Unraveling The Tapestry Of Japan: A Geographic Exploration
Unraveling the Tapestry of Japan: A Geographic Exploration
Related Articles: Unraveling the Tapestry of Japan: A Geographic Exploration
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Tapestry of Japan: A Geographic Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Tapestry of Japan: A Geographic Exploration
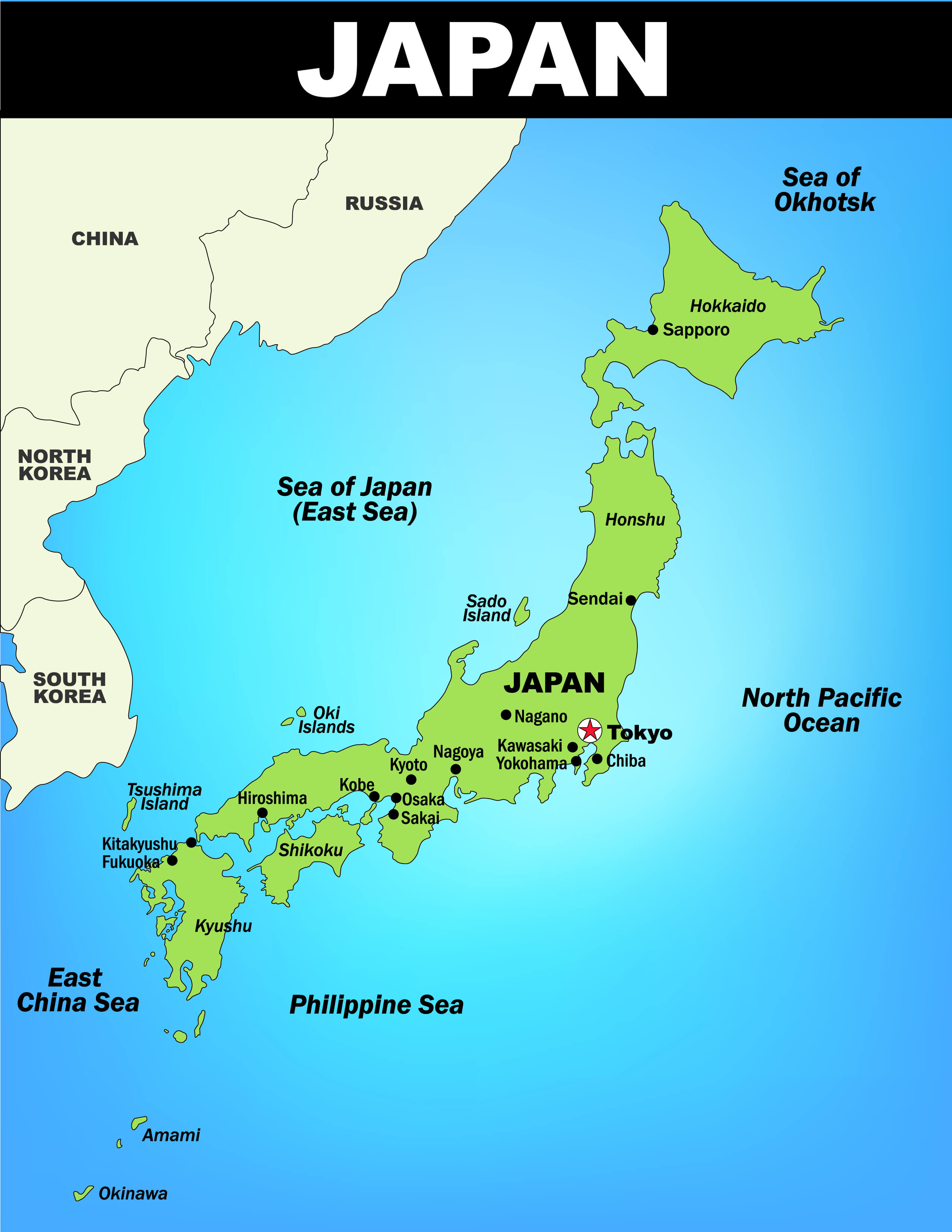
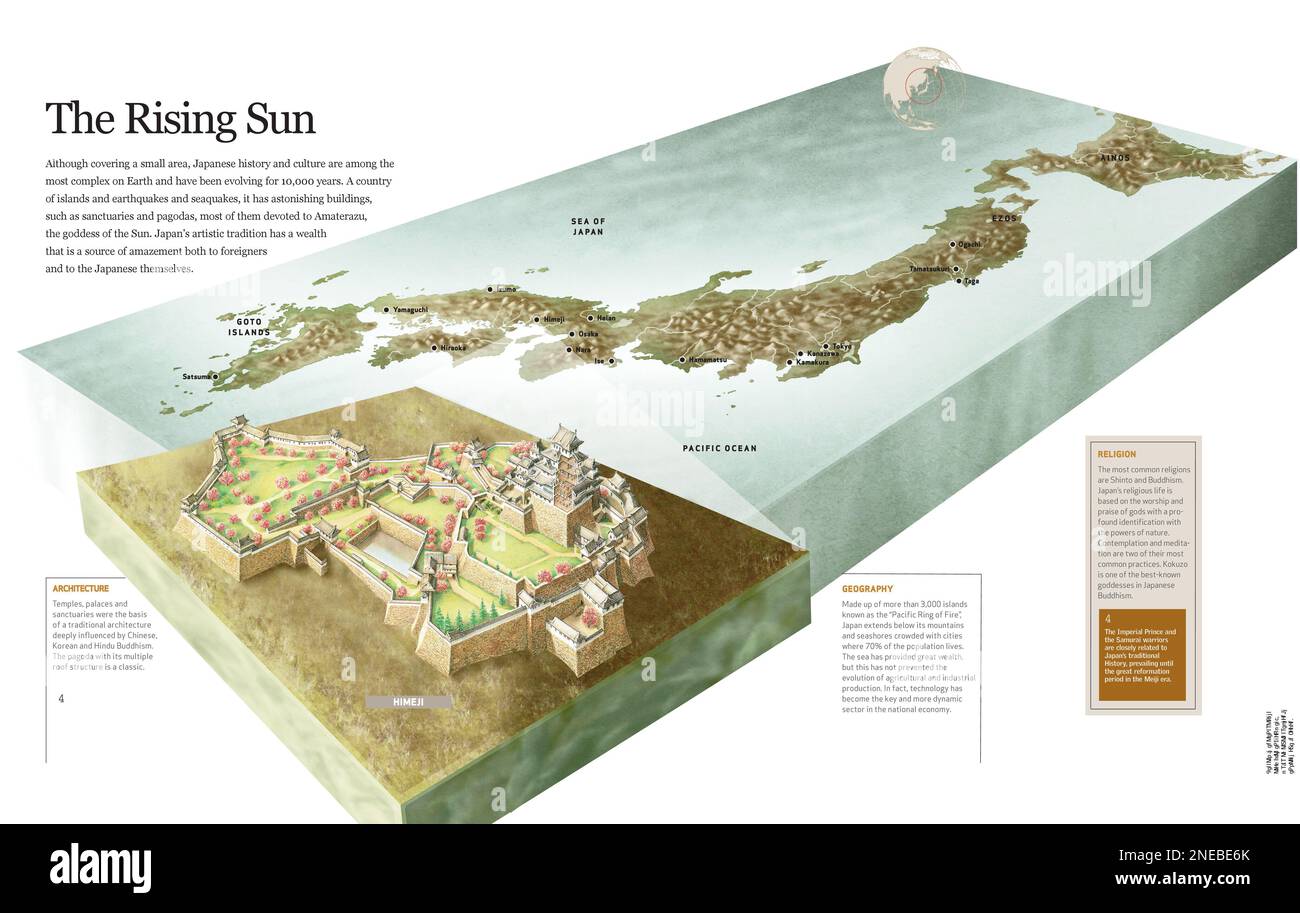
Japan, an archipelago nation nestled in the northwest Pacific Ocean, is a captivating blend of natural beauty, cultural richness, and technological prowess. Its unique geographic features, shaped over millennia by tectonic forces and volcanic activity, have profoundly influenced its history, culture, and even its very identity. Understanding Japan’s geography is key to appreciating the complexities and intricacies of this fascinating nation.
A Chain of Islands:
Japan’s archipelago comprises four main islands – Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu – along with thousands of smaller islands. These islands are strung together like pearls on a necklace, stretching over 3,000 kilometers from north to south. This linear arrangement has historically facilitated trade and cultural exchange, while also creating distinct regional identities.
