The Power Of Visualization: Understanding The Landscape Of Your Data With Grandscape Maps
The Power of Visualization: Understanding the Landscape of Your Data with Grandscape Maps
Related Articles: The Power of Visualization: Understanding the Landscape of Your Data with Grandscape Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Power of Visualization: Understanding the Landscape of Your Data with Grandscape Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Visualization: Understanding the Landscape of Your Data with Grandscape Maps
In the modern world of data analysis, the ability to visualize complex information is paramount. While traditional charts and graphs offer valuable insights, they often struggle to represent the intricate relationships and patterns that exist within large datasets. This is where Grandscape Maps, a powerful visualization technique, emerges as a game-changer.
What are Grandscape Maps?
Grandscape Maps are a type of data visualization that leverages the power of spatial representation to illuminate the complex interplay of data points within a multidimensional landscape. Unlike conventional maps, which primarily depict geographical locations, Grandscape Maps utilize a multidimensional space to represent various data variables. This allows for a deeper understanding of the connections, clusters, and outliers within the data, providing a holistic view of the information landscape.
The Essence of Grandscape Maps:
At the core of Grandscape Maps lies the principle of dimensionality reduction. By projecting high-dimensional data into a lower-dimensional space, typically two or three dimensions, Grandscape Maps enable visualization without sacrificing crucial information. This transformation is achieved through sophisticated algorithms that identify the most significant data relationships and project them onto the map.
Key Features of Grandscape Maps:
- Multidimensional Representation: Grandscape Maps can accommodate a wide range of data variables, allowing for the visualization of complex relationships between multiple factors.
- Spatial Arrangement: The spatial arrangement of data points on the Grandscape Map reflects the underlying relationships and patterns within the data.
- Interactive Exploration: Grandscape Maps are typically interactive, allowing users to zoom, pan, and filter the data to explore specific regions of interest.
- Data Insights: By visualizing the data in a spatial context, Grandscape Maps facilitate the identification of clusters, outliers, and trends that may be hidden in traditional data representations.
Applications of Grandscape Maps:
The versatility of Grandscape Maps makes them applicable across a wide spectrum of disciplines, including:
- Business Analytics: Understanding customer segmentation, market trends, and product performance.
- Healthcare: Identifying patient cohorts, analyzing disease patterns, and optimizing treatment strategies.
- Finance: Recognizing investment opportunities, predicting market volatility, and managing risk.
- Research & Development: Exploring scientific data, uncovering hidden correlations, and identifying potential breakthroughs.
Benefits of Using Grandscape Maps:
- Enhanced Data Understanding: Grandscape Maps provide a holistic and intuitive view of data, making it easier to grasp complex relationships and patterns.
- Improved Decision-Making: By revealing hidden insights and trends, Grandscape Maps empower informed decision-making based on a deeper understanding of the data.
- Increased Efficiency: Grandscape Maps streamline the data analysis process by providing a comprehensive visual representation of the information landscape.
- Enhanced Collaboration: The visual nature of Grandscape Maps facilitates effective communication and collaboration among stakeholders, fostering shared understanding and insights.
FAQs about Grandscape Maps:
1. What type of data can be visualized with Grandscape Maps?
Grandscape Maps can handle a wide range of data types, including numerical, categorical, and textual data. The key requirement is that the data can be represented as points in a multidimensional space.
2. How are Grandscape Maps created?
Grandscape Maps are created using sophisticated algorithms that reduce the dimensionality of the data while preserving the most relevant information. These algorithms typically employ techniques such as Principal Component Analysis (PCA), t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding (t-SNE), or Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP).
3. What software tools are available for creating Grandscape Maps?
There are various software tools available for creating Grandscape Maps, including:
- Tableau: A popular business intelligence platform with powerful visualization capabilities.
- Power BI: A comprehensive data analysis and visualization tool from Microsoft.
- R: A statistical programming language with extensive libraries for data visualization.
- Python: A versatile programming language with libraries like scikit-learn and matplotlib for data analysis and visualization.
