Unveiling The Past: The Oldest Maps Of Palestine And Their Enduring Significance
Unveiling the Past: The Oldest Maps of Palestine and Their Enduring Significance
Related Articles: Unveiling the Past: The Oldest Maps of Palestine and Their Enduring Significance
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Past: The Oldest Maps of Palestine and Their Enduring Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Past: The Oldest Maps of Palestine and Their Enduring Significance
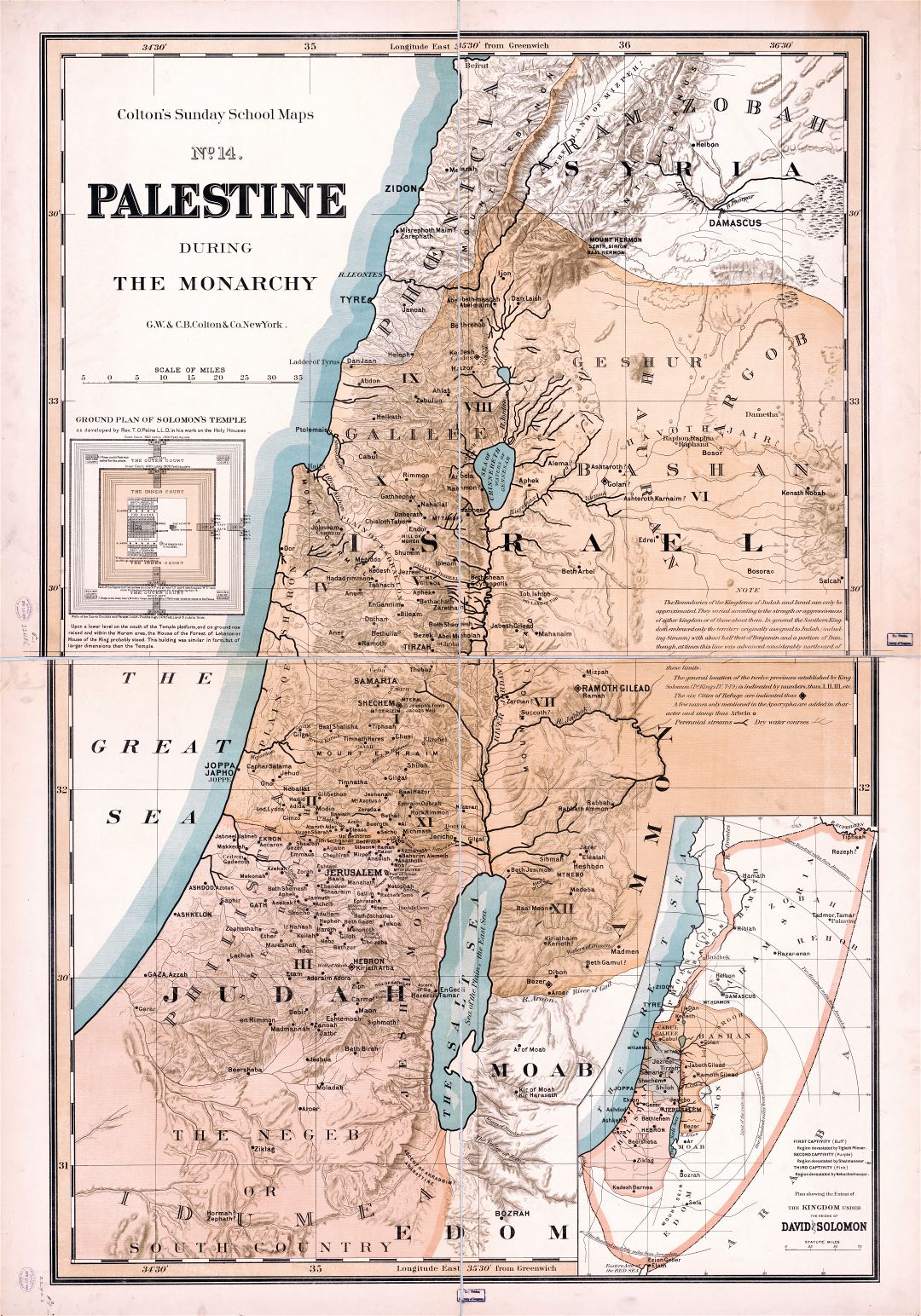
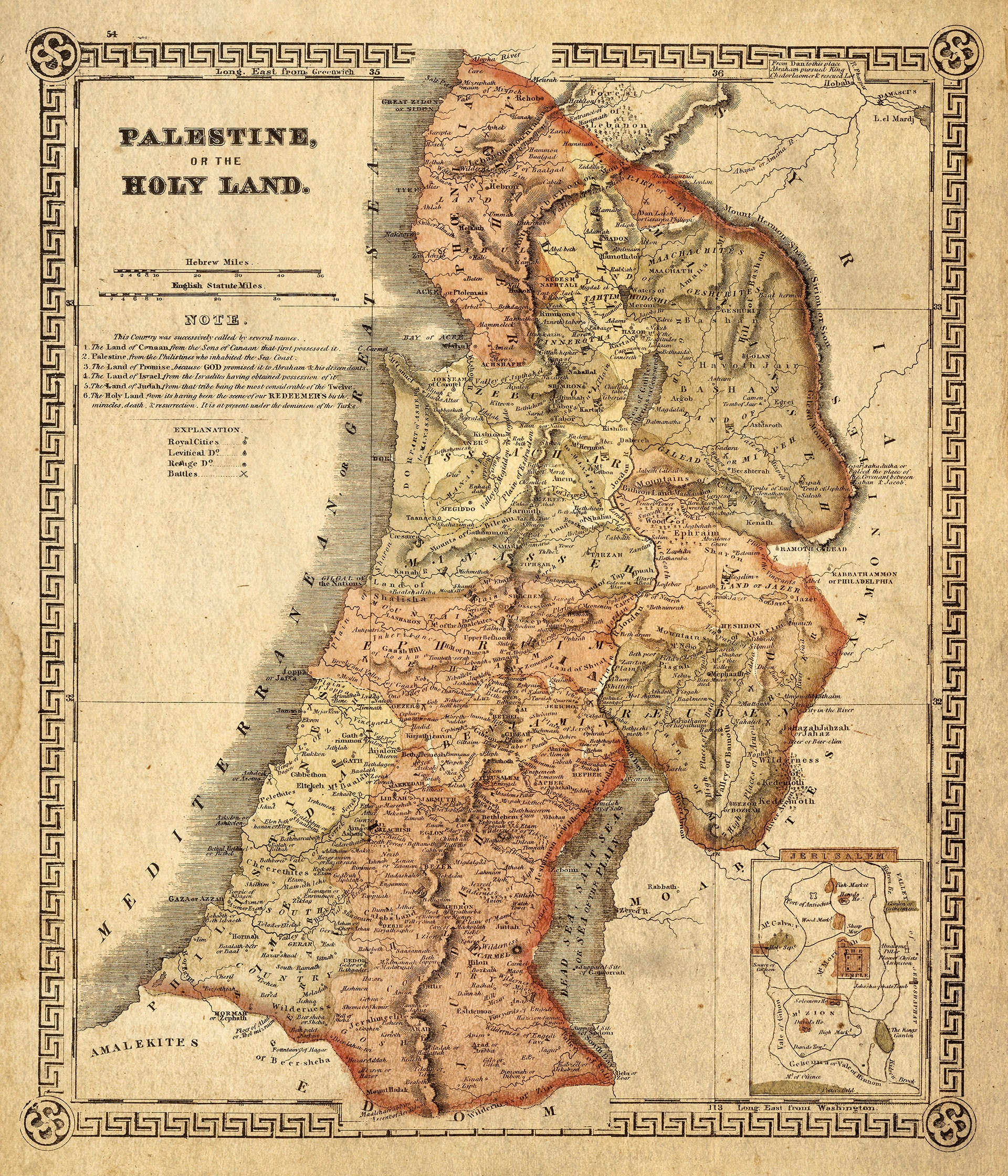
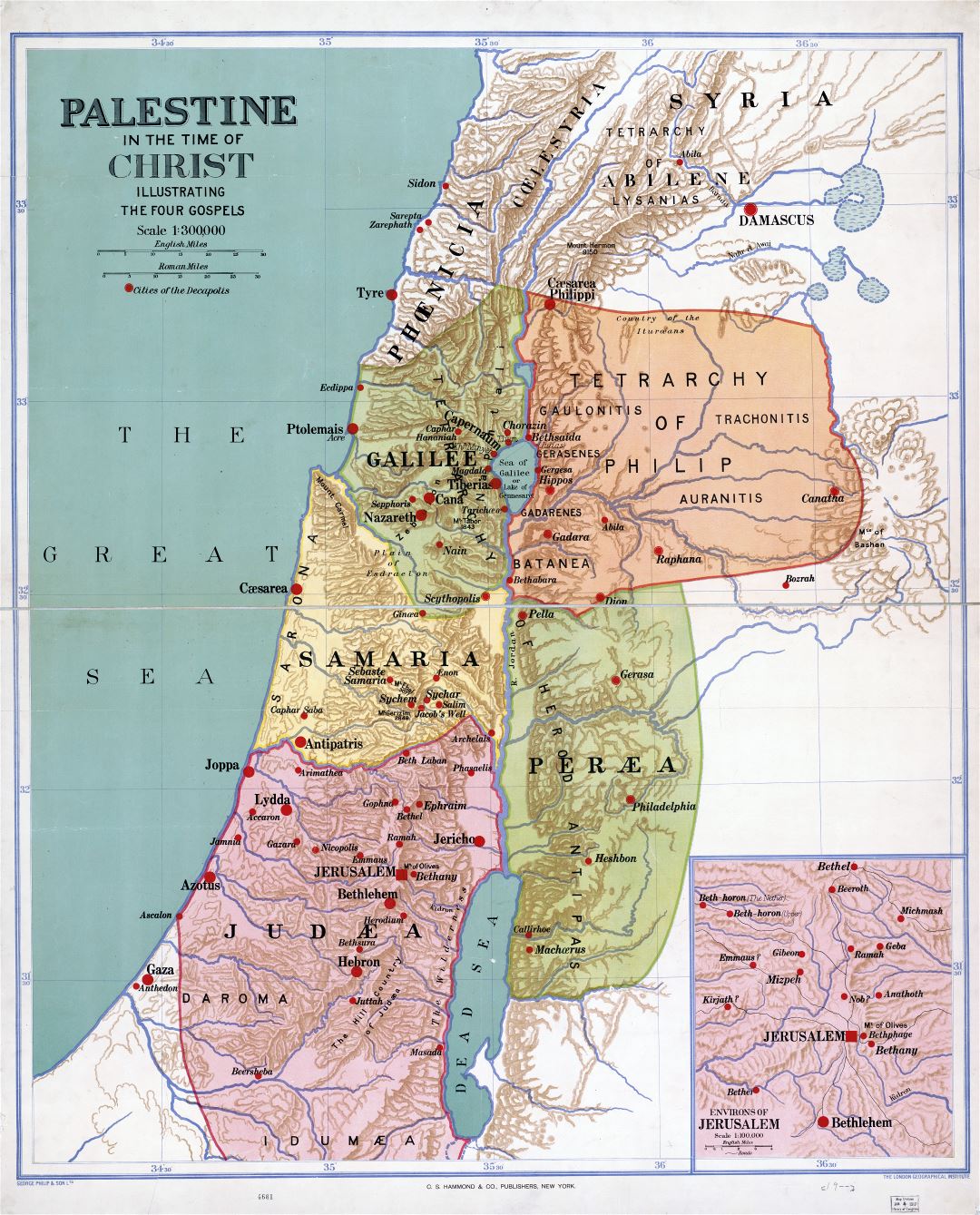
The quest to understand the past often begins with a map. Maps, those silent guides to time and space, serve as invaluable windows into bygone eras, offering a glimpse into the landscapes, settlements, and cultural interactions of civilizations long gone. In the case of Palestine, a region steeped in history and contested narratives, the oldest surviving maps hold particular significance. These ancient cartographic representations provide not only geographical insights but also illuminate the evolving political, religious, and social dynamics of the region throughout millennia.