Mountains and Volcanoes:
Japan’s landscape is dominated by mountains, with over 73% of the country covered by them. The Japanese Alps, a majestic range in central Honshu, showcases some of the country’s most impressive peaks. Volcanic activity is a defining feature, with over 100 active volcanoes, including Mount Fuji, the nation’s highest peak and a cultural icon. These volcanoes have shaped the landscape, providing fertile soil for agriculture and creating breathtaking scenery.
Coastlines and Seas:
Japan is surrounded by the Sea of Japan to the west and the Pacific Ocean to the east, offering a vast coastline. This proximity to the sea has been pivotal in Japan’s history, fostering a strong fishing industry and facilitating trade with neighboring countries. The country’s diverse coastline, ranging from sandy beaches to rugged cliffs, provides a breathtaking backdrop for a variety of activities, from surfing to whale watching.
Climate and Seasons:
Japan experiences a diverse range of climates, influenced by its position on the eastern edge of the Asian continent and its proximity to warm ocean currents. The north experiences cold, snowy winters, while the south enjoys subtropical conditions. The country’s temperate climate, with four distinct seasons, is a key factor in its agricultural production and the vibrant beauty of its natural landscapes.
Natural Resources and Challenges:
Japan’s mountainous terrain limits its agricultural land and natural resources. The country relies heavily on imports for energy, food, and raw materials. However, its abundant forests and diverse marine ecosystems provide valuable resources. The archipelago’s location in a tectonically active region poses significant challenges, as it is prone to earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and tsunamis.
The Importance of Japan’s Geography:
1. Shaping History and Culture:
Japan’s geography has played a crucial role in shaping its history and culture. The archipelago’s isolation from the mainland has fostered a unique cultural identity, while its mountainous terrain has led to the development of distinct regional cultures. The sea has been a vital source of sustenance and trade, connecting Japan to the wider world.
2. Influencing Economic Development:
Japan’s geography has significantly influenced its economic development. The country’s abundant marine resources have fueled its fishing industry. The mountainous terrain, while challenging for agriculture, has led to the development of innovative farming techniques and a strong forestry industry. The availability of hydroelectric power from its numerous rivers has contributed to its industrial growth.
3. Impact on Urbanization and Infrastructure:
Japan’s limited land area has driven its urbanization and the development of sophisticated infrastructure. The concentration of population in major cities has led to the creation of advanced transportation systems, including high-speed rail networks and efficient public transportation. The country’s vulnerability to natural disasters has prompted the development of resilient infrastructure and disaster preparedness strategies.
4. Fostering Environmental Awareness:
Japan’s geography has heightened its awareness of environmental issues. The country’s vulnerability to natural disasters, limited land resources, and dependence on imports have underscored the importance of sustainable development and environmental conservation. Japan has become a leader in renewable energy development and waste management.
FAQs on Japan’s Geography:
1. Why is Japan so mountainous?
Japan’s mountainous landscape is a result of its location at the convergence of four tectonic plates. The constant collision and subduction of these plates have created a chain of volcanic mountains and uplifted the landmass.
2. What are the major natural disasters that affect Japan?
Japan is highly prone to earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, tsunamis, typhoons, and landslides. These natural hazards pose significant risks to its infrastructure, economy, and population.
3. How does Japan’s geography affect its climate?
Japan’s location on the eastern edge of the Asian continent, its proximity to warm ocean currents, and its mountainous terrain create a diverse range of climates. The country experiences four distinct seasons, with varying temperatures and precipitation patterns.
4. What are the main challenges faced by Japan due to its geography?
Japan faces challenges related to limited land resources, natural disasters, and dependence on imports. The country has to carefully manage its land use, mitigate the risks of natural hazards, and ensure its energy security.
5. How has Japan adapted to its geographic challenges?
Japan has developed innovative solutions to address its geographic challenges. These include advanced infrastructure, disaster preparedness measures, efficient land use practices, and sustainable development strategies.
Tips for Understanding Japan’s Geography:
1. Study a map: Utilize a detailed map of Japan to familiarize yourself with the major islands, mountain ranges, and cities.
2. Explore online resources: Websites like Google Maps, Wikipedia, and Japan’s official tourism website offer comprehensive information about the country’s geography.
3. Watch documentaries: Explore documentaries and videos that delve into Japan’s unique geography, including its volcanic activity, seismic zones, and coastal landscapes.
4. Read books and articles: Engage with written materials that discuss Japan’s geography, history, and culture.
5. Travel to Japan: Experiencing Japan firsthand allows you to appreciate the diverse landscapes, cultural influences, and the impact of its geography on everyday life.