4. How can I interpret the information presented on a Grandscape Map?
The interpretation of Grandscape Maps involves understanding the spatial arrangement of data points. Clusters of points suggest similar characteristics, while outliers represent unique data points that deviate from the general trend. The proximity of points indicates a stronger relationship between the corresponding data variables.
5. What are the limitations of Grandscape Maps?
While Grandscape Maps offer a powerful visualization approach, they also have limitations:
- Dimensionality Reduction: The process of dimensionality reduction can sometimes lead to information loss, especially in cases of high-dimensional data.
- Visual Complexity: Grandscape Maps can become visually complex when dealing with large datasets, potentially hindering interpretability.
- Data Bias: The choice of algorithm and parameters can influence the resulting visualization, potentially introducing bias.
Tips for Using Grandscape Maps Effectively:
- Start with Clear Objectives: Define the specific questions you want to answer before creating the Grandscape Map.
- Choose Appropriate Data: Ensure that the data you use is relevant to your objectives and can be effectively represented in a multidimensional space.
- Select Suitable Algorithms: Choose algorithms that are appropriate for your data type and the desired level of dimensionality reduction.
- Explore Interactively: Utilize the interactive features of Grandscape Maps to zoom, pan, and filter the data to explore specific regions of interest.
- Collaborate and Validate: Share your findings with colleagues and stakeholders to ensure accurate interpretation and validation of the results.
Conclusion:
Grandscape Maps represent a significant advancement in data visualization, empowering analysts to gain a deeper understanding of complex data landscapes. By leveraging the power of spatial representation, Grandscape Maps provide a holistic and intuitive view of