The Berlin Wall: A Tangible Reminder Of Division And Freedom
The Berlin Wall: A Tangible Reminder of Division and Freedom
Related Articles: The Berlin Wall: A Tangible Reminder of Division and Freedom
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Berlin Wall: A Tangible Reminder of Division and Freedom. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Berlin Wall: A Tangible Reminder of Division and Freedom
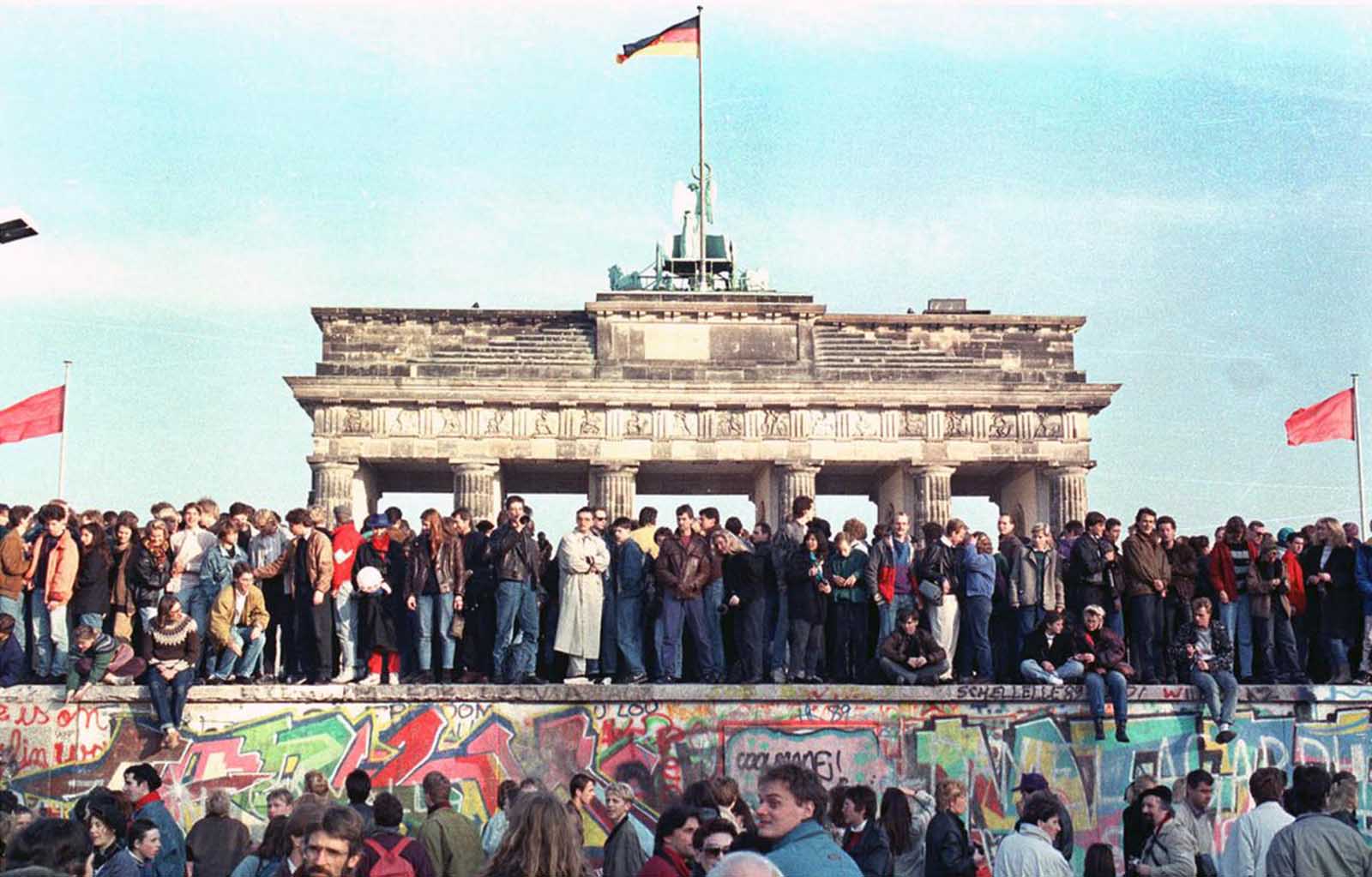

The Berlin Wall, a stark symbol of Cold War division, remains etched in the collective memory of the world. Its physical presence, though dismantled in 1989, continues to exist in the form of maps and photographs, serving as poignant reminders of a turbulent period in history. Understanding the Berlin Wall’s location and its impact requires a nuanced approach, considering its historical context, geographical significance, and lasting legacy.
