The Arabian Peninsula: A Crossroads Of History And Culture
The Arabian Peninsula: A Crossroads of History and Culture
Related Articles: The Arabian Peninsula: A Crossroads of History and Culture
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Arabian Peninsula: A Crossroads of History and Culture. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Arabian Peninsula: A Crossroads of History and Culture

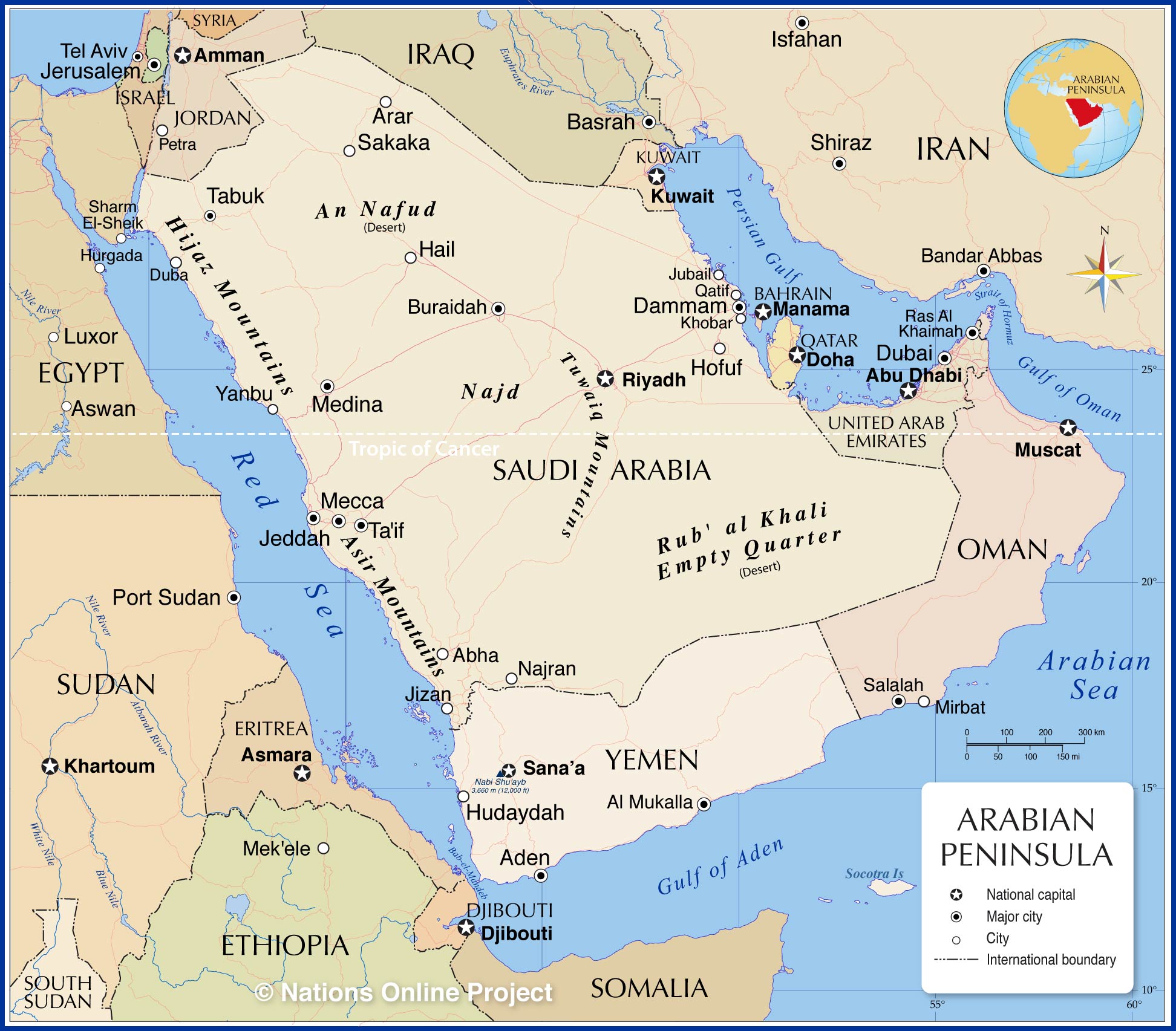
The Arabian Peninsula, a vast and arid landmass situated in southwest Asia, holds a unique and pivotal position in global history and geography. It is a region where ancient civilizations flourished, empires rose and fell, and trade routes crisscrossed, connecting the East and West for millennia. Understanding the Arabian Peninsula’s geographical features, cultural diversity, and historical significance is crucial for comprehending the complex tapestry of the modern world.
A Land of Extremes:
The Arabian Peninsula is characterized by its extreme geographical features. It is the largest peninsula in the world, covering an area of approximately 3,237,500 square kilometers. The peninsula’s topography is dominated by vast, desolate deserts, including the Rub’ al Khali, the largest sand desert in the world. These deserts are interspersed with mountain ranges, such as the Asir Mountains in southwestern Saudi Arabia, which offer a stark contrast to the surrounding arid landscape.
The peninsula’s coastline is fringed by the Red Sea to the west, the Gulf of Oman and the Arabian Sea to the east, and the Persian Gulf to the northeast. These waterways have played a crucial role in the region’s history, facilitating trade and cultural exchange. The peninsula also boasts a number of oases, fertile pockets of land where water sources sustain life and agriculture.
A Cradle of Civilizations:
The Arabian Peninsula has been home to numerous ancient civilizations, each leaving its mark on the region’s cultural landscape. The Nabataeans, known for their impressive rock-cut architecture in Petra, Jordan, flourished in the 1st century BC. The Sabaeans, who established a powerful kingdom in present-day Yemen, were renowned for their trade in frankincense and myrrh. The Himyarites, who succeeded the Sabaeans, further developed the region’s commercial network, connecting the peninsula to the Roman Empire and the East.
The rise of Islam in the 7th century AD transformed the Arabian Peninsula. The Prophet Muhammad, born in Mecca, established Islam as a new faith, and the peninsula became the birthplace of the Islamic world. The subsequent expansion of the Islamic empire spread the religion and its cultural influence across vast swathes of the world, leaving an indelible mark on history.
A Crossroads of Trade and Culture:
The Arabian Peninsula’s strategic location at the crossroads of continents has made it a vital hub for trade and cultural exchange throughout history. The ancient Incense Route, traversing the peninsula from the south to the north, carried precious commodities like frankincense and myrrh to markets across the Mediterranean. The Silk Road, connecting the East and West, also passed through the peninsula, contributing to the region’s prosperity and cultural diversity.
The peninsula’s diverse cultural heritage is evident in its rich tapestry of languages, religions, and traditions. Arabic, the dominant language of the region, has evolved over centuries, incorporating influences from other cultures. Islam, the dominant religion, has shaped the peninsula’s social and legal systems, while other faiths, such as Christianity and Judaism, have also played significant roles in the region’s history.
Modern Challenges and Opportunities:
The Arabian Peninsula faces a number of challenges in the 21st century. The region’s dependence on oil revenue makes it vulnerable to global economic fluctuations. Political instability, fueled by regional conflicts and sectarian tensions, poses a threat to peace and security. Climate change, with its potential to exacerbate water scarcity and desertification, presents a formidable challenge to the region’s sustainability.