The Madaba Map: A Mosaic Masterpiece
One of the most renowned and oldest maps of Palestine is the Madaba Map, a stunning mosaic floor created in the 6th century CE in the Jordanian city of Madaba. This remarkable artifact, meticulously preserved for centuries, depicts the Holy Land with remarkable detail, showcasing cities, towns, rivers, and even the iconic Dead Sea. The map’s intricate design and wealth of information offer a unique perspective on the landscape of Byzantine Palestine, revealing the geographic understanding and cultural significance of the region during that era.
The Madaba Map goes beyond a mere geographical representation. It highlights the importance of Jerusalem and other holy sites to the Byzantine Christian community. The map’s portrayal of these locations reflects the religious and political context of the time, demonstrating the central role of Palestine in the Byzantine world. It also provides invaluable insights into the urban planning and infrastructure of the region, revealing the extent of Roman and Byzantine influence on the landscape.
The Peutinger Table: A Roman Road Map
While the Madaba Map offers a detailed view of Palestine, the Peutinger Table, a 13th-century copy of a 4th-century Roman map, provides a broader perspective on the Roman road network across the empire. This extensive map, spanning from Britain to India, includes a segment dedicated to the Roman province of Syria Palaestina, revealing the strategic importance of Palestine within the Roman Empire.
The Peutinger Table highlights the Roman infrastructure and communication routes that connected Palestine to other parts of the empire. It showcases the major roads, cities, and military outposts that facilitated trade, administration, and military movements. This map serves as a testament to the Roman engineering prowess and the crucial role Palestine played in the Roman world.
Beyond the Maps: The Importance of Interpretation
The oldest maps of Palestine are not merely static images but dynamic representations of a complex and evolving landscape. Their interpretation requires a nuanced understanding of the historical context, the motivations of the mapmakers, and the cultural biases that may have influenced their depictions.
For example, the Madaba Map, created during a period of Byzantine Christian dominance, reflects the religious perspective of the era. While it offers valuable insights into the geographic understanding of the time, it also reflects the Christian viewpoint, highlighting the importance of Jerusalem and other holy sites. Similarly, the Peutinger Table, a product of the Roman Empire, reflects the Roman perspective, emphasizing the strategic importance of Palestine within the empire.
The Enduring Legacy: Maps as Historical Narratives
The oldest maps of Palestine offer a unique and irreplaceable window into the past. They provide invaluable insights into the geographic, political, religious, and social dynamics of the region throughout centuries. These maps serve as a testament to the enduring human desire to map and understand the world around us.
However, it is crucial to acknowledge the limitations of these maps. They are products of their time, reflecting the biases and perspectives of the mapmakers. By understanding these limitations, we can approach these ancient artifacts with a critical eye, appreciating their value as historical documents while recognizing their inherent limitations.
The study of these maps continues to be a dynamic and evolving field. As new discoveries are made and technologies advance, our understanding of these ancient cartographic representations will continue to evolve. The oldest maps of Palestine, far from being static artifacts, serve as a constant reminder of the ever-changing nature of history and the ongoing quest to understand the past.