A Divided City, A Divided World:
The Berlin Wall’s construction in 1961 was a direct result of the Cold War’s ideological divide. Following World War II, Germany was partitioned into two distinct entities: East Germany, under Soviet influence, and West Germany, aligned with the Western powers. Berlin, located within East Germany, was also divided, with the eastern sector controlled by the Soviet Union and the western sectors governed by the United States, the United Kingdom, and France.
The Berlin Wall, a physical manifestation of this division, was erected to prevent East Germans from fleeing to the West. It ran for 155 kilometers, slicing through the heart of the city, separating families, friends, and communities. This concrete barrier was fortified with barbed wire, watchtowers, and armed guards, symbolizing the iron curtain that had descended across Europe.
Mapping the Wall: A Visual Representation of Division
Maps of the Berlin Wall provide a visual representation of this historical event, illustrating its physical presence within the city. These maps highlight the wall’s path, showcasing its impact on urban planning, transportation routes, and daily life. They reveal the intricate network of checkpoints, watchtowers, and border crossings that dotted the wall’s length, showcasing the stringent control exercised by the East German authorities.
Maps also offer a glimpse into the wall’s evolution over time. They demonstrate how the wall was expanded and reinforced over the years, reflecting the increasing tensions between the East and West. They also illustrate the numerous attempts to escape, highlighting the human cost of this division, and the determination of those seeking freedom.
The Wall’s Legacy: A Symbol of Freedom and Unity
The Berlin Wall’s fall in 1989 marked a pivotal moment in history, symbolizing the end of the Cold War and the triumph of freedom and democracy. Its dismantling was a testament to the power of peaceful protest and the yearning for reunification.
Maps of the Berlin Wall, in addition to serving as historical documents, are also powerful tools for education and remembrance. They provide a tangible connection to this significant event, allowing individuals to visualize the wall’s impact on the city and its inhabitants. They encourage reflection on the importance of human rights, freedom, and the pursuit of peace.
Beyond the Map: Exploring the Wall’s Impact
The Berlin Wall’s significance transcends its physical presence. It serves as a reminder of the devastating consequences of division, highlighting the importance of dialogue, understanding, and collaboration. Its legacy continues to inspire discussions on political ideologies, human rights, and the pursuit of freedom.
FAQs about the Berlin Wall:
1. Why was the Berlin Wall built?
The Berlin Wall was built to prevent East Germans from fleeing to West Germany. The East German government, under Soviet influence, feared an exodus of its citizens, particularly skilled workers, to the West, which offered greater economic opportunities and freedom.
2. When was the Berlin Wall built and dismantled?
The Berlin Wall was built on August 13, 1961, and dismantled on November 9, 1989.
3. How long was the Berlin Wall?
The Berlin Wall extended for approximately 155 kilometers, stretching across the city and separating East and West Berlin.
4. How many people died trying to cross the Berlin Wall?
The exact number of deaths associated with the Berlin Wall is disputed, but estimates range from 136 to 200. Many individuals perished while attempting to cross the wall, either by being shot by border guards or killed in accidents.