Despite these challenges, the Arabian Peninsula also presents significant opportunities. The region’s vast natural resources, including oil and gas reserves, offer potential for economic diversification and development. The peninsula’s strategic location, connecting Asia, Africa, and Europe, positions it as a vital hub for trade and investment. The region’s rich cultural heritage and historical significance provide a foundation for tourism and cultural exchange.
FAQs about the Arabian Peninsula:
1. What are the major countries located in the Arabian Peninsula?
The Arabian Peninsula is home to seven countries: Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Oman, United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Bahrain, and Kuwait.
2. What is the climate like in the Arabian Peninsula?
The Arabian Peninsula experiences an arid climate, with hot summers and mild winters. The region receives very little rainfall, making water resources scarce and contributing to the dominance of desert landscapes.
3. What is the significance of the Arabian Peninsula in Islamic history?
The Arabian Peninsula is the birthplace of Islam and home to the two holiest cities in the Islamic world: Mecca and Medina. The Prophet Muhammad, the founder of Islam, was born in Mecca, and the city is the site of the Kaaba, the holiest shrine in Islam. Medina is the site of the Prophet Muhammad’s first mosque and the location of his burial.
4. What are the major economic activities in the Arabian Peninsula?
The Arabian Peninsula’s economy is dominated by the extraction and export of oil and gas. However, the region is increasingly diversifying its economy, investing in sectors such as tourism, technology, and renewable energy.
5. What are the major cultural influences on the Arabian Peninsula?
The Arabian Peninsula’s cultural heritage is shaped by a confluence of influences, including Arab traditions, Islamic beliefs, and historical interactions with other civilizations. The region’s culture is characterized by its rich literature, music, art, and cuisine.
Tips for Understanding the Arabian Peninsula:
- Study the region’s geography: Understanding the Arabian Peninsula’s unique geographical features, including its deserts, mountains, and coastlines, is essential for comprehending its history, culture, and challenges.
- Explore its history: Delving into the Arabian Peninsula’s rich history, from ancient civilizations to the rise of Islam and the modern era, provides valuable insights into the region’s complex past and present.
- Engage with its diverse cultures: The Arabian Peninsula is home to a diverse array of cultures, languages, and traditions. Engaging with these diverse perspectives fosters a deeper understanding of the region’s complexity and richness.
- Recognize the challenges and opportunities: The Arabian Peninsula faces significant challenges, but it also presents opportunities for progress and development. Understanding these challenges and opportunities is crucial for navigating the region’s future.
Conclusion:
The Arabian Peninsula, a land of extremes and a cradle of civilizations, holds a pivotal position in global history and geography. Its unique geographical features, rich cultural heritage, and strategic location have shaped its past, present, and future. Understanding the Arabian Peninsula’s complex tapestry of history, culture, and challenges is essential for comprehending the intricate dynamics of the modern world. As the region navigates the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century, its role in shaping the future of the Middle East and beyond remains significant.


![Arabia: Cultural-Historical Zones by Dr Michael Izady [6101x3947] : MapPorn](https://external-preview.redd.it/_CbAqLByBrB4es-AeQyG1EC8YrqVJJny-PNPFcVVmLk.png?auto=webpu0026s=0ee8b2f2dc76923ec59d6e4bbbaeb653b05277d1)



+Claimed+descendants+of+M%E2%80%99s+uncle.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Arabian Peninsula: A Crossroads of History and Culture. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!