Conclusion:
Japan’s geography is a tapestry woven with intricate threads of mountains, volcanoes, coastlines, and diverse climates. It has shaped the nation’s history, culture, and economic development, while also posing significant challenges. Understanding Japan’s geography is essential for appreciating its uniqueness, resilience, and the enduring spirit of its people. Through exploration and engagement, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities and beauty of this fascinating archipelago nation.

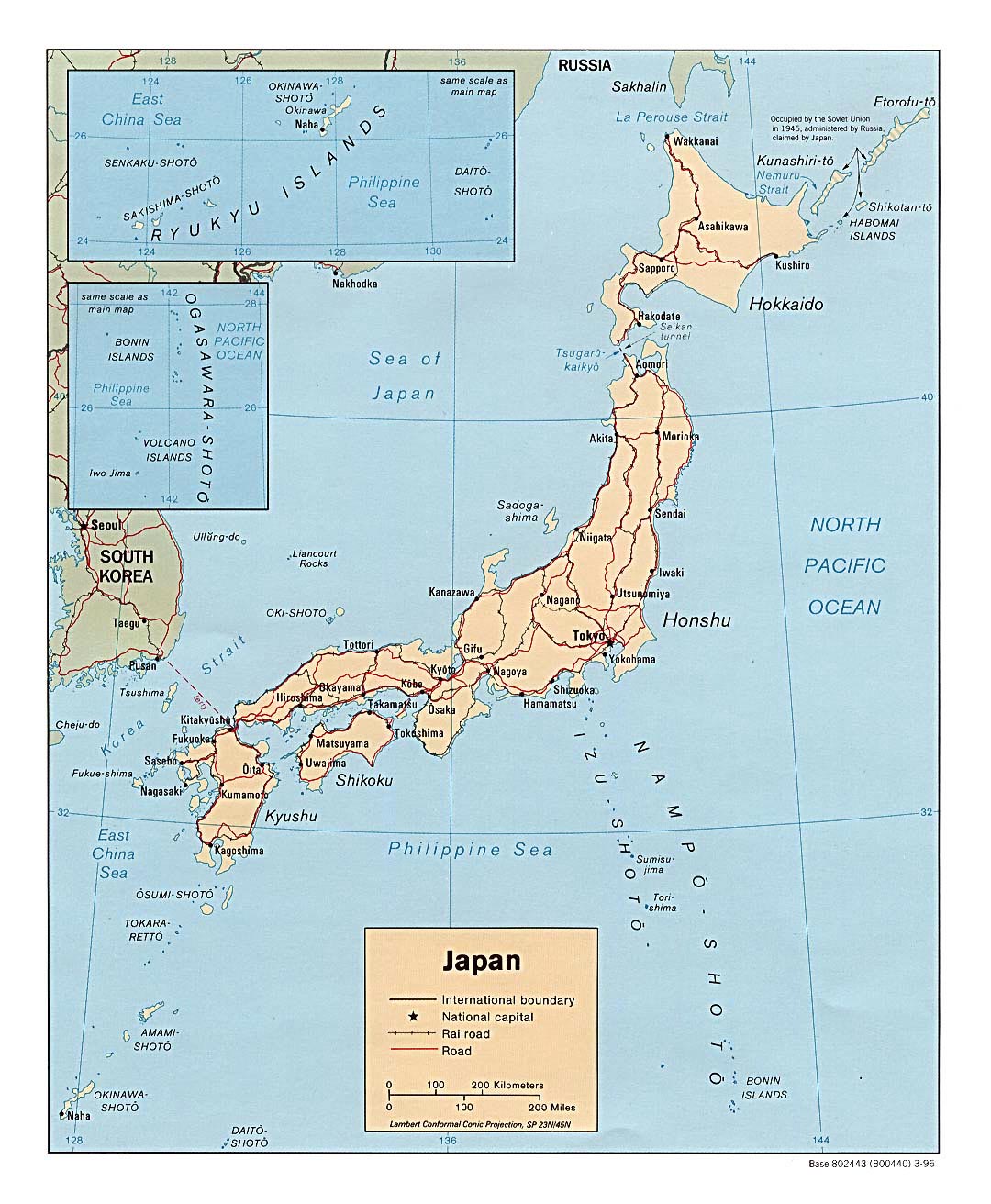



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Tapestry of Japan: A Geographic Exploration. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!