5. What is the East Side Gallery?
The East Side Gallery is a section of the Berlin Wall that has been transformed into an open-air art gallery. Over 100 artists from around the world have painted murals on this section, creating a vibrant and symbolic reminder of the wall’s history and the importance of freedom.
Tips for Understanding the Berlin Wall:
1. Visit the Berlin Wall Memorial:
The Berlin Wall Memorial, located at Bernauer Strasse, offers a comprehensive and moving experience for visitors. It features exhibits, historical information, and a preserved section of the wall, providing a tangible understanding of its history and impact.
2. Explore the East Side Gallery:
The East Side Gallery is a must-visit for anyone interested in the Berlin Wall’s legacy. It provides a unique and artistic perspective on the wall’s history, showcasing the power of art to express freedom and unity.
3. Read books and watch documentaries:
There are numerous books and documentaries available that offer insightful perspectives on the Berlin Wall. These resources provide detailed historical accounts, personal stories, and analysis of the wall’s significance.
4. Engage in discussions and share your knowledge:
Sharing your knowledge of the Berlin Wall with others can help promote understanding and appreciation for this significant historical event. Engaging in discussions and sharing personal perspectives can foster a deeper understanding of its impact.
Conclusion:
The Berlin Wall, a symbol of division and a testament to the power of freedom, continues to hold a powerful place in history. Its physical presence, though gone, lives on in the form of maps, photographs, and memorials, reminding us of the importance of human rights, unity, and the pursuit of peace. Understanding the Berlin Wall’s history and its impact remains crucial, ensuring that its lessons are not forgotten and its legacy continues to inspire generations to come.
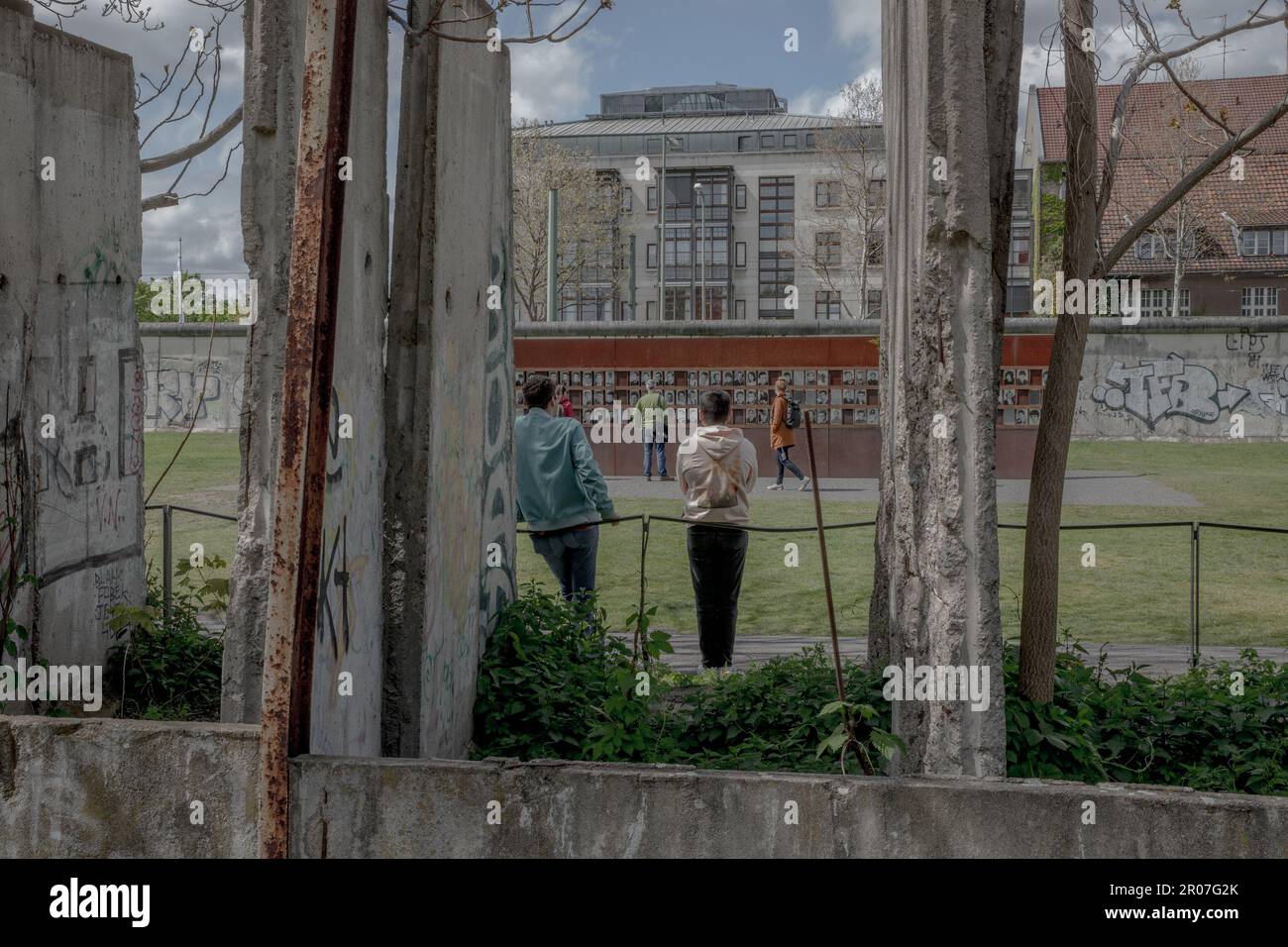
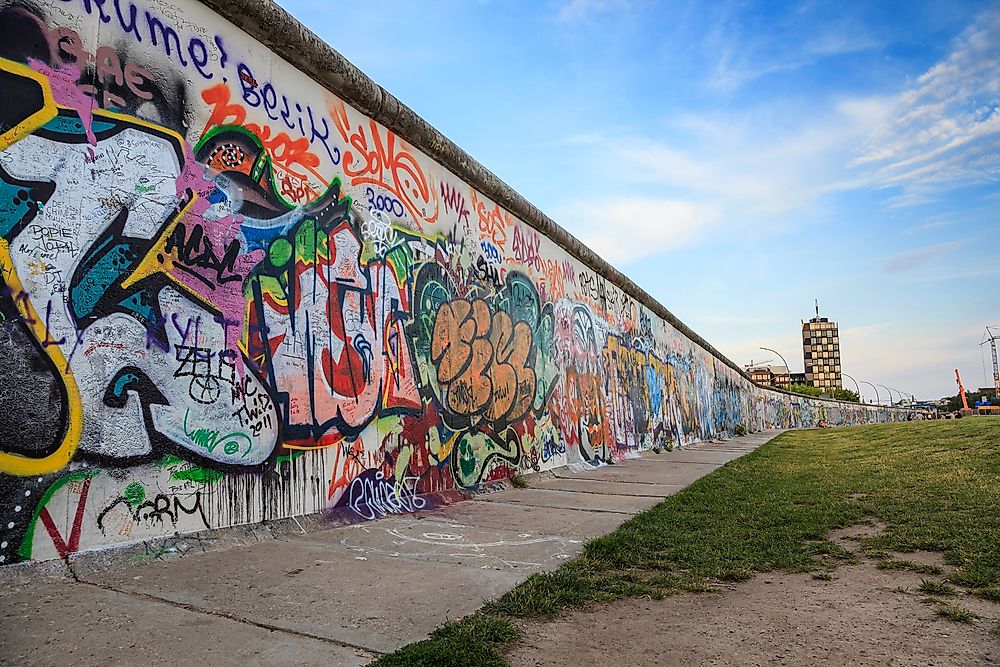
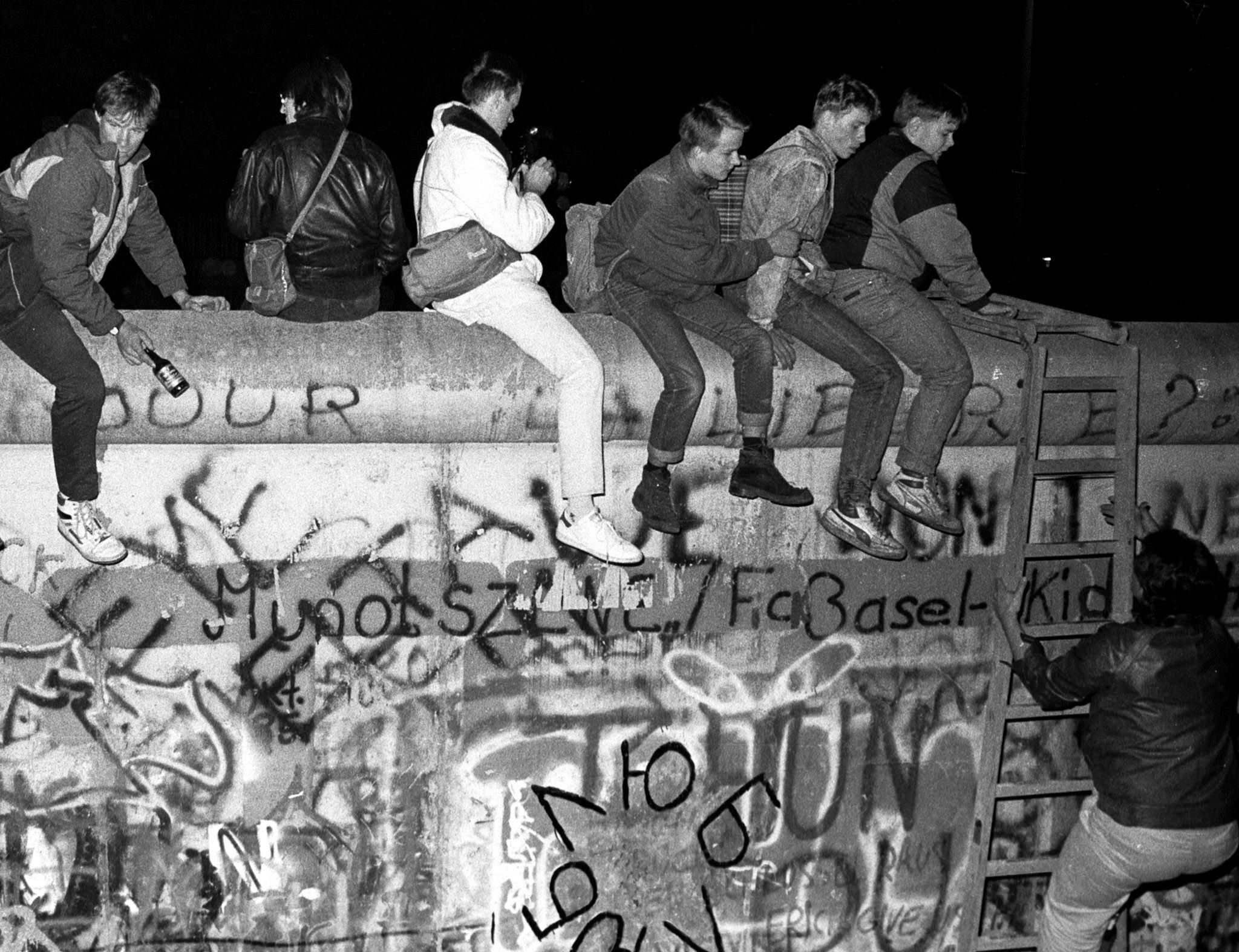







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Berlin Wall: A Tangible Reminder of Division and Freedom. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!