FAQs
Q: How were these maps created?
A: The oldest maps of Palestine were created using various techniques. The Madaba Map was crafted using mosaic tiles, while the Peutinger Table was painted on parchment. Both maps reflect the technological capabilities and artistic conventions of their respective eras.
Q: Why are these maps important?
A: These maps offer a unique perspective on the history of Palestine, providing insights into the geography, political structures, and cultural dynamics of the region. They also demonstrate the evolution of cartographic techniques and the role of maps in shaping our understanding of the world.
Q: What are some of the challenges in interpreting these maps?
A: Interpreting these maps requires a nuanced understanding of the historical context, the motivations of the mapmakers, and the cultural biases that may have influenced their depictions. It is also essential to consider the limitations of the technology available at the time.
Q: What are some of the ongoing research efforts related to these maps?
A: Researchers continue to study these maps using advanced technologies, such as digital imaging and GIS analysis, to uncover hidden details and gain a deeper understanding of the historical and geographical context.
Tips
- Study the historical context: To understand the maps fully, it is crucial to research the historical period during which they were created, including the political, religious, and social dynamics of the time.
- Consider the mapmaker’s perspective: Understanding the motivations and biases of the mapmaker is essential for a comprehensive interpretation.
- Compare different maps: Comparing maps from different eras can reveal how our understanding of Palestine has evolved over time.
- Utilize digital tools: Digital imaging and GIS analysis can enhance the study of these maps, revealing hidden details and allowing for more accurate interpretations.
Conclusion
