusion
Displacement mapping, a powerful technique within Blender, empowers artists to create intricate surface details and enhance the realism of their 3D models. By leveraging grayscale images to manipulate geometry, this technique provides a balance of detail and performance, enabling the creation of stunning visual effects. As artists continue to explore the potential of displacement mapping, it remains a vital tool in the pursuit of photorealistic and captivating 3D representations.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Sculpting with Light: A Comprehensive Guide to Displacement Maps in Blender. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
