Streamlining Network Access: A Guide To Group Policy-Managed Network Drives
Streamlining Network Access: A Guide to Group Policy-Managed Network Drives
Related Articles: Streamlining Network Access: A Guide to Group Policy-Managed Network Drives
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Streamlining Network Access: A Guide to Group Policy-Managed Network Drives. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Streamlining Network Access: A Guide to Group Policy-Managed Network Drives
In the realm of network administration, providing consistent and secure access to shared resources is paramount. One powerful tool for achieving this goal is the use of Group Policy to manage network drive mappings. This approach, often referred to as "GPO-managed network drives," offers a centralized and efficient way to ensure that users have the necessary access to shared files and folders, while adhering to established security policies.
Understanding the Fundamentals
Group Policy Objects (GPOs) are powerful administrative tools within the Windows operating system. They allow administrators to define and enforce a wide range of settings across an entire network, including user accounts, security configurations, and software installations. In the context of network drive mappings, GPOs enable administrators to define specific drive letters, connection paths, and access permissions for users or groups.
Benefits of Centralized Network Drive Management
GPO-managed network drives offer a range of advantages over manually configuring drive mappings on individual workstations:
- Consistency: All users within a specific group will automatically receive the same drive mappings, ensuring consistent access to shared resources. This eliminates the need for individual configuration, promoting uniformity across the network.
- Security: By defining access permissions within the GPO, administrators can control which users or groups have access to specific network drives. This centralized control enhances security and prevents unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- Scalability: Managing network drive mappings through GPOs is highly scalable. Administrators can easily apply changes to a large number of users or groups with minimal effort.
- Efficiency: GPO-managed network drives streamline the process of network drive configuration, saving administrators time and effort compared to manual methods.
- Flexibility: Administrators can easily modify drive mappings, permissions, or connection paths through the GPO interface, ensuring that users have access to the most up-to-date resources.
Implementing GPO-Managed Network Drives
The implementation of GPO-managed network drives involves several key steps:
- Defining the Scope: Identify the users or groups that require access to specific network drives. This involves defining the target audience for the GPO.
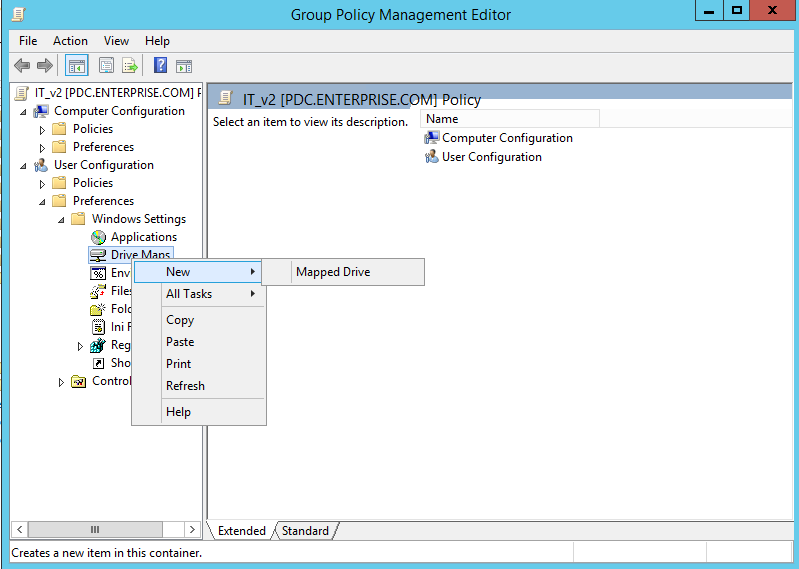
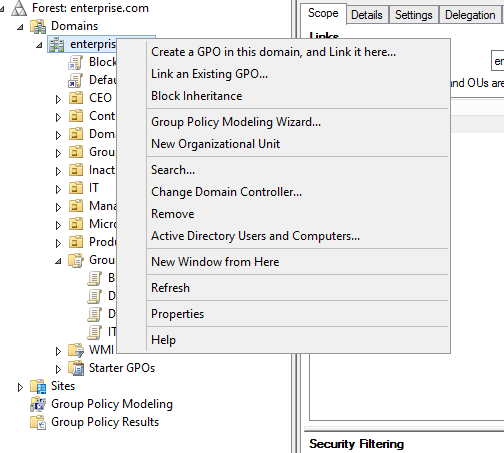
- Creating the GPO: Create a new GPO within the Active Directory environment. This GPO will contain the configuration for the network drive mappings.
- Configuring Drive Mappings: Within the GPO, define the drive letter, connection path, and access permissions for the network drive. The connection path can be a UNC path (Universal Naming Convention) or a specific server name and share.
- Linking the GPO: Link the newly created GPO to the appropriate organizational units (OUs) within Active Directory. This ensures that the GPO applies to the targeted users or groups.
- Deployment and Testing: Deploy the GPO to the network. This involves replicating the GPO to domain controllers and allowing it to take effect on user workstations. Thorough testing is crucial to ensure the mappings work correctly.
Troubleshooting and Best Practices
While GPO-managed network drives offer a robust solution for network drive management, troubleshooting issues may arise. Common problems include:
- Incorrect Connection Path: Verify that the UNC path or server name and share are correctly configured within the GPO.
- Access Permissions: Ensure that users have the necessary permissions to access the network drive.
- GPO Replication: Ensure that the GPO has replicated correctly to all domain controllers.
- User Profile Settings: Check for conflicting settings within the user’s profile that may override the GPO configuration.
Tips for Successful Implementation:
- Use clear and descriptive names for GPOs and network drives. This makes it easier to identify and manage them.
- Document the configuration of the GPO. This provides a reference point for troubleshooting and future updates.
- Test thoroughly before deploying the GPO. Ensure that the drive mappings work as expected and that users have the necessary access.
- Monitor the GPO for any errors or issues. Regularly check the event logs for any warnings or errors related to the GPO.
FAQs about GPO-Managed Network Drives
1. How can I prevent users from manually mapping network drives?
Administrators can configure a GPO setting to disable the ability for users to manually map network drives. This ensures that only the GPO-defined mappings are active.
2. Can I use GPOs to map network drives to specific applications?
Yes, GPOs can be used to map network drives to specific applications, ensuring that the application has access to the required resources.
3. What are the security considerations for GPO-managed network drives?
Security considerations include defining appropriate access permissions, using strong passwords for network accounts, and implementing network security measures like firewalls and intrusion detection systems.
4. How can I manage the storage space allocated to network drives?
GPOs can be used to define quotas for user accounts on network drives, limiting the amount of storage space available. This helps to prevent excessive storage usage and optimize network performance.
5. What are the limitations of GPO-managed network drives?
While GPO-managed network drives offer a powerful solution, they may not be suitable for all scenarios. For example, they may not be appropriate for highly dynamic environments where access requirements change frequently.
Conclusion
GPO-managed network drives provide a powerful and efficient method for managing network drive mappings within a Windows environment. By centralizing configuration and enforcing security policies, administrators can ensure consistent and secure access to shared resources across the network. Implementing GPO-managed network drives requires careful planning and configuration, but the benefits in terms of efficiency, security, and scalability outweigh the initial effort. By leveraging the power of Group Policy, organizations can streamline network access and enhance productivity, while maintaining a secure and reliable network environment.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Streamlining Network Access: A Guide to Group Policy-Managed Network Drives. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!