The oldest maps of Palestine offer a glimpse into a fascinating and complex past. They provide invaluable insights into the geography, history, and culture of the region, showcasing the evolving relationship between humans and their environment. While these maps are products of their time, reflecting the biases and limitations of their creators, they remain essential tools for understanding the past and appreciating the enduring legacy of Palestine. By studying these ancient cartographic representations, we can gain a deeper understanding of the region’s rich and multifaceted history, contributing to a more nuanced and informed understanding of the present.

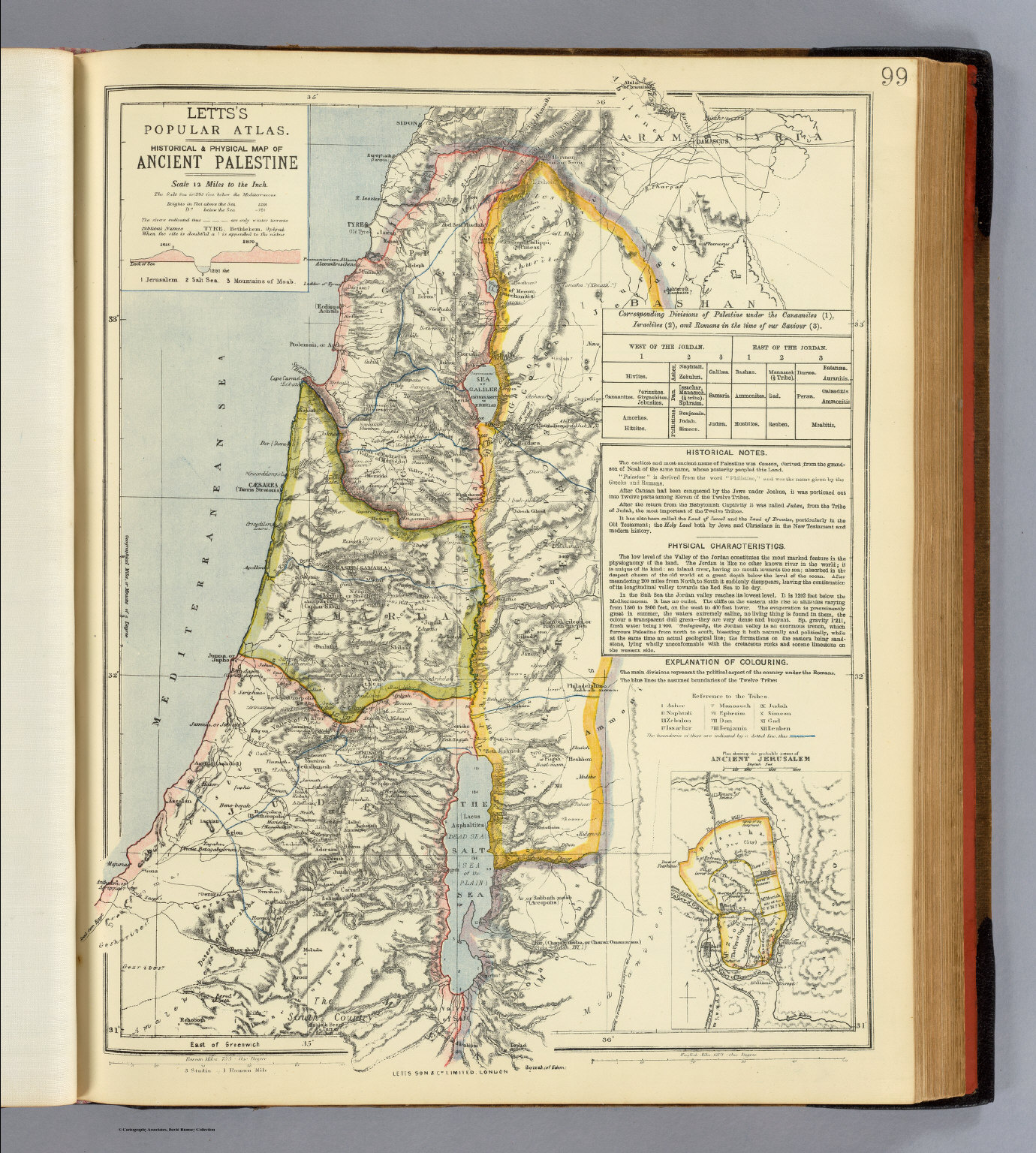
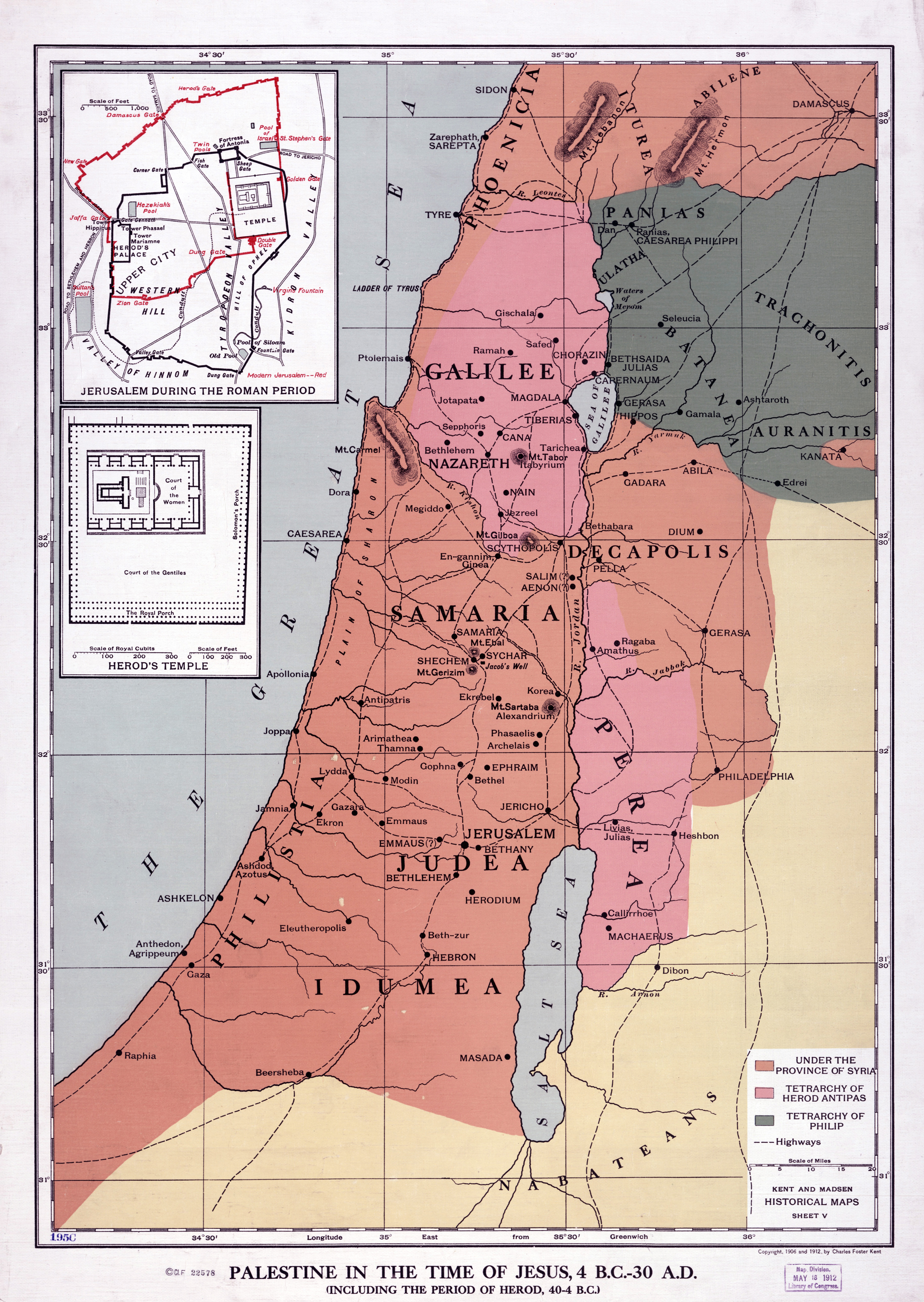
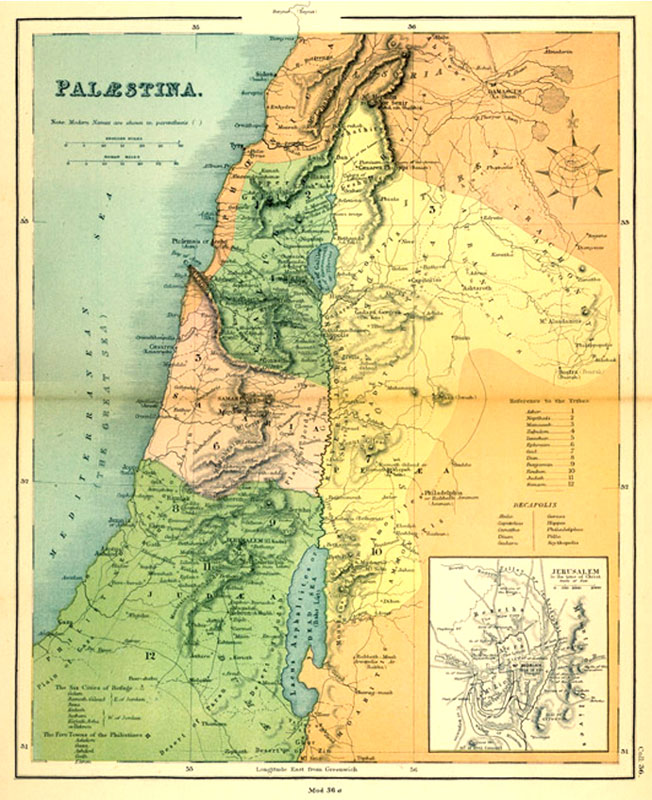


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Past: The Oldest Maps of Palestine and Their Enduring Significance. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!