the data, revealing hidden relationships and patterns that may be overlooked in traditional data representations. As data continues to grow in volume and complexity, Grandscape Maps will play an increasingly important role in unlocking valuable insights and driving informed decision-making across diverse domains.

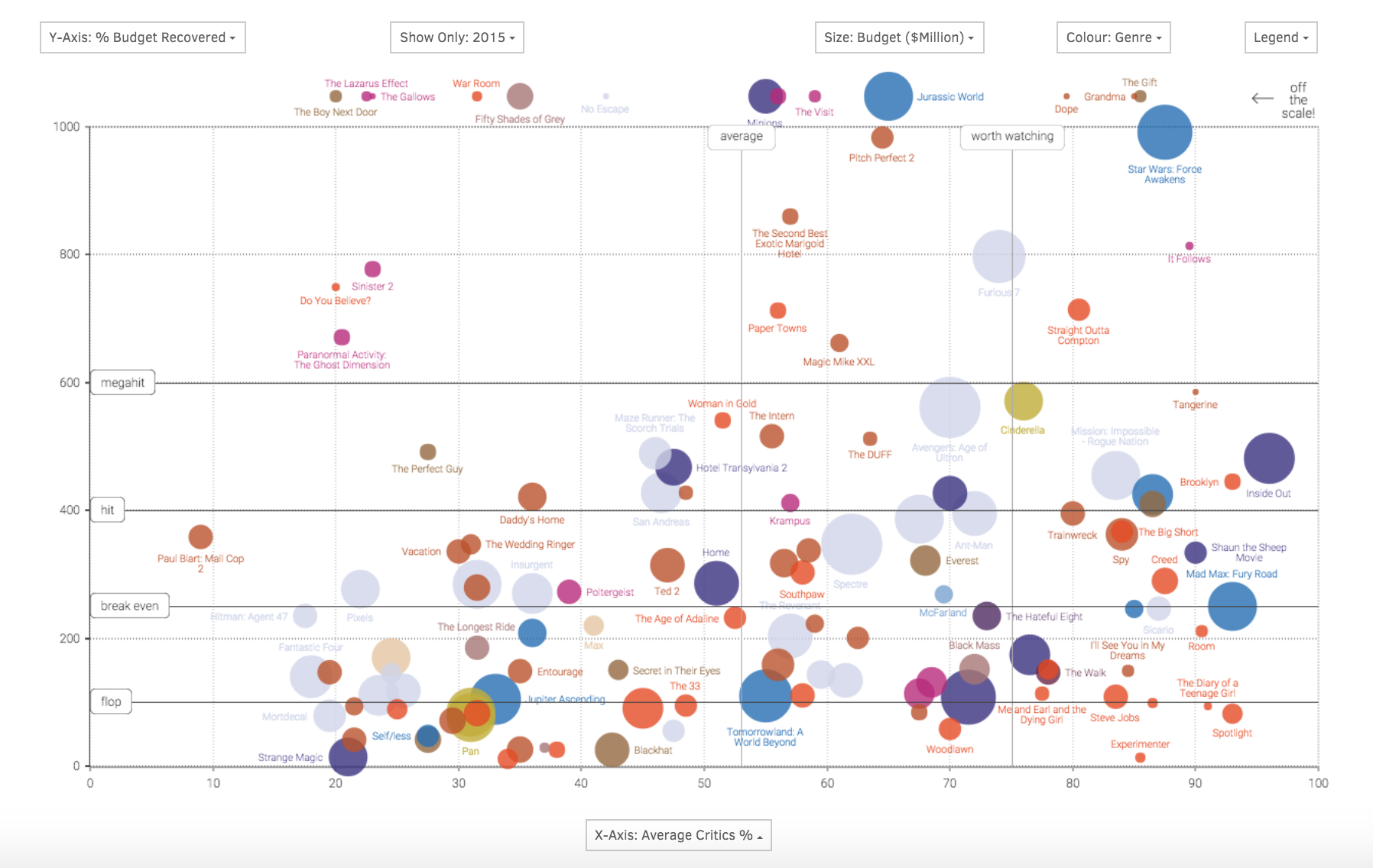

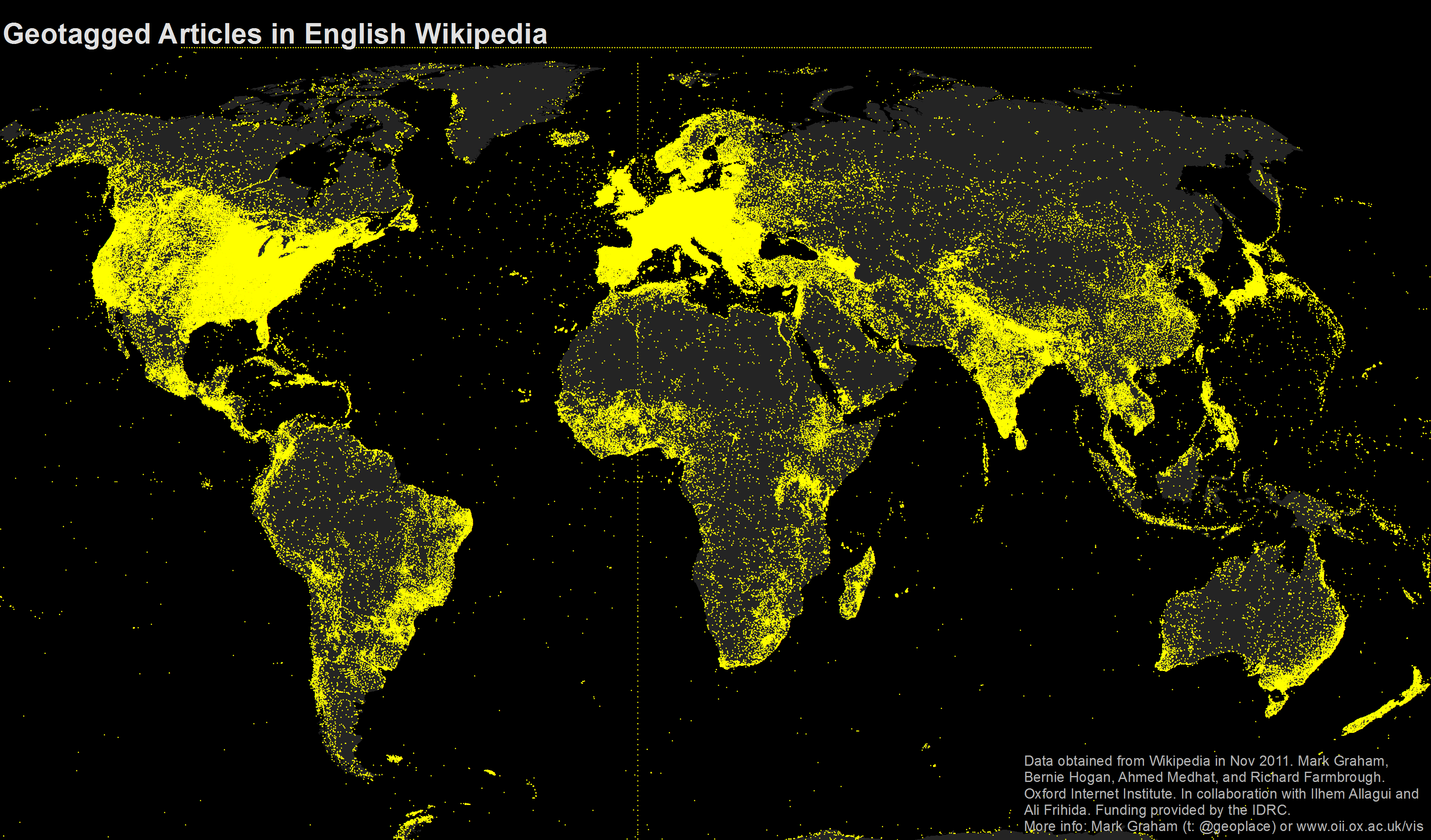
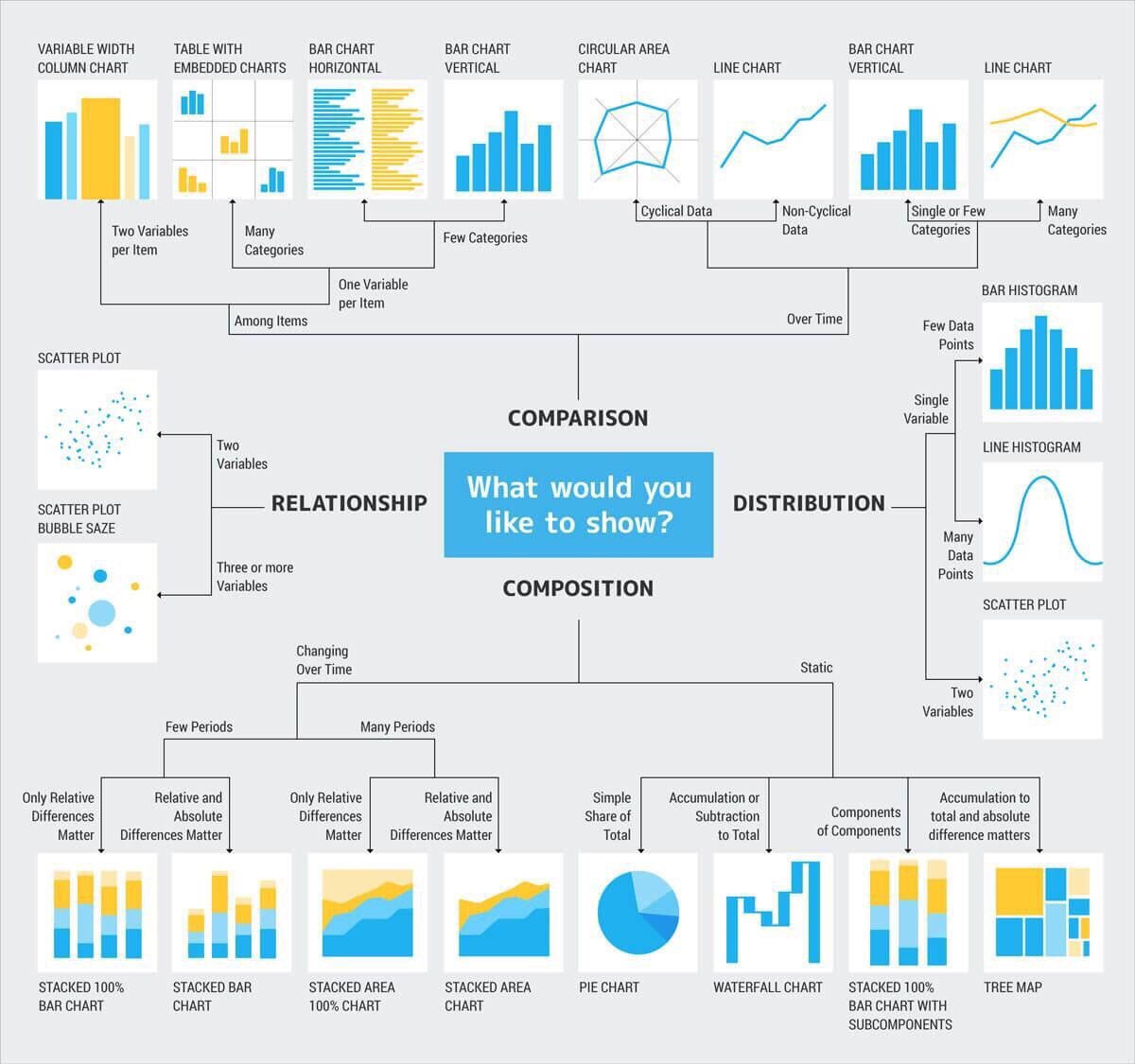
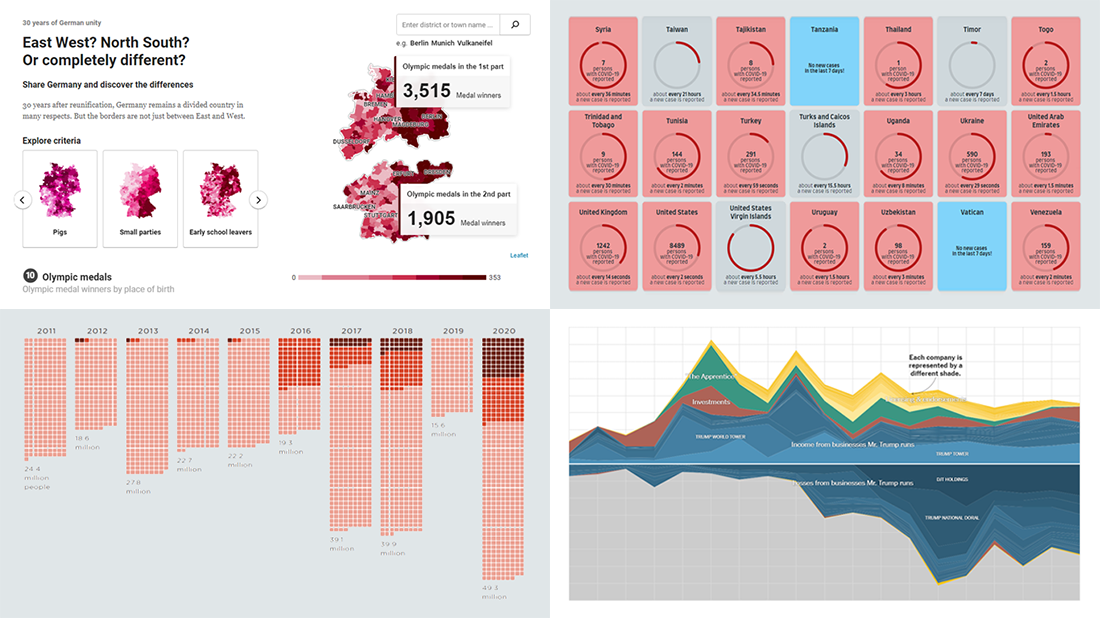

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Visualization: Understanding the Landscape of Your Data with Grandscape Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!