The Straight Line On The Map: A Journey Beyond The Curve
The Straight Line on the Map: A Journey Beyond the Curve
Related Articles: The Straight Line on the Map: A Journey Beyond the Curve
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Straight Line on the Map: A Journey Beyond the Curve. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Straight Line on the Map: A Journey Beyond the Curve

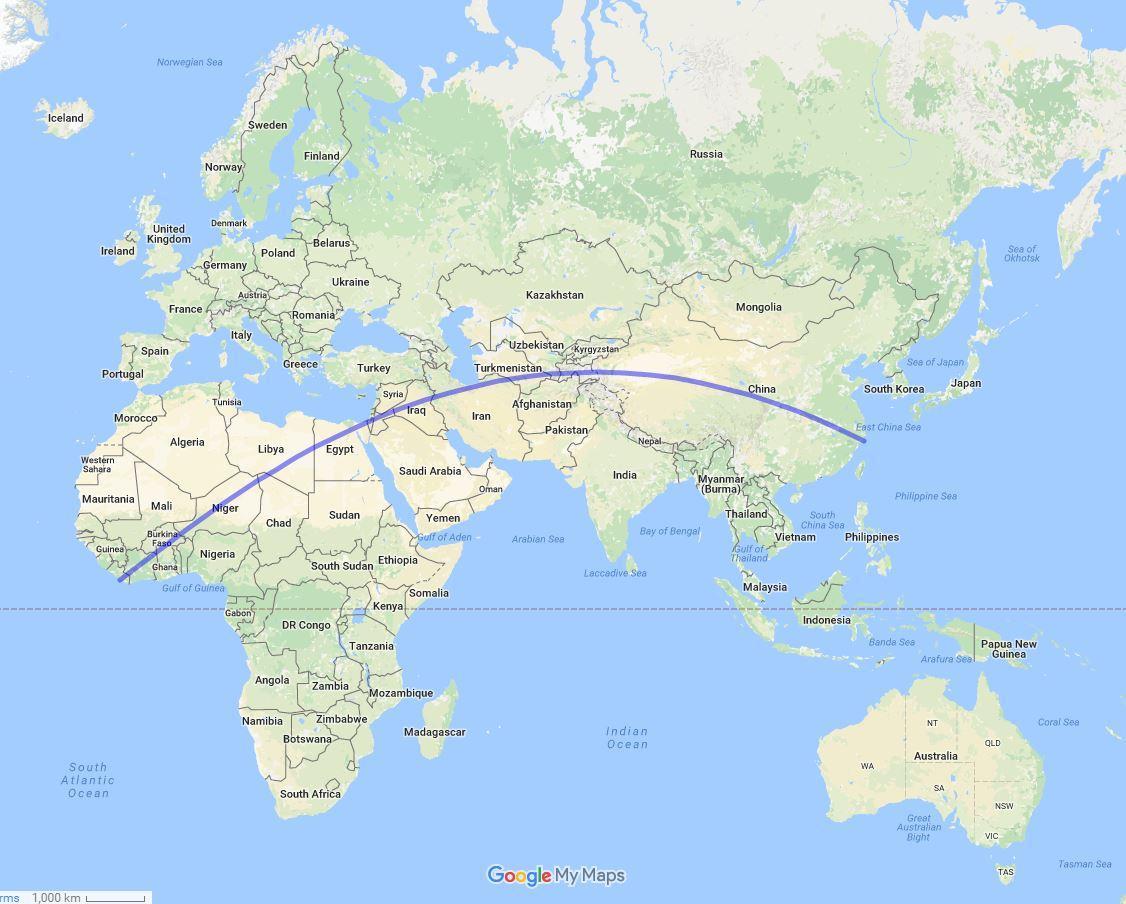
Maps, those invaluable tools for navigating the world, often present us with a seemingly straightforward path: a straight line connecting two points. However, the reality of travel rarely aligns with this idealized representation. While the straight line on a map might appear as the shortest distance, it seldom reflects the actual distance traveled. This discrepancy arises from the Earth’s curvature, which necessitates winding routes, often following roads or waterways, to traverse the globe.
The straight line distance, also known as the great-circle distance, is a theoretical concept that calculates the shortest distance between two points on the Earth’s surface, assuming the Earth is a perfect sphere. This distance is measured along the great circle, which is the largest circle that can be drawn on the surface of a sphere, passing through its center.
Understanding the Concept
Imagine holding a string taut between two points on a globe. The string’s path represents the great-circle distance, the shortest possible route between those points. This contrasts with the straight line distance on a flat map, which often exaggerates distances, especially at higher latitudes.
Calculating the Great-Circle Distance
The great-circle distance can be calculated using various methods, including:
- Haversine formula: This formula uses the spherical coordinates of two points to determine the distance along the great circle.
- Vincenty’s formula: This formula provides a more accurate calculation, accounting for the Earth’s ellipsoidal shape.
Applications of Straight Line Distance
While the straight line distance may not accurately reflect the distance traveled by road, it holds significant value in various applications:
- Navigation and Planning: Pilots and sailors utilize great-circle distances for efficient route planning, particularly for long-distance travel.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS applications use straight line distances to analyze spatial data, such as calculating the distance between points of interest or determining the proximity of different features.
- Mapping and Cartography: Straight line distances are used to create accurate maps and projections, representing distances and locations with greater precision.
- Distance Measurement Tools: Numerous online tools and apps utilize the great-circle distance to calculate distances between locations, providing a quick and easy way to estimate the distance between two points.
The Importance of Straight Line Distance
Despite its theoretical nature, the straight line distance remains a crucial concept for understanding distances on a global scale. Its significance lies in its ability to:
- Provide a Baseline: The straight line distance serves as a benchmark for comparing different routes and travel options, allowing for a more informed decision-making process.
- Simplify Calculations: The great-circle distance provides a straightforward way to calculate the shortest distance between two points, without the complexities of accounting for road networks and terrain.
- Enhance Accuracy: The straight line distance, when appropriately applied, can improve the accuracy of maps and geographic data, leading to better navigation and planning.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How is the straight line distance different from the road distance?
A: The straight line distance measures the shortest distance between two points on the Earth’s surface, assuming a perfect sphere. Road distance, on the other hand, considers the actual path taken by roads, which often involves curves and detours.
Q: Is the straight line distance always the shortest distance?
A: Yes, the great-circle distance represents the shortest possible distance between two points on the Earth’s surface, assuming the Earth is a perfect sphere.
Q: Can the straight line distance be used to calculate the distance between two points in different countries?
A: Yes, the straight line distance can be used to calculate the distance between any two points on the Earth’s surface, regardless of their location.
Q: How can I calculate the straight line distance between two points?
A: Various online tools and apps are available that allow you to calculate the straight line distance between two points, simply by entering their coordinates.
Tips for Using Straight Line Distance
- Consider the Context: The straight line distance is a valuable tool for planning and navigation, but it’s essential to consider the context of your journey. Factors like road networks, terrain, and obstacles can significantly influence the actual travel distance.
- Use Appropriate Tools: Utilize online tools and apps specifically designed to calculate straight line distances, ensuring accurate results.
- Combine with Other Information: Pair the straight line distance with other information, such as road maps and travel time estimates, to gain a comprehensive understanding of your journey.
Conclusion
The straight line on the map, while not always representing the actual path traveled, holds immense significance in understanding distances on a global scale. It provides a theoretical baseline for comparing routes, simplifying calculations, and enhancing the accuracy of geographic data. By recognizing the limitations and applications of the straight line distance, we can utilize this concept effectively in planning, navigation, and understanding the world around us.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Straight Line on the Map: A Journey Beyond the Curve. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!